Abstract
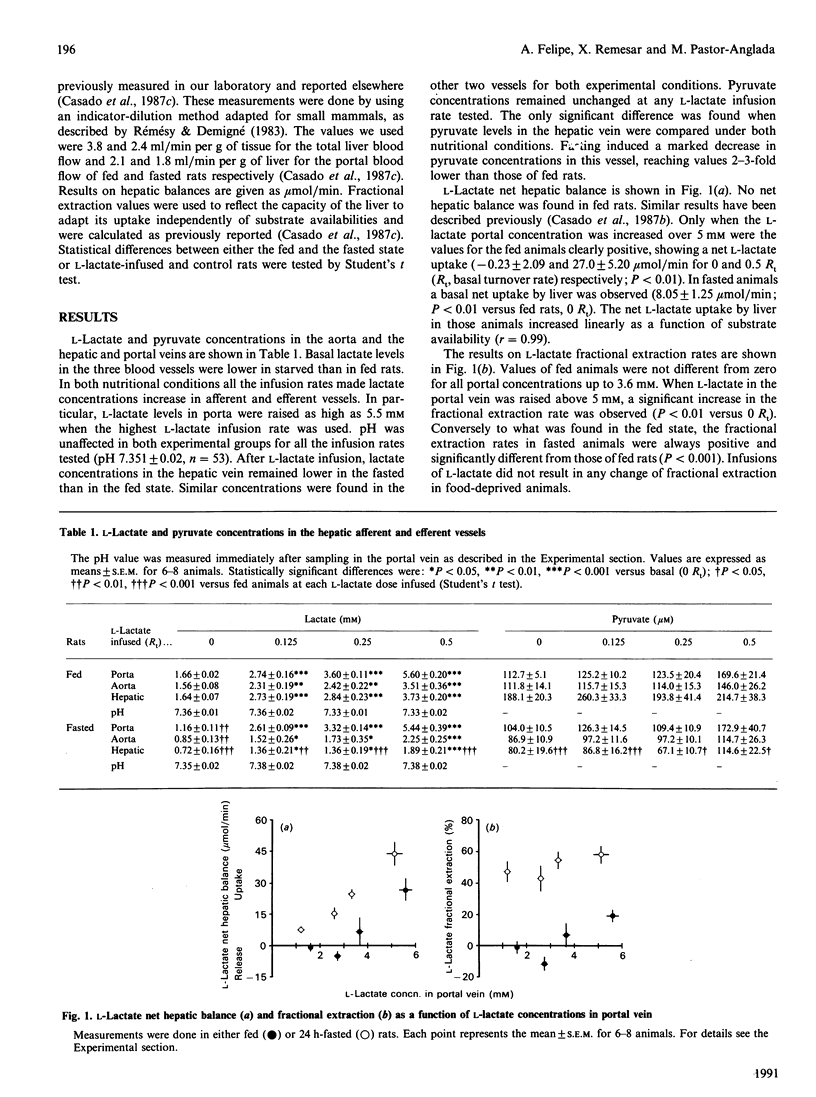
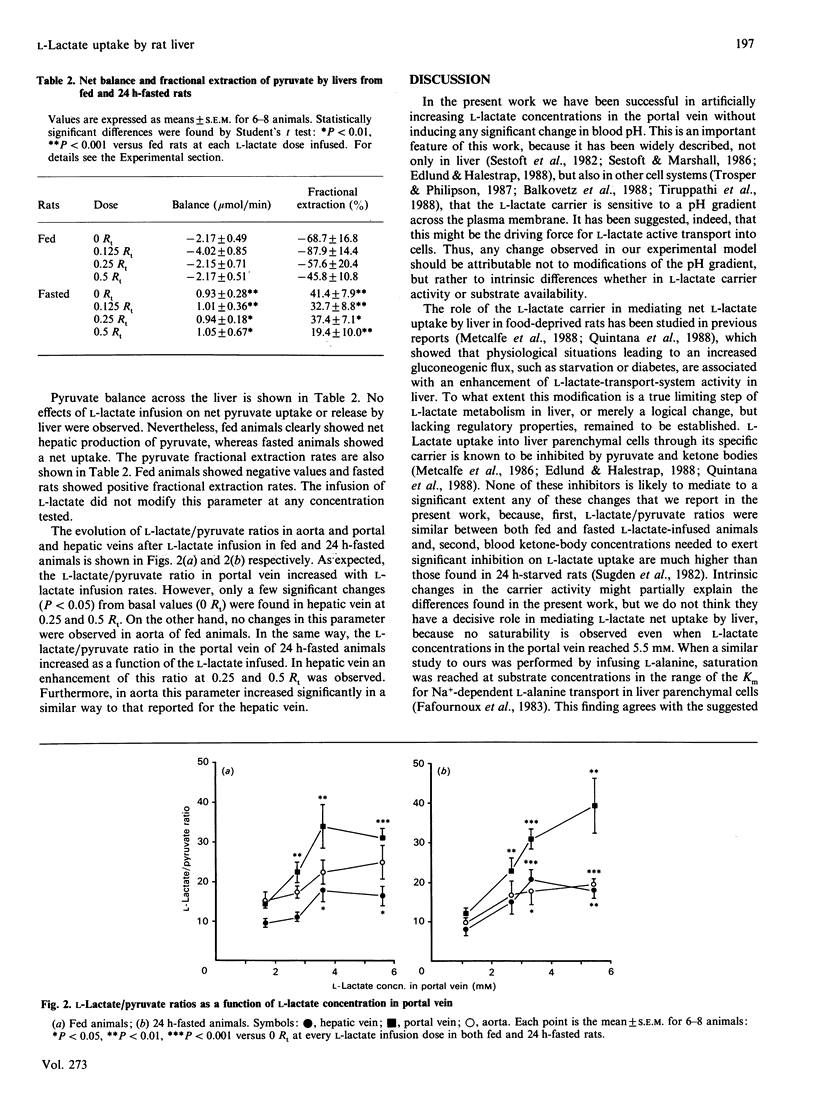
We have studied the role of substrate availability on net L-lactate uptake by liver of anaesthetized fed and 24 h-fasted rats. L-Lactate was infused through a mesenteric vein at infusion rates equivalent to 0, 0.125, 0.25 and 0.5 times the basal turnover rate (Rt). By these means we were able to increase L-lactate portal concentrations up to 5.5 mM, without significant changes in portal pH. In the basal state (0 Rt), a net L-lactate uptake by liver was found in 24 h-fasted animals. No net balance was observed in fed rats. Infusion of L-lactate in fed animals failed to induce a net hepatic uptake, except when L-lactate levels in portal vein were raised above 5 mM. In fasted animals, net L-lactate uptake by liver increased linearly (r = 0.99) as a function of L-lactate concentration in the portal vein, even beyond the saturation of its specific carrier. It is concluded that, first, the L-lactate carrier does not limit net L-lactate uptake, and second, that substrate availability is an important factor modulating net L-lactate uptake by liver.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkovetz D. F., Leibach F. H., Mahesh V. B., Ganapathy V. A proton gradient is the driving force for uphill transport of lactate in human placental brush-border membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13823–13830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casado J., Pastor-Anglada M., Remesar X. Hepatic uptake of amino acids at mid-lactation in the rat. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):297–300. doi: 10.1042/bj2450297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casado J., Remesar X., Pastor-Anglada M. Hepatic uptake of amino acids in late-pregnant rats. Effect of food deprivation. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):117–122. doi: 10.1042/bj2480117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casado J., Remesar X., Pastor-Anglada M. Hepatic uptake of gluconeogenic substrates in late-pregnant and mid-lactating rats. Biosci Rep. 1987 Jul;7(7):587–592. doi: 10.1007/BF01119776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. A., Williams P. E., Cherrington A. D. Net hepatic lactate balance following mixed meal feeding in the four-day fasted conscious dog. Metabolism. 1987 Sep;36(9):856–862. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund G. L., Halestrap A. P. The kinetics of transport of lactate and pyruvate into rat hepatocytes. Evidence for the presence of a specific carrier similar to that in erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):117–126. doi: 10.1042/bj2490117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fafournoux P., Demigné C., Rémésy C. Carrier-mediated uptake of lactate in rat hepatocytes. Effects of pH and possible mechanisms for L-lactate transport. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):292–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fafournoux P., Rémésy C., Demigné C. Control of alanine metabolism in rat liver by transport processes or cellular metabolism. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):645–652. doi: 10.1042/bj2100645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe H. K., Monson J. P., Cohen R. D., Padgham C. Enhanced carrier-mediated lactate entry into isolated hepatocytes from starved and diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19505–19509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe H. K., Monson J. P., Welch S. G., Cohen R. D. Inhibition of lactate removal by ketone bodies in rat liver. Evidence for a quantitatively important role of the plasma membrane lactate transporter in lactate metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):743–747. doi: 10.1172/JCI112635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson J. P., Smith J. A., Cohen R. D., Iles R. A. Evidence for a lactate transporter in the plasma membrane of the rat hepatocyte. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Apr;62(4):411–420. doi: 10.1042/cs0620411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., el-Maghrabi M. R., Claus T. H. Hormonal regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:755–783. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pénicaud L., Ferré P., Kande J., Leturque A., Issad T., Girard J. Effect of anesthesia on glucose production and utilization in rats. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):E365–E369. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.3.E365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintana I., Felipe A., Remesar X., Pastor-Anglada M. Carrier-mediated uptake of L-(+)-lactate in plasma membrane vesicles from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rémésy C., Demigné C. Changes in availability of glucogenic and ketogenic substrates and liver metabolism in fed or starved rats. Ann Nutr Metab. 1983;27(1):57–70. doi: 10.1159/000176624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rémésy C., Demigné C. Impaired lactate utilization in livers of rats fed high protein-diets. J Nutr. 1982 Jan;112(1):60–69. doi: 10.1093/jn/112.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sestoft L., Bartels P. D., Folke M. Pathophysiology of metabolic acidosis: effect of low pH on the hepatic uptake of lactate, pyruvate and alanine. Clin Physiol. 1982 Feb;2(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-097x.1982.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sestoft L., Marshall M. O. Hepatic lactate uptake is enhanced by low pH at low lactate concentrations in perfused rat liver. Clin Sci (Lond) 1986 Jan;70(1):19–22. doi: 10.1042/cs0700019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sips H. J., Groen A. K., Tager J. M. Plasma-membrane transport of alanine is rate-limiting for its metabolism in rat-liver parenchymal cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden M. C., Watts D. I., Marshall C. E. Effects of adrenaline on ketogenesis from long- and medium-chain fatty acids in starved rats. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 15;204(3):749–756. doi: 10.1042/bj2040749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiruppathi C., Balkovetz D. F., Ganapathy V., Miyamoto Y., Leibach F. H. A proton gradient, not a sodium gradient, is the driving force for active transport of lactate in rabbit intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):219–223. doi: 10.1042/bj2560219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trosper T. L., Philipson K. D. Lactate transport by cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):C483–C489. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.5.C483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcarce C., Cuezva J. M., Medina J. M. Increased gluconeogenesis in the rat at term gestation. Life Sci. 1985 Aug 12;37(6):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90468-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Herrera E. Effects of anesthetics and starvation on in vivo gluconeogenesis in virgin and pregnant rats. Metabolism. 1984 Jun;33(6):553–558. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


