Abstract
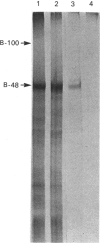
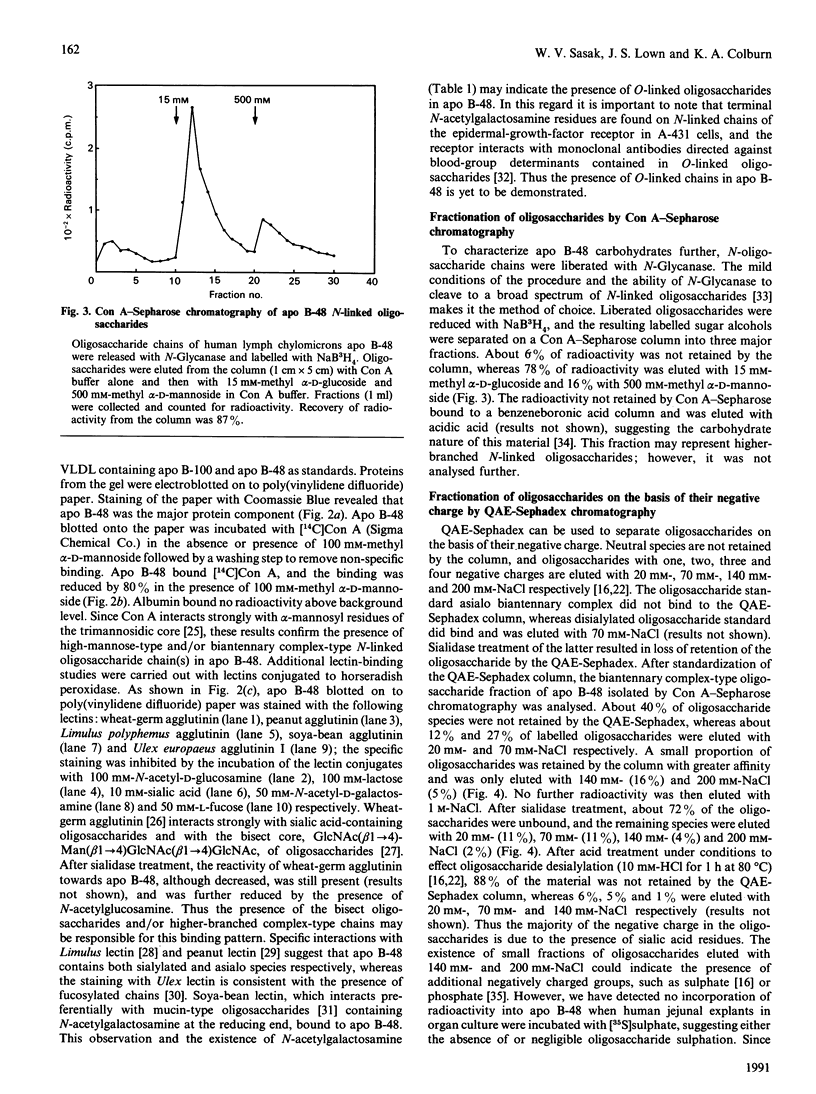
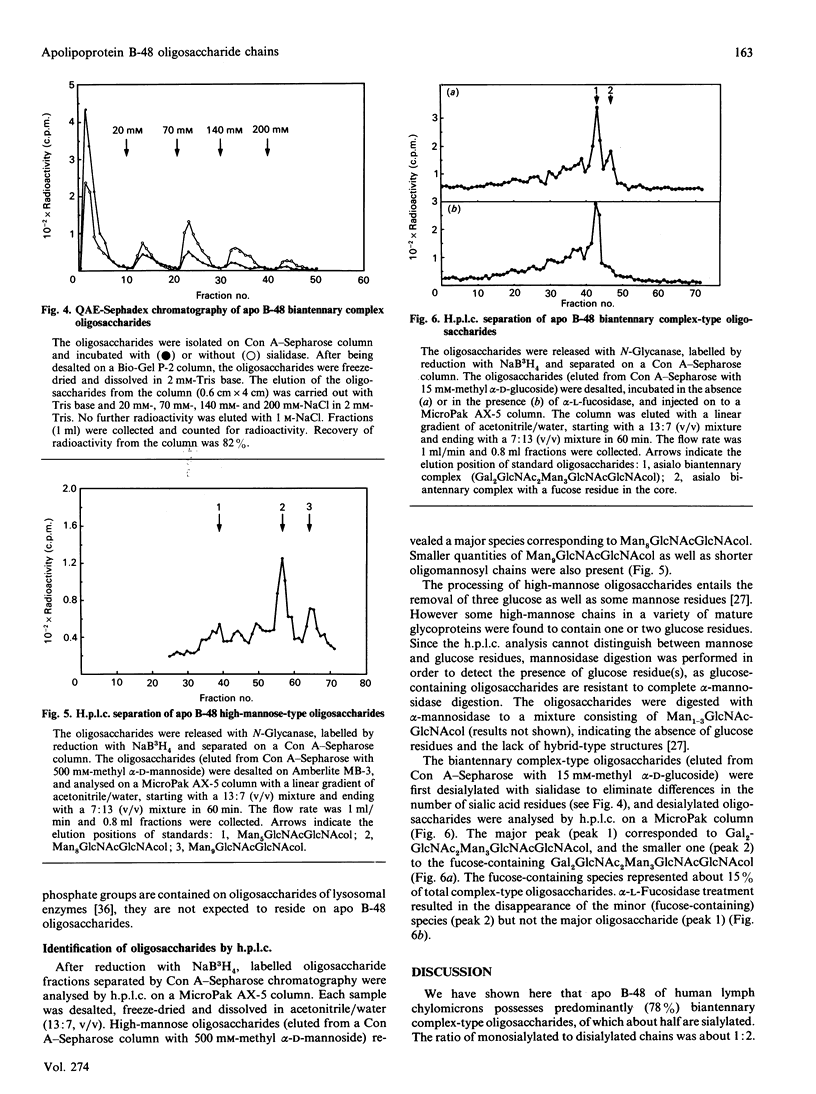
Hepatic apolipoprotein (apo) B-100 isolated from human plasma is known to contain N-linked oligosaccharides of high-mannose-type and complex-type structures. Sequencing data have revealed that apo B-48 of small-intestinal origin, which represents about 48% of apo B-100 polypeptide from the N-terminus, possesses six potential sites for N-linked oligosaccharides, of which five are likely to be glycosylated. The characterization of the carbohydrate moiety of apo B-48 is the focus of this study. Apo B-48 was labelled with L-[35S]methionine and D-[3H]glucosamine in organ culture of human small-intestinal explants. N-Glycanase treatment resulted in loss of radioactivity from D-[3H]glucosamine-labelled but not L-[35S]methionine-labelled apo B-48 secreted into the medium, and caused no distinct change in mobility of apo B-48 upon electrophoresis on 5% polyacrylamide gel. Analysis of monosaccharide content revealed the presence of 16.8, 17.8, 13.4, 3.4, 2.4 and 2.3 residues of N-acetylglucosamine, mannose, galactose, fucose, xylose and N-acetylgalactosamine respectively. Small-intestinal apo B-48 from human lymph chylomicrons bound to [14C]concanavalin A, and the binding could be inhibited with methyl alpha-D-mannoside. In addition, wheat-germ, peanut, Limulus, soya-bean and Ulex lectins bound apo B-48 specifically. To characterize the carbohydrate moiety further, N-linked oligosaccharides were released by N-Glycanase treatment and reduced with NaB3H4. Labelled oligosaccharides were separated on a concanavalin A-Sepharose column. The majority (78%) were biantennary complex-type structures, 16% were high-mannose type and 6% (not retained by the column) most probably represented higher-branched oligosaccharides. These results suggest the presence of one high-mannose-type and four biantennary complex-type oligosaccharides, as well as probable O-linked sugars in apo B-48. By the use of h.p.l.c., exoglycosidase treatments and ion-exchange chromatography, a mixture of high-mannose-type species with predominant Man8GlcNAc2 as well as monosialylated, desialylated and fucosylated forms of complex-type oligosaccharides were detected.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhattacharyya L., Ceccarini C., Lorenzoni P., Brewer C. F. Concanavalin A interactions with asparagine-linked glycopeptides. Bivalency of high mannose and bisected hybrid type glycopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1288–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisgaier C. L., Glickman R. M. Intestinal synthesis, secretion, and transport of lipoproteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:625–636. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büller H. A., Rings E. H., Montgomery R. K., Sasak W. V., Grand R. J. Further studies of glycosylation and intracellular transport of lactase-phlorizin hydrolase in rat small intestine. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 1;263(1):249–254. doi: 10.1042/bj2630249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. H., Habib G., Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Lee B. R., Weng S. A., Silberman S. R., Cai S. J., Deslypere J. P., Rosseneu M. Apolipoprotein B-48 is the product of a messenger RNA with an organ-specific in-frame stop codon. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):363–366. doi: 10.1126/science.3659919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couso R., Lang L., Roberts R. M., Kornfeld S. Phosphorylation of the oligosaccharide of uteroferrin by UDP-GlcNAc:glycoprotein N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferases from rat liver, Acanthamoeba castellani, and Dictyostelium discoideum requires alpha 1,2-linked mannose residues. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6326–6331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings R. D., Kornfeld S., Schneider W. J., Hobgood K. K., Tolleshaug H., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Biosynthesis of N- and O-linked oligosaccharides of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15261–15273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings R. D., Soderquist A. M., Carpenter G. The oligosaccharide moieties of the epidermal growth factor receptor in A-431 cells. Presence of complex-type N-linked chains that contain terminal N-acetylgalactosamine residues. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11944–11952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirani S., Bernasconi R. J., Rasmussen J. R. Use of N-glycanase to release asparagine-linked oligosaccharides for structural analysis. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 1;162(2):485–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90424-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda S., Suzuki S. Common conditions for high-performance liquid chromatographic microdetermination of aldoses, hexosamines, and sialic acids in glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1984 Oct;142(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90533-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Young S. G., Poksay K. S., Mahley R. W., Smith R. S., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L., Weisgraber K. H. Structural relationship of human apolipoprotein B48 to apolipoprotein B100. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1794–1798. doi: 10.1172/JCI113273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobata A. Use of endo- and exoglycosidases for structural studies of glycoconjugates. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Marcel Y., Deckelbaum R. J., Milne R., Lepage G., Seidman E., Bendayan M., Roy C. C. Intestinal apoB synthesis, lipids, and lipoproteins in chylomicron retention disease. J Lipid Res. 1987 Nov;28(11):1263–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Skutelsky E., Danon D., Sharon N. The purification, composition, and specificity of the anti-T lectin from peanut (Arachis hypogaea). J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8518–8523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellis S. J., Baenziger J. U. Structures of the oligosaccharides present at the three asparagine-linked glycosylation sites of human IgD. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11546–11556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muresan V., Iwanij V., Smith Z. D., Jamieson J. D. Purification and use of limulin: a sialic acid-specific lectin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Sep;30(9):938–946. doi: 10.1177/30.9.6897073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa T., Tsuji T. Fractionation and structural assessment of oligosaccharides and glycopeptides by use of immobilized lectins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:21–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh R. B., Tse A. G., Dwek R. A., Williams A. F., Rademacher T. W. Tissue-specific N-glycosylation, site-specific oligosaccharide patterns and lentil lectin recognition of rat Thy-1. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1233–1244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Kisailus E. C., Gruezo F., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies on the combining site of the blood group H-specific lectin 1 from Ulex europeus seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 15;185(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Edwards Y. H., Knott T. J., Scott J. A novel form of tissue-specific RNA processing produces apolipoprotein-B48 in intestine. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasak V. W., Ordovas J. M., Elbein A. D., Berninger R. W. Castanospermine inhibits glucosidase I and glycoprotein secretion in human hepatoma cells. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):759–766. doi: 10.1042/bj2320759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasak W. V., Buller H. A., Reinhold R. Biosynthetic precursor (214 kDa) of apolipoprotein B-48 is not secreted by Caco-2 cells and normal human intestine. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):365–370. doi: 10.1042/bj2640365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasak W., Herscovics A., Quaroni A. Cell-density-dependent changes in cell-surface glycopeptides and in adhesion of cultured intestinal epithelial cells. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 1;201(2):359–366. doi: 10.1042/bj2010359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siuta-Mangano P., Howard S. C., Lennarz W. J., Lane M. D. Synthesis, processing, and secretion of apolipoprotein B by the chick liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4292–4300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siuta-Mangano P., Janero D. R., Lane M. D. Association and assembly of triglyceride and phospholipid with glycosylated and unglycosylated apoproteins of very low density lipoprotein in the intact liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11463–11467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Hounsell E. F. Selective purification of reduced oligosaccharides using a phenylboronic acid bond elut column: potential application in HPLC, mass spectrometry, reductive amination procedures and antigenic/serum analysis. Biomed Chromatogr. 1988 Nov;2(6):249–253. doi: 10.1002/bmc.1130020605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Ishikawa Y., Tsunemitsu M., Fukuzaki H. The structures of the asparagine-linked sugar chains of human apolipoprotein B-100. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Aug 15;273(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Gómez C. M., Plummer T. H., Jr Deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans by peptide:N-glycosidase F. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4665–4671. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunemitsu M., Ishikawa Y., Taniguchi T., Fukuzaki H. Heterogeneity of N-linked sugar chains of apolipoprotein B-100 in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic and fasting rabbits. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):386–393. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki A., Kornfeld S. The spectrum of anionic oligosaccharides released by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H from glycoproteins. Structural studies and interactions with the phosphomannosyl receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2808–2818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vauhkonen M., Viitala J., Parkkinen J., Rauvala H. High-mannose structure of apolipoprotein-B from low-density lipoproteins of human plasma. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):43–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Hitoi A., Irie M., Kobata A. Fractionation by lectin affinity chromatography indicates that the glycosylation of most ribonucleases in human viscera and body fluids is organ specific. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Oct;250(1):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90725-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. Y., Gu Z. W., Weng S. A., Kim T. W., Chen S. H., Pownall H. J., Sharp P. M., Liu S. W., Li W. H., Gotto A. M., Jr Structure of apolipoprotein B-100 of human low density lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):96–108. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Characterization of an abnormal species of apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein B-37, associated with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1172/JCI113025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]