Abstract
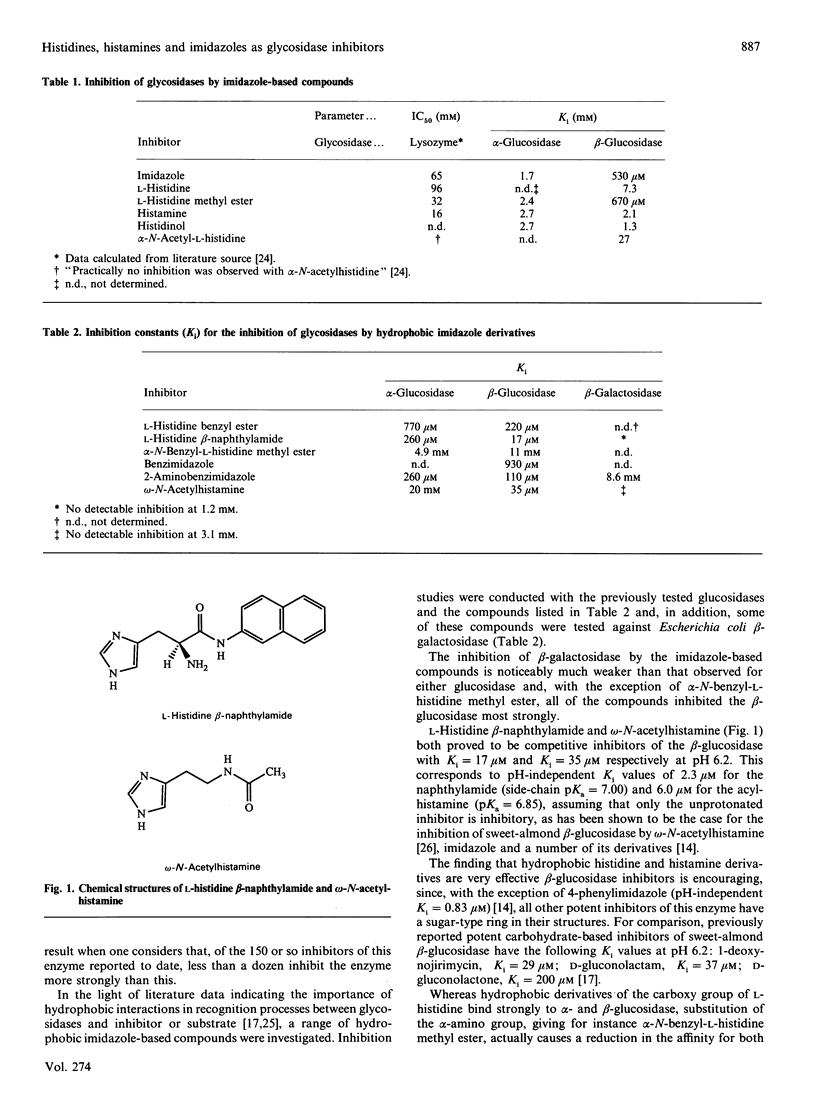
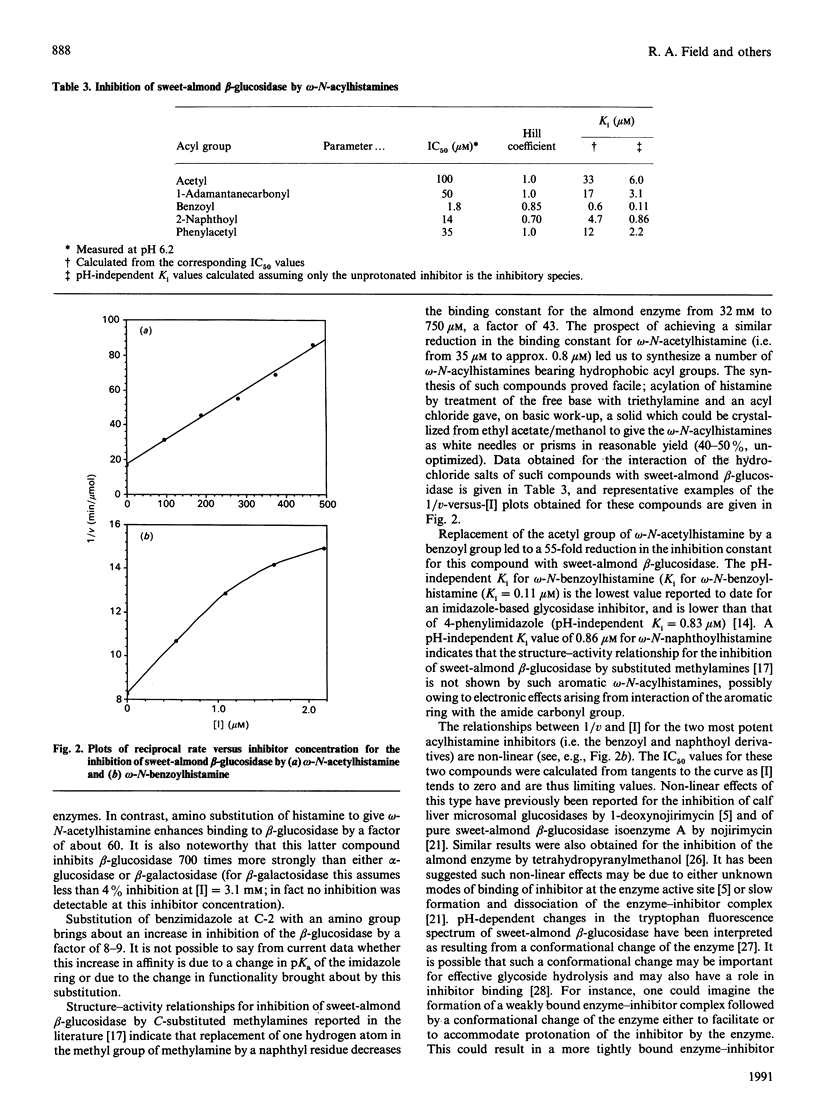
This present study reports the ability of a range of derivatives of L-histidine, histamine and imidazole to act as inhibitors of sweet-almond beta-glucosidase, yeast alpha-glucosidase and Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase. The addition of a hydrophobic group to the basic imidazole nucleus greatly enhances binding to both the alpha- and beta-glucosidases. L-Histidine (beta-naphthylamide (Ki 17 microM) is a potent competitive inhibitor of sweet-almond beta-glucosidase as is omega-N-acetylhistamine (K1 35 microM), which inhibits the sweet-almond beta-glucosidase at least 700 times more strongly than either yeast alpha-glucosidase or Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase, and suggests potential for the development of selective reversible beta-glucosidase inhibitors. A range of hydrophobic omega-N-acylhistamines were synthesized and shown to be among the most potent inhibitors of sweet-almond beta-glucosidase reported to date.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernacki R. J., Niedbala M. J., Korytnyk W. Glycosidases in cancer and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1985;4(1):81–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00047738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady L., Brzozowski A. M., Derewenda Z. S., Dodson E., Dodson G., Tolley S., Turkenburg J. P., Christiansen L., Huge-Jensen B., Norskov L. A serine protease triad forms the catalytic centre of a triacylglycerol lipase. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):767–770. doi: 10.1038/343767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheron G., Noat G., Ricard J. Hysteresis of plant cell-wall beta-glucosidase. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):389–392. doi: 10.1042/bj2690389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Wilks H. M., Barstow D. A., Atkinson T., Chia W. N., Holbrook J. J. An investigation of the contribution made by the carboxylate group of an active site histidine-aspartate couple to binding and catalysis in lactate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1617–1622. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale M. P., Ensley H. E., Kern K., Sastry K. A., Byers L. D. Reversible inhibitors of beta-glucosidase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3530–3539. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale M. P., Kopfler W. P., Chait I., Byers L. D. Beta-glucosidase: substrate, solvent, and viscosity variation as probes of the rate-limiting steps. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2522–2529. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover A. K., Cushley R. J. Studies on almond emulsin beta-D-glucosidase. II. Kinetic evidence for independent glucosidase and galactosidase sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 12;482(1):109–124. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALVORSON H., ELLIAS L. The purification and properties of an alpha-glucosidase of Saccharomyces italicus Y1225. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Oct;30(1):28–40. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hettkamp H., Legler G., Bause E. Purification by affinity chromatography of glucosidase I, an endoplasmic reticulum hydrolase involved in the processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 2;142(1):85–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii S., Fukase H., Matsuo T., Kameda Y., Asano N., Matsui K. Synthesis and alpha-D-glucosidase inhibitory activity of N-substituted valiolamine derivatives as potential oral antidiabetic agents. J Med Chem. 1986 Jun;29(6):1038–1046. doi: 10.1021/jm00156a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R. E., Gaunt M. T. Importance of hydroxyls at positions 3, 4, and 6 for binding to the "galactose" site of beta-galactosidase (Escherichia coli). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jan;220(1):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpas A., Fleet G. W., Dwek R. A., Petursson S., Namgoong S. K., Ramsden N. G., Jacob G. S., Rademacher T. W. Aminosugar derivatives as potential anti-human immunodeficiency virus agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9229–9233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby A. J. Mechanism and stereoelectronic effects in the lysozyme reaction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1987;22(4):283–315. doi: 10.3109/10409238709086959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalégerie P., Legler G., Yon J. M. The use of inhibitors in the study of glycosidases. Biochimie. 1982 Nov-Dec;64(11-12):977–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G., Jülich E. Synthesis of 5-amino-5-deoxy-D-mannopyranose and 1,5-dideoxy-1,5-imino-D-mannitol, and inhibition of alpha- and beta-D-mannosidases. Carbohydr Res. 1984 May 15;128(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(84)85084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. K., Byers L. D. Inhibition of beta-glucosidase by imidazoles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 21;999(3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Katchalski E., Grisaro V., Sharon N. Inhibition of lysozyme by imidazole and indole derivatives. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):332–343. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler F. K., D'Arcy A., Hunziker W. Structure of human pancreatic lipase. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):771–774. doi: 10.1038/343771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


