Abstract
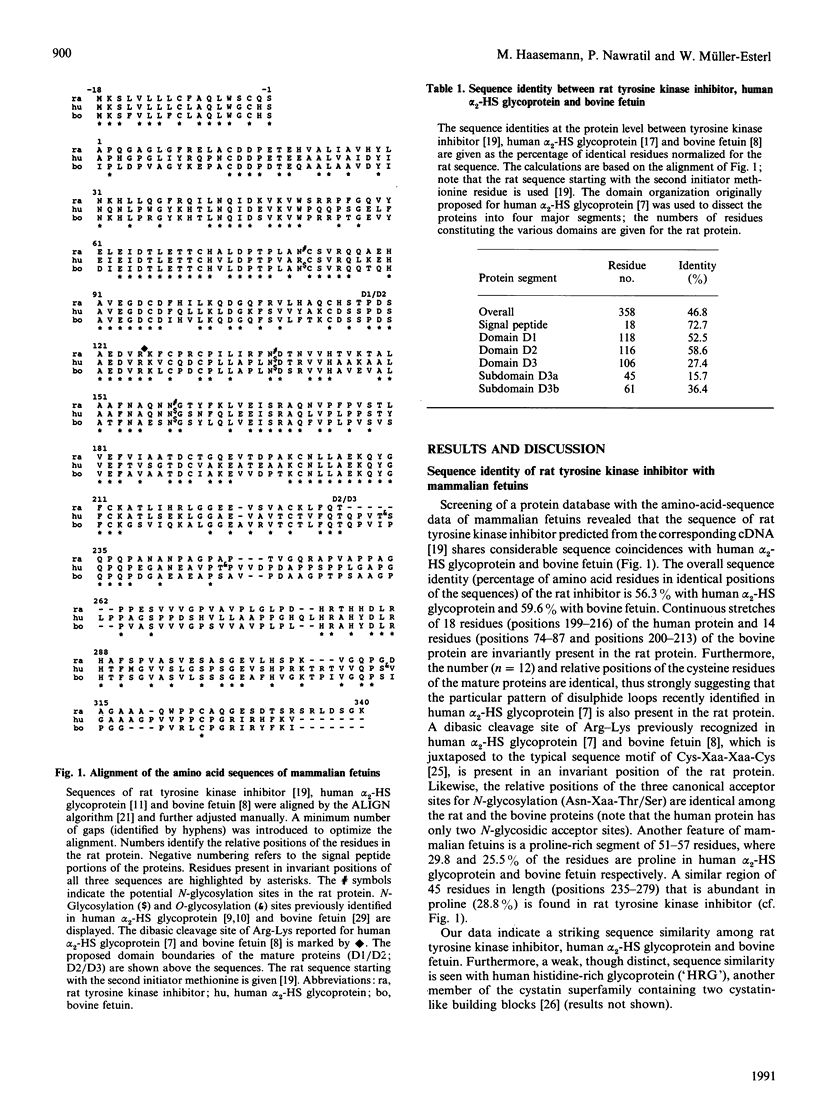
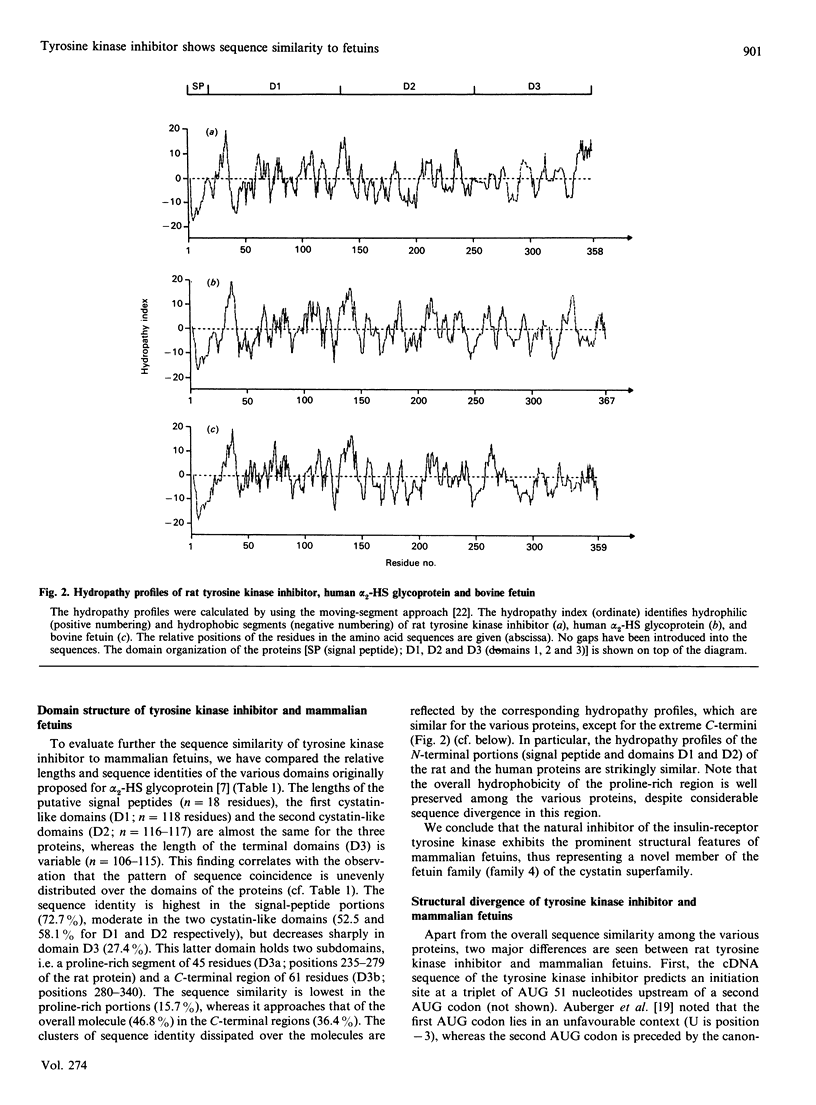
Human alpha 2-HS glycoprotein and bovine fetuin, abundant proteins of fetal plasma, are structural members of the fetuin family within the cystatin superfamily. They are characterized by the presence of two N-terminally located cystatin-like units and a unique C-terminal sequence segment not present in the other members of the cystatin superfamily. Search for related sequences revealed that the natural inhibitor of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase [Auberger, Falquerho, Contreres, Pages, Le Cam, Rossi & Le Cam (1989) Cell (Cambridge, Mass.) 58, 631-640] shows sequence similarity to the mammalian fetuins. The sequence identity between rat tyrosine kinase inhibitor, human alpha 2-HS glycoprotein and bovine fetuin is 56 and 60% respectively (percentage of residues in identical positions). The sequence similarity extends over the entire protein structures, except the extreme C-terminal portions. In particular, the number and relative positions of the cysteine residues are invariant among the proteins, suggesting that the characteristic array of linearly arranged and tandemly repeated disulphide loops of the cystatin superfamily is also present in rat tyrosine kinase inhibitor. We conclude that rat tyrosine kinase inhibitor may be classified as a novel member of the mammalian fetuin family.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auberger P., Falquerho L., Contreres J. O., Pages G., Le Cam G., Rossi B., Le Cam A. Characterization of a natural inhibitor of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase: cDNA cloning, purification, and anti-mitogenic activity. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):631–640. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayatte A. J., Kumbla L., Subbiah M. T. Marked acceleration of exogenous fatty acid incorporation into cellular triglycerides by fetuin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5883–5888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Dziegielewska K. M., Hill R. M., Saunders N. R. Fetuin: the bovine homologue of human alpha 2HS glycoprotein. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):45–49. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colclasure G. C., Lloyd W. S., Lamkin M., Gonnerman W., Troxler R. F., Offner G. D., Bürgi W., Schmid K., Nimberg R. B. Human serum alpha 2HS-glycoprotein modulates in vitro bone resorption. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jan;66(1):187–192. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziegielewska K. M., Bock E., Cornelis M. E., Møllgard K., New H., Saunders N. R. Identification of fetuin in human and rat fetuses and in other species. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1983;76(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(83)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziegielewska K. M., Brown W. M., Casey S. J., Christie D. L., Foreman R. C., Hill R. M., Saunders N. R. The complete cDNA and amino acid sequence of bovine fetuin. Its homology with alpha 2HS glycoprotein and relation to other members of the cystatin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4354–4357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziegielewska K. M., Møllgård K., Reynolds M. L., Saunders N. R. A fetuin-related glycoprotein (alpha 2HS) in human embryonic and fetal development. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Apr;248(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01239959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzanowski A., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T., Seibel-Ross E. Cystatin domains in alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein and fetuin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80890-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gejyo F., Chang J. L., Bürgi W., Schmid K., Offner G. D., Troxler R. F., Van Halbeek H., Dorland L., Gerwig G. J., Vliegenthart J. F. Characterization of the B-chain of human plasma alpha 2HS-glycoprotein. The complete amino acid sequence and primary structure of its heteroglycan. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4966–4971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann J., Haupt H., Auerswald E. A., Müller-Ester W. The arrangement of disulfide loops in human alpha 2-HS glycoprotein. Similarity to the disulfide bridge structures of cystatins and kininogens. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14121–14128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann J., Thelen C., Lottspeich F., Henschen A., Vogel R., Müller-Esterl W. Arrangement of the disulphide bridges in human low-Mr kininogen. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):15–21. doi: 10.1042/bj2470015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide T., Odani S. Histidine-rich glycoprotein is evolutionarily related to the cystatin superfamily. Presence of two cystatin domains in the N-terminal region. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80748-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Magnaldo I., Le Cam G., Auberger P. Secretion of a major phosphorylated glycoprotein by hepatocytes. Characterization of specific antibodies and investigations of the processing, excretion kinetics, and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15965–15971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Bowman B. H., Yang F. M. Human alpha 2-HS-glycoprotein: the A and B chains with a connecting sequence are encoded by a single mRNA transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. G., André C. M. Effect of human alpha 2HS glycoprotein on mouse macrophage function. Immunology. 1980 Mar;39(3):317–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Esterl W., Fritz H., Kellermann J., Lottspeich F., Machleidt W., Turk V. Genealogy of mammalian cysteine proteinase inhibitors. Common evolutionary origin of stefins, cystatins and kininogens. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T., Waldren C. A., Jones C. Mammalian cell growth proteins. I. Growth stimulation of fetuin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):192–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings N. D., Barrett A. J. Evolution of proteins of the cystatin superfamily. J Mol Evol. 1990 Jan;30(1):60–71. doi: 10.1007/BF02102453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrlich S. T., Rifkin D. B. Isolation of the major serine protease inhibitor from the 5-day serum-free conditioned medium of human embryonic lung cells and demonstration that it is fetuin. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Oct;109(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel R., Assfalg-Machleidt I., Esterl A., Machleidt W., Müller-Esterl W. Proteinase-sensitive regions in the heavy chain of low molecular weight kininogen map to the inter-domain junctions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12661–12668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yet M. G., Chin C. C., Wold F. The covalent structure of individual N-linked glycopeptides from ovomucoid and asialofetuin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka Y., Gejyo F., Marti T., Rickli E. E., Bürgi W., Offner G. D., Troxler R. F., Schmid K. The complete amino acid sequence of the A-chain of human plasma alpha 2HS-glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1665–1676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F., Bronson P. M., Border J. R. Opsonic properties of human serum alpha-2 hs glycoprotein. Immunol Commun. 1974;3(4):329–335. doi: 10.3109/08820137409061113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


