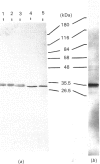
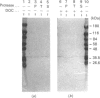
Abstract
Antibodies raised against purified components of glucose-6-phosphatase were used to study the transmembrane orientation of the complex. Measurements of glucose-6-phosphatase activities and immunoblot analysis of sealed microsomes and detergent-solubilized microsomes after treatment with proteases suggested that most of the catalytic subunit resides within the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. In contrast, other components of glucose-6-phosphatase are accessible to the cytoplasm. Treatment of the partially purified glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme with glycopeptide N-glycosidase indicated that the catalytic subunit of the enzyme was a glycoprotein.
Full text
PDF

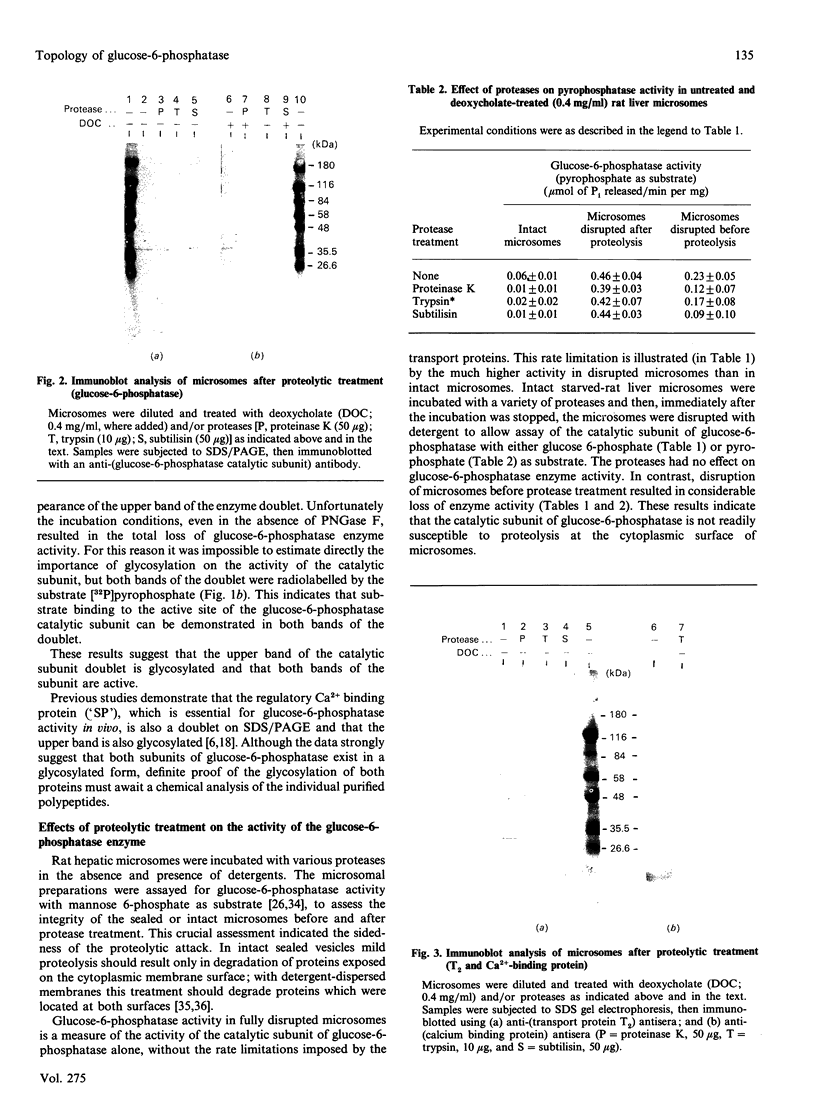
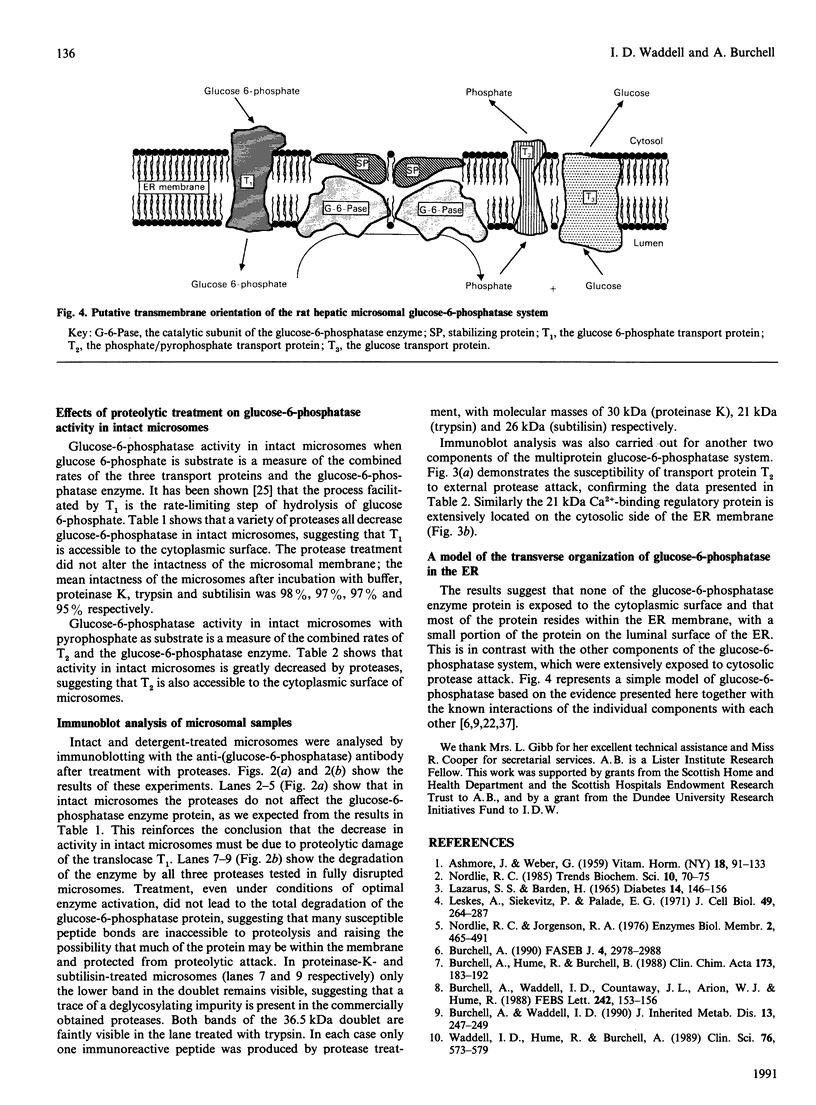

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion W. J., Lange A. J., Ballas L. M. Quantitative aspects of relationship between glucose 6-phosphate transport and hydrolysis for liver microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. Selective thermal inactivation of catalytic component in situ at acid pH. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6784–6790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion W. J., Lange A. J., Walls H. E., Ballas L. M. Evidence for the participation of independent translocation for phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate in the microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. Interactions of the system with orthophosphate, inorganic pyrophosphate, and carbamyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10396–10406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Bell J. E., Busuttil A., Hume R. Hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system and sudden infant death syndrome. Lancet. 1989 Aug 5;2(8658):291–294. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Burchell B. Identification and purification of a liver microsomal glucose 6-phosphatase. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 1;205(3):567–573. doi: 10.1042/bj2050567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Burchell B., Monaco M., Walls H. E., Arion W. J. Stabilization of glucose-6-phosphatase activity by a 21 000-dalton hepatic microsomal protein. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 1;230(2):489–495. doi: 10.1042/bj2300489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Hume R., Burchell B. A new microtechnique for the analysis of the human hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. Clin Chim Acta. 1988 Apr 15;173(2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(88)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Jung R. T., Lang C. C., Bennet W., Shepherd A. N. Diagnosis of type 1a and type 1c glycogen storage diseases in adults. Lancet. 1987 May 9;1(8541):1059–1062. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90484-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A. Molecular pathology of glucose-6-phosphatase. FASEB J. 1990 Sep;4(12):2978–2988. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.12.2168325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Waddell I. D., Countaway J. L., Arion W. J., Hume R. Identification of the human hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell A., Waddell I. D. Diagnosis of a novel glycogen storage disease: type 1aSP. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1990;13(3):247–249. doi: 10.1007/BF01799362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchell B., Burchell A. Molecular pathologies of the hepatic endoplasmic reticulum. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;1(4):712–717. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countaway J. L., Waddell I. D., Burchell A., Arion W. J. The phosphohydrolase component of the hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system is a 36.5-kilodalton polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2673–2678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAZARUS S. S., BARDEN H. SPECIFICITY AND ULTRASTRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF PANCREATIC B CELL GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATASE. Diabetes. 1965 Mar;14:146–156. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.3.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange A. J., Arion W. J., Beaudet A. L. Type Ib glycogen storage disease is caused by a defect in the glucose-6-phosphate translocase of the microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8381–8384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narisawa K., Igarashi Y., Otomo H., Tada K. A new variant of glycogen storage disease type I probably due to a defect in the glucose-6-phosphate transport system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1360–1364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91371-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelles L. P., Bamburg J. R. Rapid visualization of protein--dodecyl sulfate complexes in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jun;73(2):522–531. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen N. Y., Chrambach A. A three-step method for isolating a few to several hundred milligrams of protein. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1979 Jul;1(3):171–187. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(79)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson O. S., Arion W. J., Depierre J. W., Dallner G., Ernster L. Evidence for the involvement of a glucose-6-phosphate carrier in microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase activity. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 16;82(2):627–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlie R. C., Sukalski K. A., Muñoz J. M., Baldwin J. J. Type Ic, a novel glycogenosis. Underlying mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9739–9744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd S. R., Baird S. J., Hallinan T., Burchell B. An investigation of the transverse topology of bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase in rat hepatic endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2590617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speth M., Baake N., Schulze H. U. Topographical localization and characterization of microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase binding sites accessible to 4,4'-diazidostilbene 2,2'-disulfonic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 15;275(1):202–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Gómez C. M., Plummer T. H., Jr Deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans by peptide:N-glycosidase F. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4665–4671. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell I. D., Burchell A. The microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme of pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):471–476. doi: 10.1042/bj2550471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell I. D., Hume R., Burchell A. A direct method for the diagnosis of human hepatic type 1b and type 1c glycogen-storage disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989 Jun;76(6):573–579. doi: 10.1042/cs0760573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell I. D., Lindsay J. G., Burchell A. The identification of T2; the phosphate/pyrophosphate transport protein of the hepatic microsomal glucose-6-phosphatase system. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]