Abstract
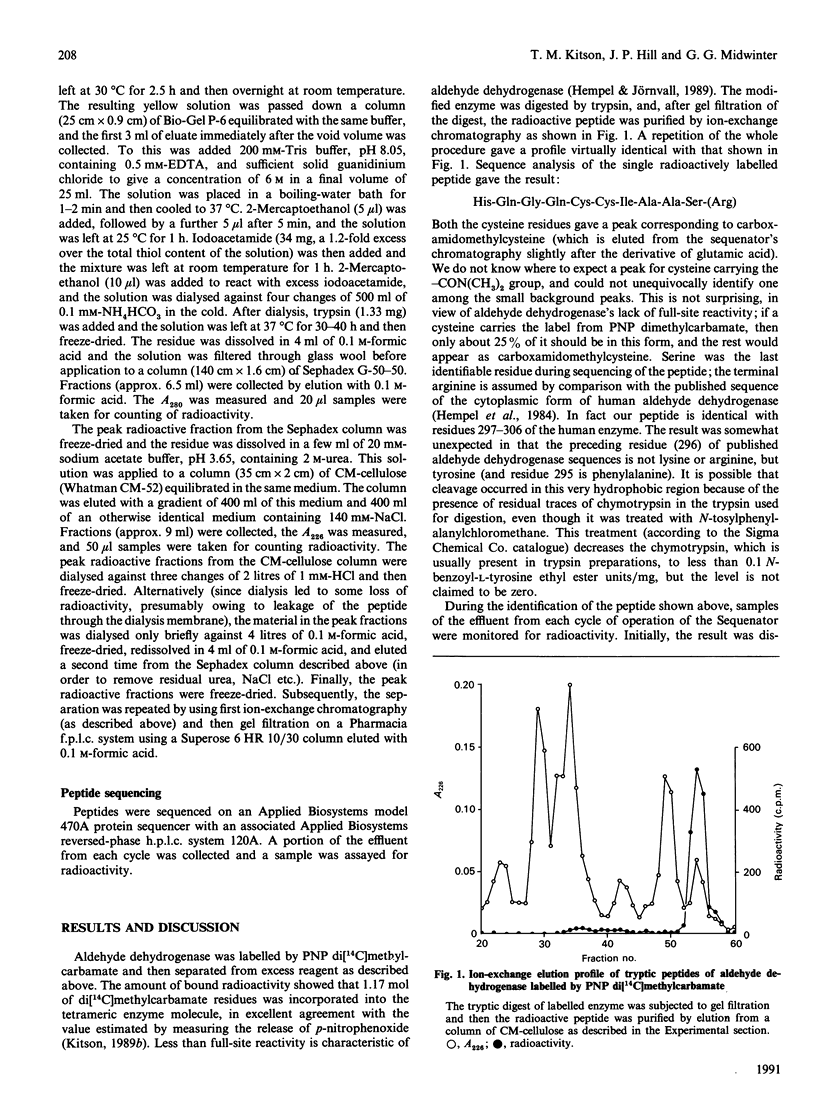
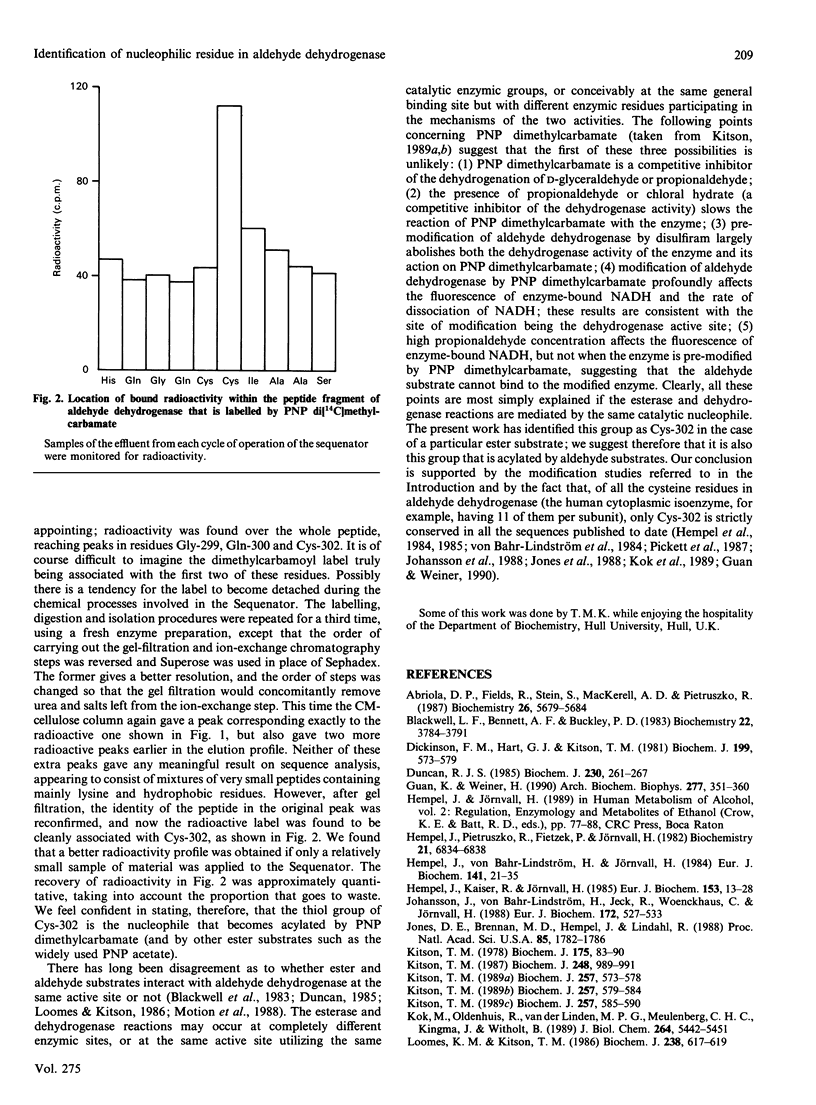
Sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase was labelled by reaction with the substrate p-nitrophenyl di[14C]methylcarbamate. After tryptic digestion and peptide fractionation the labelled residue was identified as Cys-302. This is the first unequivocal identification of the essential enzymic nucleophile in the esterase activity of aldehyde dehydrogenase. By implication, Cys-302 is probably also the residue that is acylated by aldehyde substrates and the first residue that is modified by disulfiram.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abriola D. P., Fields R., Stein S., MacKerell A. D., Jr, Pietruszko R. Active site of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5679–5684. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell L. F., Bennett A. F., Buckley P. D. Relationship between the mechanisms of the esterase and dehydrogenase activities of the cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver. An alternative view. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3784–3791. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Hart G. J., Kitson T. M. The use of pH-gradient ion-exchange chromatography to separate sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from mitochondrial enzyme contamination, and observations on the interaction between the pure cytoplasmic enzyme and disulfiram. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):573–579. doi: 10.1042/bj1990573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R. J. Aldehyde dehydrogenase. An enzyme with two distinct catalytic activities at a single type of active site. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj2300261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Weiner H. Sequence of the precursor of bovine liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase as determined from its cDNA, its gene, and its functionality. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Mar;277(2):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90590-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., Kaiser R., Jörnvall H. Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase from human liver. Primary structure, differences in relation to the cytosolic enzyme, and functional correlations. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;153(1):13–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., Pietruszko R., Fietzek P., Jörnvall H. Identification of a segment containing a reactive cysteine residue in human liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase (isoenzyme E1). Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6834–6838. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., von Bahr-Lindström H., Jörnvall H. Aldehyde dehydrogenase from human liver. Primary structure of the cytoplasmic isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):21–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson J., von Bahr-Lindström H., Jeck R., Woenckhaus C., Jörnvall H. Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase from horse liver. Correlations of the same species variants for both the cytosolic and the mitochondrial forms of an enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):527–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Jr, Brennan M. D., Hempel J., Lindahl R. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA encoding a catalytically functional tumor-associated aldehyde dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1782–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. Effect of disulfiram on the pre-steady-state burst in the reactions of sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):989–991. doi: 10.1042/bj2480989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. Kinetics of p-nitrophenyl pivalate hydrolysis catalysed by cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):573–578. doi: 10.1042/bj2570573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. Studies on the interaction between disulfiram and sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):83–90. doi: 10.1042/bj1750083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. The action of cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase on methyl p-nitrophenyl carbonate and p-nitrophenyl dimethylcarbamate. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):579–584. doi: 10.1042/bj2570579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitson T. M. The binding of NADH to cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase after modification with p-nitrophenyl dimethylcarbamate. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):585–590. doi: 10.1042/bj2570585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok M., Oldenhuis R., van der Linden M. P., Meulenberg C. H., Kingma J., Witholt B. The Pseudomonas oleovorans alkBAC operon encodes two structurally related rubredoxins and an aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5442–5451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes K. M., Kitson T. M. Aldehyde dehydrogenase catalyses acetaldehyde formation from 4-nitrophenyl acetate and NADH. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):617–619. doi: 10.1042/bj2380617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomes K. M., Midwinter G. G., Blackwell L. F., Buckley P. D. Evidence for reactivity of serine-74 with trans-4-(N,N-dimethylamino)cinnamaldehyde during oxidation by the cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 27;29(8):2070–2075. doi: 10.1021/bi00460a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motion R. L., Buckley P. D., Bennett A. F., Blackwell L. F. Evidence that the cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase-catalysed oxidation of aldehydes involves a different active-site group from that which catalyses the hydrolysis of 4-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):903–906. doi: 10.1042/bj2540903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett M., Gwynne D. I., Buxton F. P., Elliott R., Davies R. W., Lockington R. A., Scazzocchio C., Sealy-Lewis H. M. Cloning and characterization of the aldA gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasayco M. L., Prestwich G. D. A specific affinity reagent to distinguish aldehyde dehydrogenases and oxidases. Enzymes catalyzing aldehyde oxidation in an adult moth. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3094–3101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu G. C., Weiner H. Evidence for two distinct active sites on aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1218–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu G. C., Weiner H. Identification of the cysteine residue in the active site of horse liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1212–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr-Lindström H., Hempel J., Jörnvall H. The cytoplasmic isoenzyme of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Relationship to the corresponding human isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr-Lindström H., Jeck R., Woenckhaus C., Sohn S., Hempel J., Jörnvall H. Characterization of the coenzyme binding site of liver aldehyde dehydrogenase: differential reactivity of coenzyme analogues. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5847–5851. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


