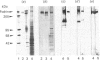
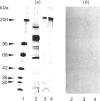
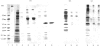Abstract
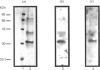
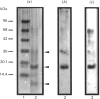
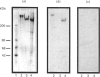
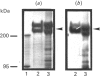
We have previously demonstrated that brain spectrin binds to the low-molecular-mass subunit of neurofilaments (NF-L) [Frappier, Regnouf & Pradel (1987) Eur. J. Biochem. 169, 651-657]. In the present study, we seek to locate their respective binding domains. In the first part we demonstrate that brain spectrin binds to a 20 kDa domain of NF-L. This domain is part of the rod domain of neurofilaments and plays a role in the polymerization process. However, the polymerization state does not seem to have any influence on the interaction. In the second part, we provide evidence that NF-L binds to the beta-subunit of not only brain spectrin but also human and avian erythrocyte spectrins. The microtubule-associated protein, MAP2, which has also been shown to bind to microfilaments and neurofilaments, binds to the same domain of NF-L as spectrin does. Finally, among the tryptic peptides of brain spectrin, we show that some peptides of low molecular mass (35, 25, 20 and 18 kDa) co-sediment with either NF-L or F-actin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. Proteins involved in membrane--cytoskeleton association in human erythrocytes: spectrin, ankyrin, and band 3. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:313–324. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers T. J., Husain-Chishti A., Dubreuil R. R., Branton D., Goldstein L. S. Sequence similarity of the amino-terminal domain of Drosophila beta spectrin to alpha actinin and dystrophin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1633–1641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassoly R., Stetzkowski-Marden F., Scheuring U. A mixing chamber to enucleate avian and fish erythrocytes: preparation of their plasma membrane. Anal Biochem. 1989 Oct;182(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90720-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. Q., Bennett V. Brain ankyrin. Purification of a 72,000 Mr spectrin-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1874–1881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J., Bennett V. Brain spectrin. Isolation of subunits and formation of hybrids with erythrocyte spectrin subunits. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7757–7766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacourte A., Filliatreau G., Boutteau F., Biserte G., Schrevel J. Study of the 10-nm-filament fraction isolated during the standard microtubule preparation. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):543–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1910543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil R. R., Byers T. J., Sillman A. L., Bar-Zvi D., Goldstein L. S., Branton D. The complete sequence of Drosophila alpha-spectrin: conservation of structural domains between alpha-spectrins and alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2197–2205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fach B. L., Graham S. F., Keates R. A. Association of fodrin with brain microtubules. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1985 May;63(5):372–381. doi: 10.1139/o85-054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G., Joly J. C., Purich D. L. The 28,000 Mr microtubule-binding domain of microtubule-associated protein-2 also contains a neurofilament-binding site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1453–1459. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80295-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler V. M., Bennett V. Erythrocyte membrane tropomyosin. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5978–5989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frappier T., Regnouf F., Pradel L. A. Binding of brain spectrin to the 70-kDa neurofilament subunit protein. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 15;169(3):651–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Fischer S., Plessmann U., Weber K. Neurofilament architecture combines structural principles of intermediate filaments with carboxy-terminal extensions increasing in size between triplet proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1295–1302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Self-assembly in Vitro of the 68,000 molecular weight component of the mammalian neurofilament triplet proteins into intermediate-sized filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Marchesi V. T. The binding of vimentin to human erythrocyte membranes: a model system for the study of intermediate filament-membrane interactions. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1955–1961. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Weber K., Geisler N., Blobel G. Binding of two desmin derivatives to the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope of avian erythrocytes: evidence for a conserved site-specificity in intermediate filament-membrane interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6780–6784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Comparison of spectrin isolated from erythroid and non-erythroid sources. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):529–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P., Osborn M., Weber K. An F-actin- and calmodulin-binding protein from isolated intestinal brush borders has a morphology related to spectrin. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):843–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P., Weber K. F-actin-binding and cross-linking properties of porcine brain fodrin, a spectrin-related molecule. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9781–9787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Weber K. Separation of fodrin subunits by affinity chromatography on calmodulin-Sepharose. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 1;150(2):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90524-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Structural associations of synemin and vimentin filaments in avian erythrocytes revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Repasky E. A., Lazarides E. Synemin and vimentin are components of intermediate filaments in avian erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):299–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. S., Morrow J. S. Proteolytic processing of human brain alpha spectrin (fodrin): identification of a hypersensitive site. J Neurosci. 1988 Jul;8(7):2640–2651. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-07-02640.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimann R., Shelanski M. L., Liem R. K. Microtubule-associated proteins bind specifically to the 70-kDa neurofilament protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12160–12166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Cross-linker system between neurofilaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):129–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly J. C., Flynn G., Purich D. L. The microtubule-binding fragment of microtubule-associated protein-2: location of the protease-accessible site and identification of an assembly-promoting peptide. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2289–2294. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Binder L. I., Rosenbaum J. L. The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):266–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J., Willard M. Fodrin: axonally transported polypeptides associated with the internal periphery of many cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):631–642. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. K., Hutchison S. B. Purification of individual components of the neurofilament triplet: filament assembly from the 70 000-dalton subunit. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3221–3226. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahboub S., Richard C., Delacourte A., Han K. K. Applications of chemical cleavage procedures to the peptide mapping of neurofilament triplet protein bands in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami Y., Sakai H. Network formation by neurofilament-induced polymerization of tubulin: 200K subunit of neurofilament triplet promotes nucleation of tubulin polymerization and enhances microtubule assembly. J Biochem. 1983 Dec;94(6):2023–2033. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. M., Wisniewski T., Merz P., De Martini J., Wisniewski H. M. Partial purification of neurofilament subunits from bovine brains and studies on neurofilament assembly. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):560–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. T., Lazarides E. Biogenesis of the avian erythroid membrane skeleton: receptor-mediated assembly and stabilization of ankyrin (goblin) and spectrin. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1899–1904. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Lazarides E. Expression of the beta subunit of spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):363–367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeed T., Ip W. Assembly properties of two CNBr fragments of avian desmin that correspond to the headpiece domain and helix 1B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1059–1066. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92709-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattilaro R. F. Interaction of microtubule-associated protein 2 with actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2003–2009. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T. Erythrocyte spectrin is comprised of many homologous triple helical segments. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):177–180. doi: 10.1038/311177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Borisy G. G. Removal of the projections from cytoplasmic microtubules in vitro by digestion with trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B. Reversible assembly purification of microtubules without assembly-promoting agents and further purification of tubulin, microtubule-associated proteins, and MAP fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:89–104. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong A. J., Kiehart D. P., Pollard T. D. Myosin from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):46–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Idler W. W., Steinert P. M., Goldman R. D. In vitro reconstitution of intermediate filaments form mammalian neurofilament triplet polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):754–757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]