Abstract
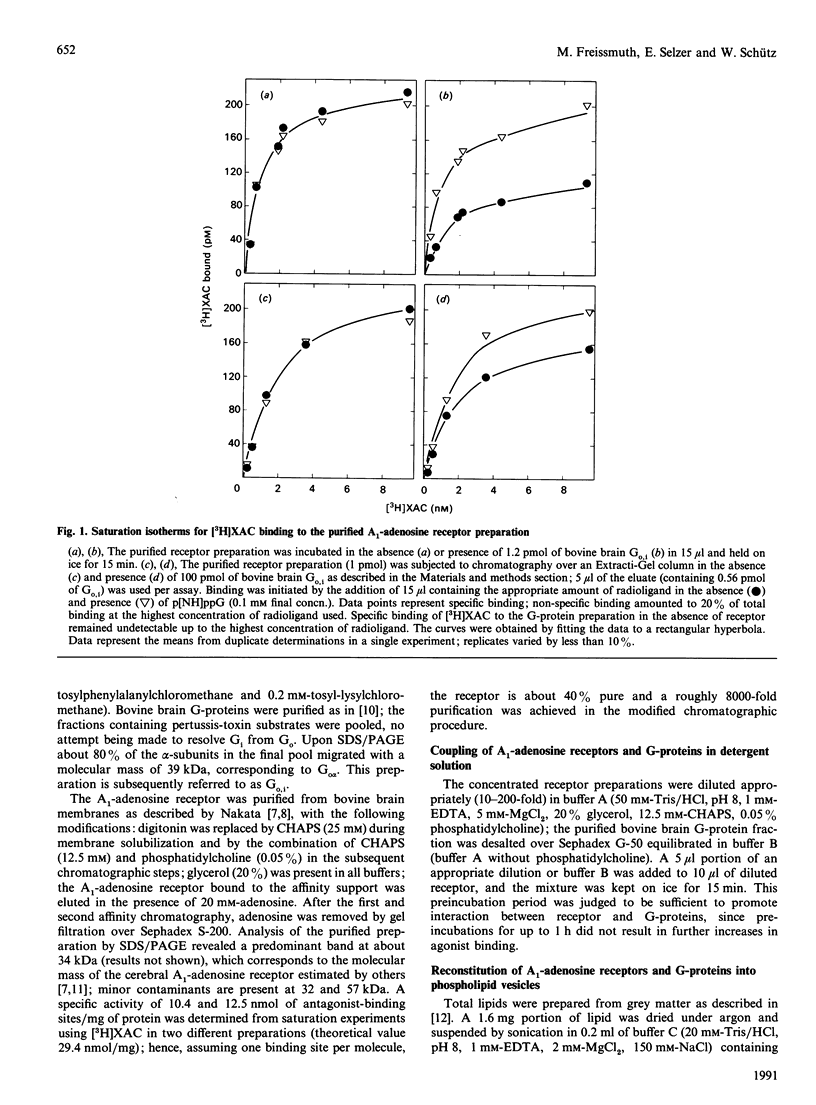
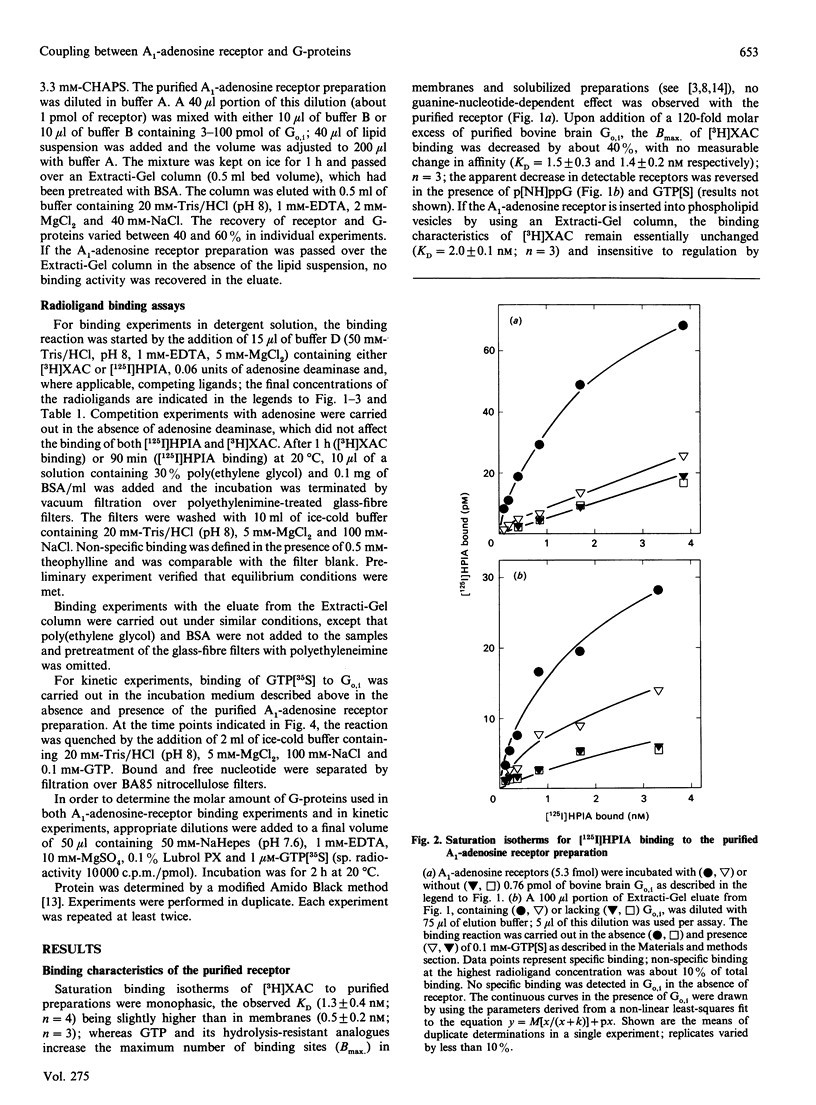
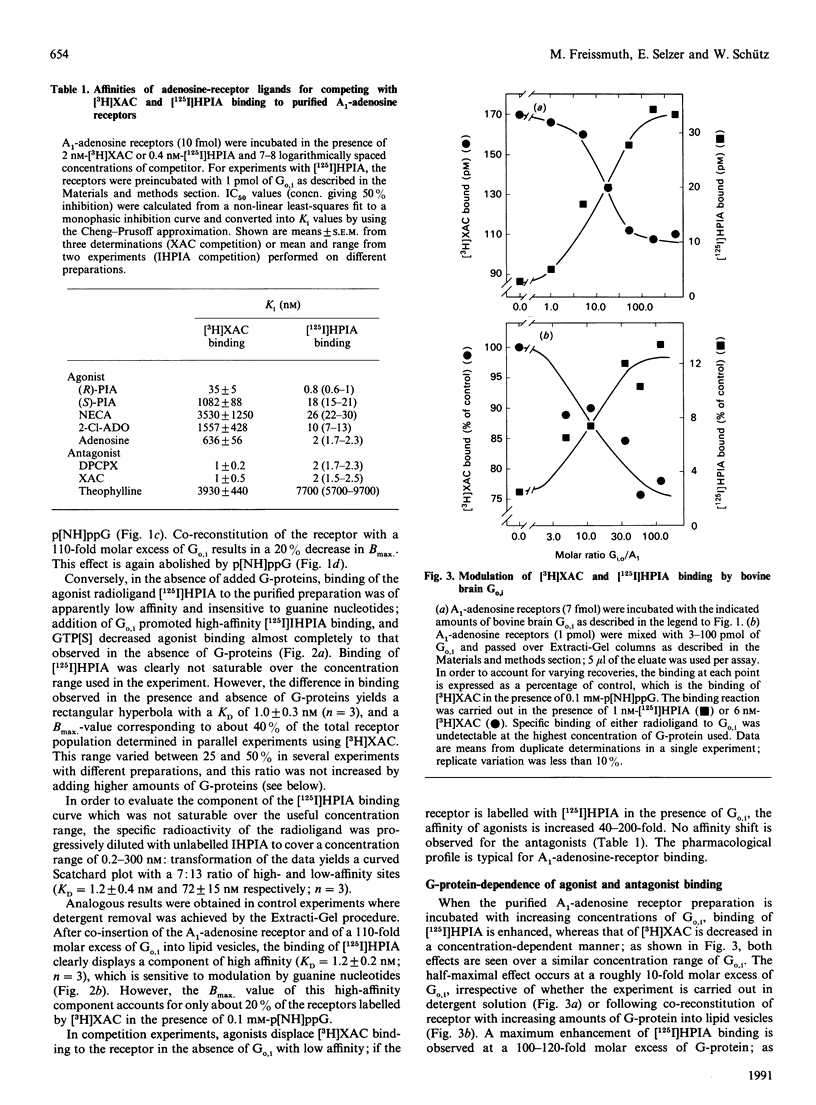
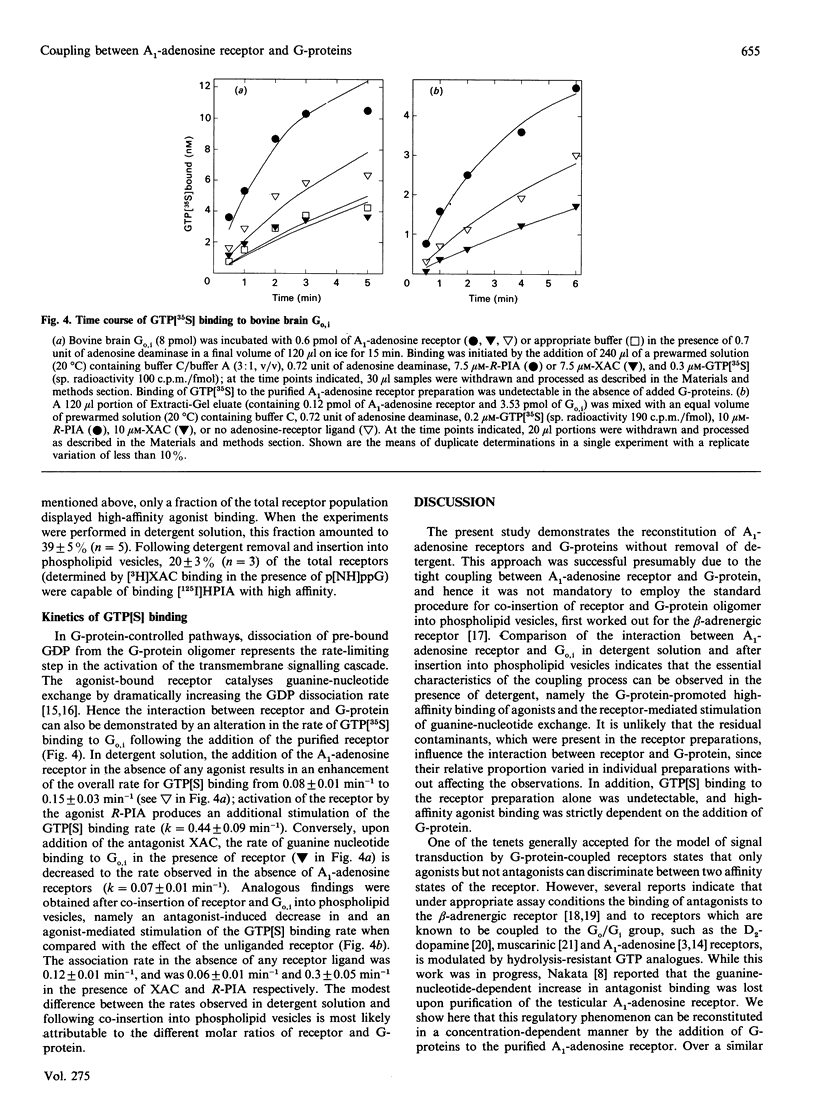
The bovine brain A1-adenosine receptor was purified 8000-fold by affinity chromatography on xanthine-amine-congener (XAC)-Sepharose. Addition of a 120-fold molar excess of a purified bovine brain G-protein preparation (Go,i a mixture of Go and Gi, containing predominantly Go) decreases the Bmax of the binding of the antagonist radioligand [3H]XAC to the receptor. This decrease is observed not only after insertion into phospholipid vesicles but also in detergent solution, and is reversed by GTP analogues. In the presence of Go,i, about 20 and 40% of the receptors display guanine-nucleotide-sensitive high-affinity binding of the agonist radioligand (-)-N6-3-([125I]iodo-4-hydroxyphenylisopropyl)adenosine after reconstitution into lipid vesicles and in detergent solution, respectively. The ability of Go,i to enhance agonist binding and decrease antagonist binding is concentration-dependent, with a half-maximal effect occurring at approximately 10-fold molar excess of G-proteins over A1-adenosine receptors. In the presence of the receptor, the rate of guanosine 5'-[gamma-[35S]thio]triphosphate (GTP[35S]) binding to Go,i is accelerated. This rate is further enhanced if the receptor is activated by the agonist (-)(R)-N6-phenylisopropyladenosine, whereas the antagonist XAC decreases the association rate of GTP[35S] to levels observed in the absence of receptor. These results show (1) that detergent removal is not a prerequisite for the observation of coupling between the A1-adenosine receptor and Go,i, and (2) that the regulatory effect of G-proteins on antagonist binding to the A1-adenosine receptor can be reconstituted by using purified components.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Brandt D. R., Pedersen S. E., Ross E. M. beta-Adrenergic receptors and regulatory GTP-binding proteins: reconstitution of coupling in phospholipid vesicles. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1985;19:47–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgisser E., De Lean A., Lefkowitz R. J. Reciprocal modulation of agonist and antagonist binding to muscarinic cholinergic receptor by guanine nucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1732–1736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Fong H. K., Simon M. I., Gilman A. G. Gz, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein with unique biochemical properties. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2383–2390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Codina J., Benovic J. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Birnbaumer L., Caron M. G. The mammalian beta 2-adrenergic receptor: reconstitution of functional interactions between pure receptor and pure stimulatory nucleotide binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4519–4525. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Benovic J. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Gierschik P., Somers R., Spiegel A. M., Codina J., Birnbaumer L. Specificity of the functional interactions of the beta-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins reconstituted in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1493–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Kilpatrick B. F., Caron M. G. Guanine nucleotides regulate both dopaminergic agonist and antagonist binding in porcine anterior pituitary. Endocrinology. 1982 Mar;110(3):1064–1066. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-3-1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio V. A., Sternweis P. C. Reconstitution of resolved muscarinic cholinergic receptors with purified GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3477–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Gilman A. G. Mutations of GS alpha designed to alter the reactivity of the protein with bacterial toxins. Substitutions at ARG187 result in loss of GTPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21907–21914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. S., Pedersen P. L. Determination of microgram quantities of protein in the presence of milligram levels of lipid with amido black 10B. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz K. N., Lohse M. J., Schwabe U. Characterization of the solubilized A1 adenosine receptor from rat brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1986 May;46(5):1528–1534. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb01772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang P. H., Lemmer B. Evidence for two specific affinity states of 3H-antagonist binding to cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors and influence of Gpp(NH)p. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(4):341–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Stadel J. M., Caron M. G. Adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors: structure and mechanisms of activation and desensitization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:159–186. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung E., Jacobson K. A., Green R. D. Analysis of agonist-antagonist interactions at A1 adenosine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;38(1):72–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden J. Purification and characterization of (-)[125I]hydroxyphenylisopropyladenosine, an adenosine R-site agonist radioligand and theoretical analysis of mixed stereoisomer radioligand binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):414–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Ewald D. A., Miller R. J., Gilman A. G. Purification and characterization of Go alpha and three types of Gi alpha after expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8243–8251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Lenschow V., Schwabe U. Two affinity states of Ri adenosine receptors in brain membranes. Analysis of guanine nucleotide and temperature effects on radioligand binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munshi R., Linden J. Co-purification of A1 adenosine receptors and guanine nucleotide-binding proteins from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14853–14859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata H. A1 adenosine receptor of rat testis membranes. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):671–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata H. Purification of A1 adenosine receptor from rat brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16545–16551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. E., Ross E. M. Functional reconstitution of beta-adrenergic receptors and the stimulatory GTP-binding protein of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7228–7232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Stiles G. L. Reciprocal modulation of agonist and antagonist binding to A1 adenosine receptors by guanine nucleotides is mediated via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):1194–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L. The A1 adenosine receptor. Solubilization and characterization of a guanine nucleotide-sensitive form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6728–6732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ströher M., Nanoff C., Schütz W. Differences in the GTP-regulation of membrane-bound and solubilized A1-adenosine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;340(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00169212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe B. B., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotides modulate the affinity of antagonists at beta-adrenergic receptors. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(5):303–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung S. M., Perez-Reyes E., Cooper D. M. Hydrodynamic properties of adenosine Ri receptors solubilized from rat cerebral-cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):635–642. doi: 10.1042/bj2480635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



