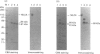Abstract
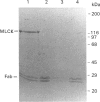
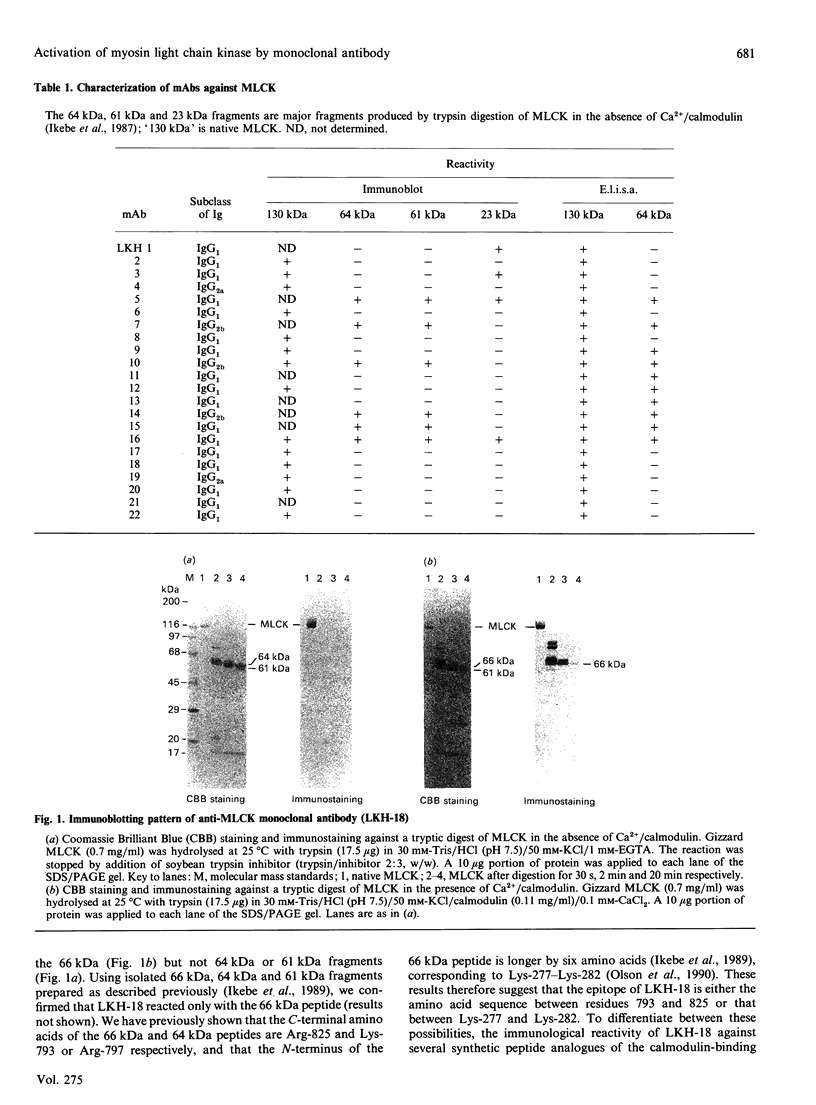
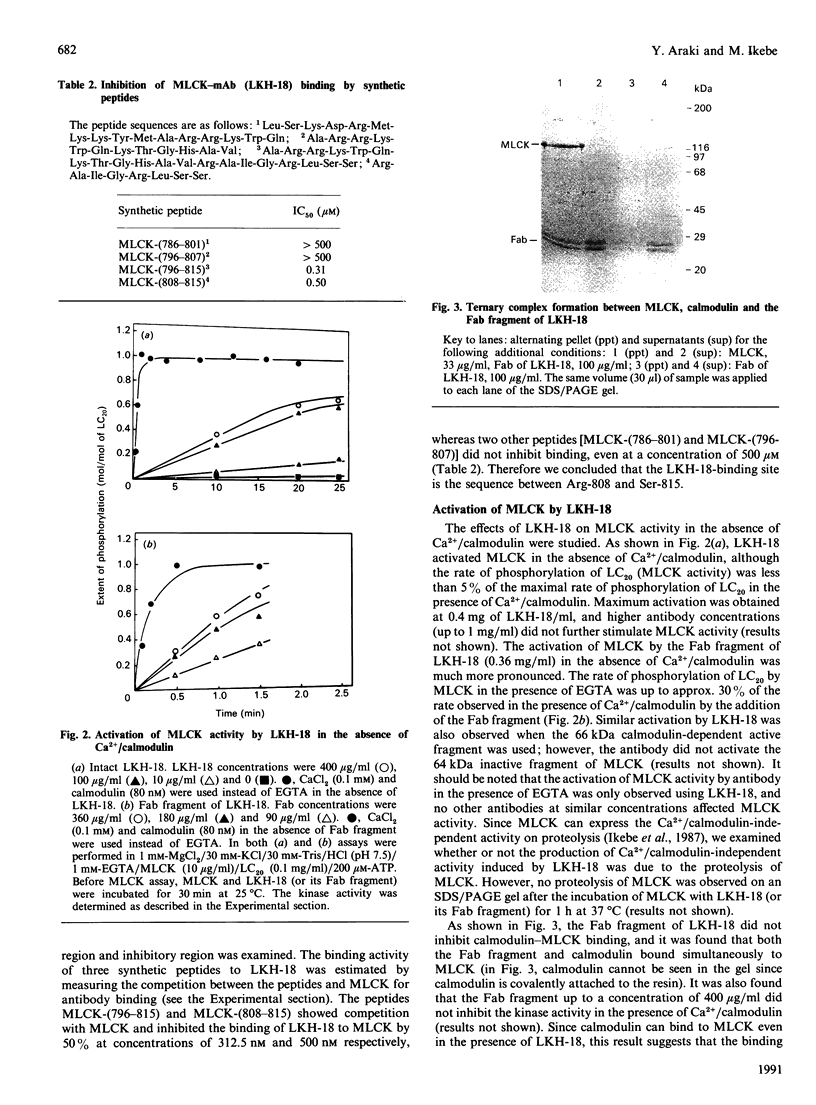
The regulatory domain of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) was studied using monoclonal antibodies. Of the 22 monoclonal antibodies tested, a monoclonal antibody designated LKH-18 was found to activate MLCK in the absence of Ca2+/calmodulin. This activation was even greater when an Fab fragment of LKH-18 was used. Consequently, the actin-dependent smooth muscle myosin ATPase activity and the superprecipitation of actomyosin were significantly activated by MLCK plus LKH-18, even in the absence of Ca2+/calmodulin. The antibody-binding site was studied using proteolytic fragments and synthetic peptide analogues of MLCK. Immunoblot analysis revealed that LKH-18 reacted with the 66 kDa calmodulin-dependent active fragment but not with the 64 kDa inactive fragment or with the 61 kDa calmodulin-independent active fragment. Furthermore, LKH-18 reacted with MLCK-(796-815)-peptide but not with MLCK-(786-801)-peptide or with MLCK-(796-807)-peptide. Therefore the LKH-18-binding site was assigned to amino acid residues 808-815 of MLCK, which are thought to be a part of the calmodulin-binding site. The present results suggest that the binding of ligand to this region induces a conformation change in MLCK and that this abolishes the action of the inhibitory region which exists next to the N-terminal side of the calmodulin-binding site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Eisenberg E. Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:921–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki Y., Kurata S., Oikawa T., Yamashita T., Hiroi M., Naiki M., Sendo F. A monoclonal antibody reacting with the zona pellucida of the oviductal egg but not with that of the ovarian egg of the golden hamster. J Reprod Immunol. 1987 Jul;11(3):193–208. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(87)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi I. C., Kemp B. E., Means A. R. Myosin light chain kinase structure function analysis using bacterial expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15843–15849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driska S., Hartshorne D. J. The contractile proteins of smooth muscle. Properties and components of a Ca2+-sensitive actomyosin from chicken gizzard. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Takio K., Blumenthal D. K., Hansen R. S., Walsh K. A., Titani K., Krebs E. G. Characterization of the calmodulin-binding and catalytic domains in skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11275–11285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara M., Tokumitsu H., Onoda K., Tanaka T., Ito M., Kato N., Hidaka H. Monoclonal antibody assessment of tissue- and species-specific myosin light chain kinase isozymes. J Biochem. 1989 Jul;106(1):71–75. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. R., Haeberle J. R. Selective purification of the 20,000-Da light chains of smooth muscle myosin. Anal Biochem. 1983 Nov;135(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90726-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highashihara M., Frado L. L., Craig R., Ikebe M. Inhibition of conformational change in smooth muscle myosin by a monoclonal antibody against the 17-kDa light chain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5218–5225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Hartshorne D. J. Effects of Ca2+ on the conformation and enzymatic activity of smooth muscle myosin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13146–13153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Hartshorne D. J. Proteolysis of smooth muscle myosin by Staphylococcus aureus protease: preparation of heavy meromyosin and subfragment 1 with intact 20 000-dalton light chains. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2380–2387. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Maruta S., Reardon S. Location of the inhibitory region of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6967–6971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M. Mode of inhibition of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by synthetic peptide analogs of the regulatory site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):714–720. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92380-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Stepinska M., Kemp B. E., Means A. R., Hartshorne D. J. Proteolysis of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. Formation of inactive and calmodulin-independent fragments. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13828–13834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., Guerriero V., Jr, Bagchi I. C., Means A. R. The calmodulin binding domain of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase contains a pseudosubstrate sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2542–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas T. J., Burgess W. H., Prendergast F. G., Lau W., Watterson D. M. Calmodulin binding domains: characterization of a phosphorylation and calmodulin binding site from myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1458–1464. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally M. H., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G., Stull J. T. Properties of a monoclonal antibody directed to the calmodulin-binding domain of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5885–5890. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. J., Pearson R. B., Needleman D. S., Hurwitz M. Y., Kemp B. E., Means A. R. Regulatory and structural motifs of chicken gizzard myosin light chain kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Wettenhall R. E., Means A. R., Hartshorne D. J., Kemp B. E. Autoregulation of enzymes by pseudosubstrate prototopes: myosin light chain kinase. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):970–973. doi: 10.1126/science.3406746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roush C. L., Kennelly P. J., Glaccum M. B., Helfman D. M., Scott J. D., Krebs E. G. Isolation of the cDNA encoding rat skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. Sequence and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10510–10516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Blumenthal D. K., Walsh K. A., Titani K., Krebs E. G. Amino acid sequence of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):8049–8057. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Hinkins S., Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J. Smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:279–288. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]