Abstract
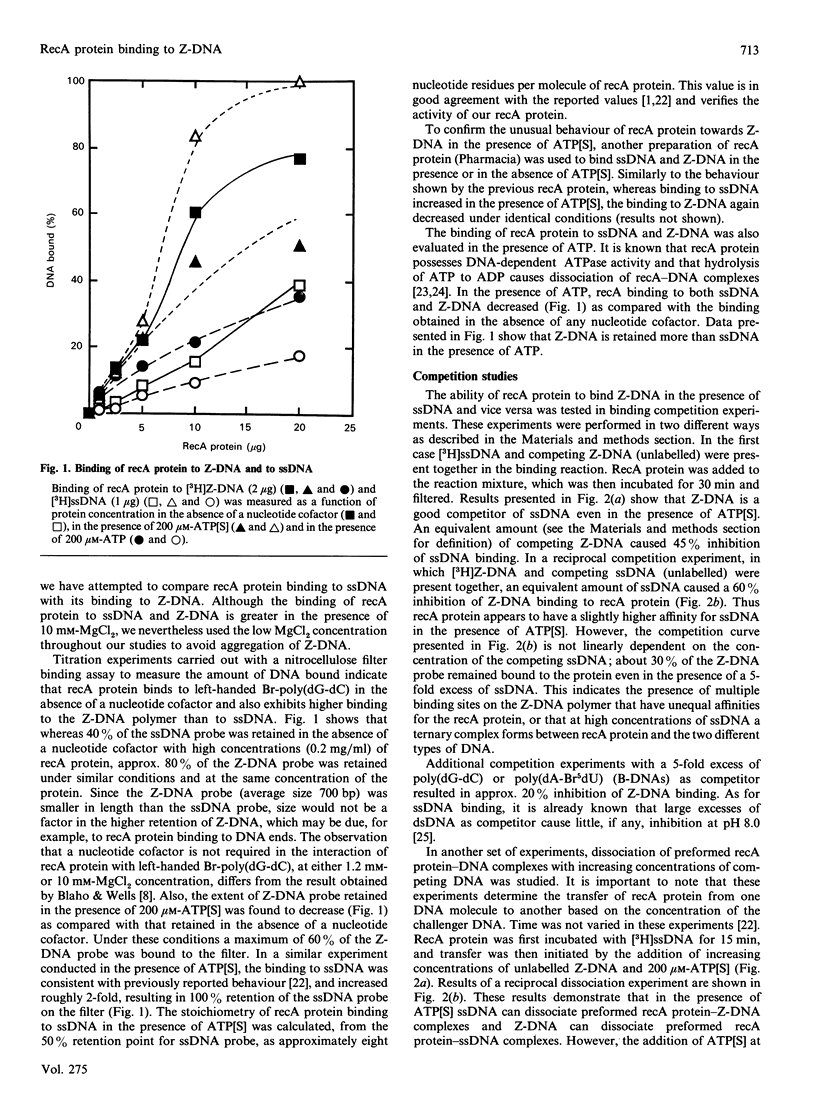
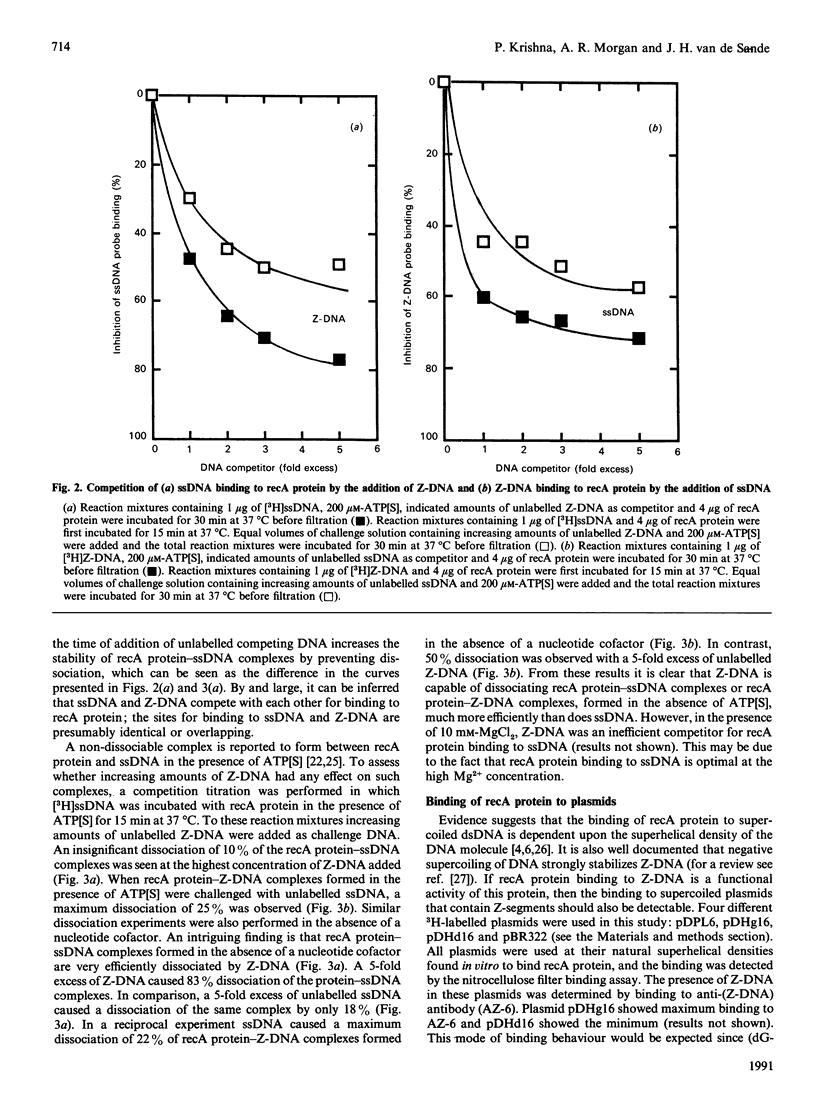
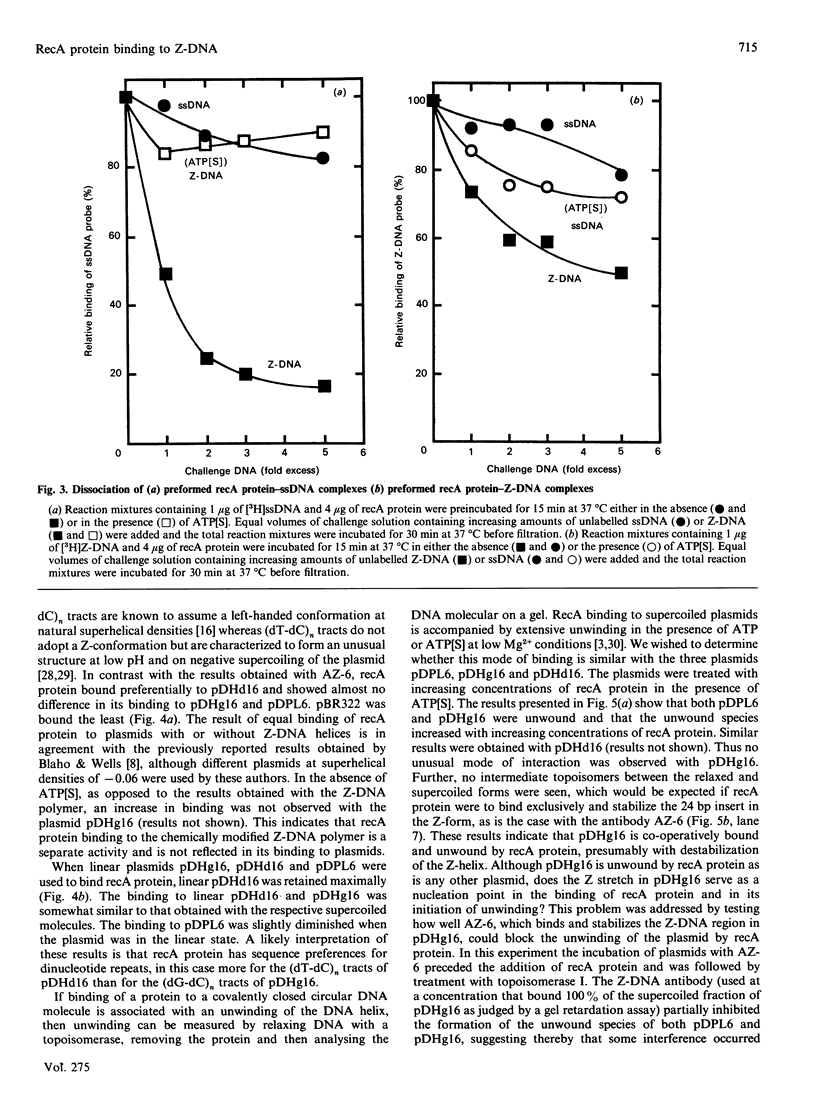
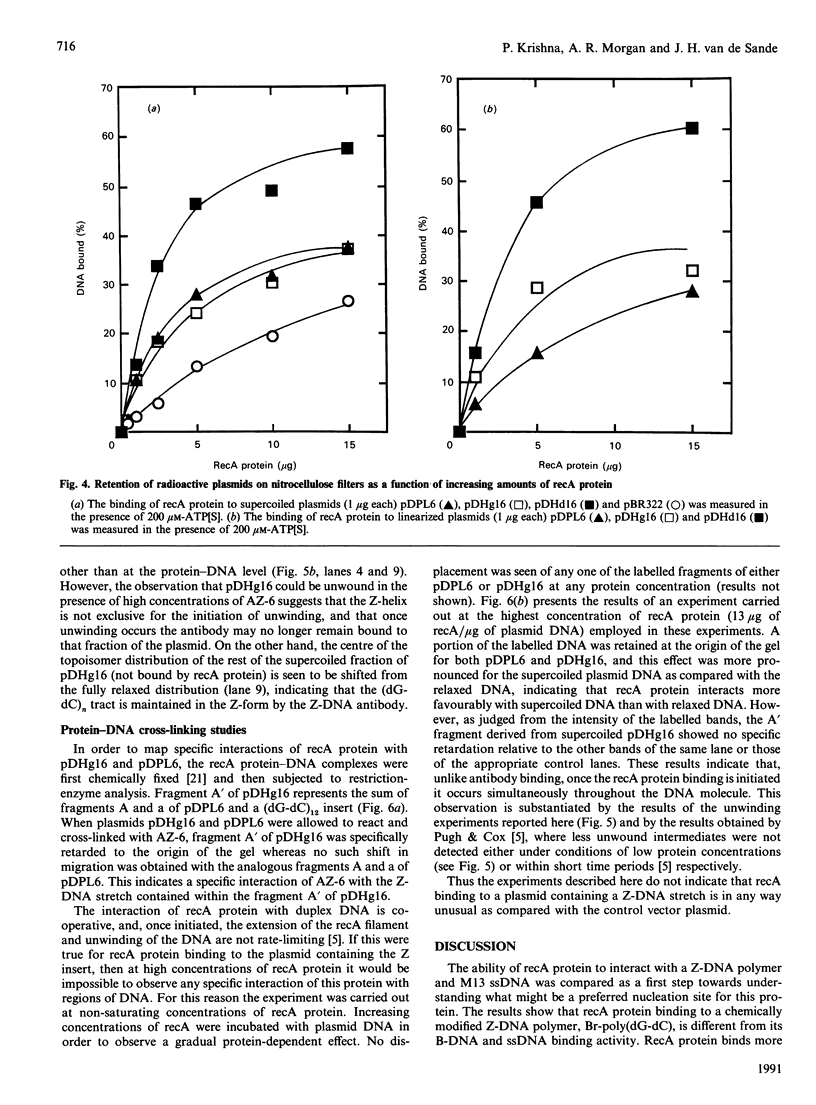
The ability of recA protein to interact with a Z-DNA polymer, Br-poly(dG-dC), or M13 bacteriophage single-stranded DNA was investigated. RecA protein binds more avidly to Z-DNA than to single-stranded DNA in the absence of a nucleotide cofactor. This binding pattern changes in the presence of adenosine 5'-(gamma-thio)triphosphate (ATP[S]), however, such that the binding to Z-DNA decreases while binding to single-stranded DNA increases roughly 2-fold. When present together, the two forms of DNA compete with each other in the presence of ATP[S]. Experiments involving recA protein binding to recombinant plasmids showed neither a preferential binding of recA protein to the plasmid containing Z-DNA nor a similar effect of ATP[S] to that observed with the Z-DNA polymer. In contrast, maximal binding was obtained with a plasmid (linear or supercoiled) containing a polypurine.polypyrimidine insert, thus suggesting that recA protein displays sequence preferences in its interaction with DNA. The results of the present study provide no evidence that recA protein specifically interacts with or stabilizes the Z-DNA insert of a recombinant plasmid in the left-handed conformation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaho J. A., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA binding by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6082–6088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant F. R., Taylor A. R., Lehman I. R. Interaction of the recA protein of Escherichia coli with single-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1196–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert M., Cazenave C., Saison-Behmoaras T., Helene C. Binding of recA protein from E. coli to double-stranded DNA: influence of the degree of superhelicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90925-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrysogelos S., Register J. C., 3rd, Griffith J. The structure of recA protein-DNA filaments. 2 recA protein monomers unwind 17 base pairs of DNA by 11.5 degrees/base pair in the presence of adenosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12624–12631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley E. C., West S. C. Homologous pairing and the formation of nascent synaptic intermediates between regions of duplex DNA by RecA protein. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):987–995. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90632-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymes of general recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:229–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. A simple and rapid procedure for the large scale purification of the recA protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4676–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Roberts J. W. Function of nucleoside triphosphate and polynucleotide in Escherichia coli recA protein-directed cleavage of phage lambda repressor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8039–8044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R. P., Shibata T., DasGupta C., Radding C. M. Single strands induce recA protein to unwind duplex DNA for homologous pairing. Nature. 1979 Sep 20;281(5728):191–195. doi: 10.1038/281191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D., Christiansen G. Electron microscope visualization of chromatin and other DNA-protein complexes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:19–35. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gut S. H., Bischoff M., Hobi R., Kuenzle C. C. Z-DNA-binding proteins from bull testis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9691–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. The in-vivo occurrence of Z DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):593–609. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi M., Shibata T., Ohtani T., Natori M., Ando T. ATP-dependent unwinding of the double helix and extensive supercoiling by Escherichia coli recA protein in the presence of topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12394–12404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. I., Heuser J., Cox M. M. Enhanced recA protein binding to Z DNA represents a kinetic perturbation of a general duplex DNA binding pathway. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21848–21856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Angelides K. J., Holloman W. K. Left-handed DNA and the synaptic pairing reaction promoted by Ustilago rec1 protein. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Holloman W. K. Homologous pairing of DNA molecules by Ustilago rec1 protein is promoted by sequences of Z-DNA. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna P., Kennedy B. P., Waisman D. M., van de Sande J. H., McGhee J. D. Are many Z-DNA binding proteins actually phospholipid-binding proteins? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1292–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna P., Kennedy B. P., van de Sande J. H., McGhee J. D. Yolk proteins from nematodes, chickens, and frogs bind strongly and preferentially to left-handed Z-DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19066–19070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Sousa R., Rosen B., Hsu A., Rich A. Isolation and characterization of Z-DNA binding proteins from wheat germ. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5070–5076. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. G., Sander M., Lowenhaupt K., Rich A. Sensitive homologous recombination strand-transfer assay: partial purification of a Drosophila melanogaster enzyme and detection of sequence effects on the strand-transfer activity of RecA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5854–5858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEntee K., Weinstock G. M., Lehman I. R. Binding of the recA protein of Escherichia coli to single- and double-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8835–8844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menetski J. P., Kowalczykowski S. C. Interaction of recA protein with single-stranded DNA. Quantitative aspects of binding affinity modulation by nucleotide cofactors. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):281–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani T., Shibata T., Iwabuchi M., Watabe H., Iino T., Ando T. ATP-dependent unwinding of double helix in closed circular DNA by recA protein of E. coli. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):86–89. doi: 10.1038/299086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Cox M. M. General mechanism for RecA protein binding to duplex DNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):479–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Cox M. M. Stable binding of recA protein to duplex DNA. Unraveling a paradox. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1326–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Homologous pairing and strand exchange in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:405–437. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Stachelek C., Konigsberg W., Rupp W. D. Sequences of the recA gene and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Kubista M., Nordén B. Binding of recA protein to Z-form DNA studied with circular and linear dichroism spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8568–8574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Kubista M., Nordén B. Binding stoichiometry and structure of RecA-DNA complexes studied by flow linear dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. Evidence for multiple heterogeneous DNA co-ordination. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90371-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., McEntee K., Lehman I. R. Hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphates catalyzed by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. Characterization of ATP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8829–8834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D. Unusual DNA structures. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1095–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]