Abstract
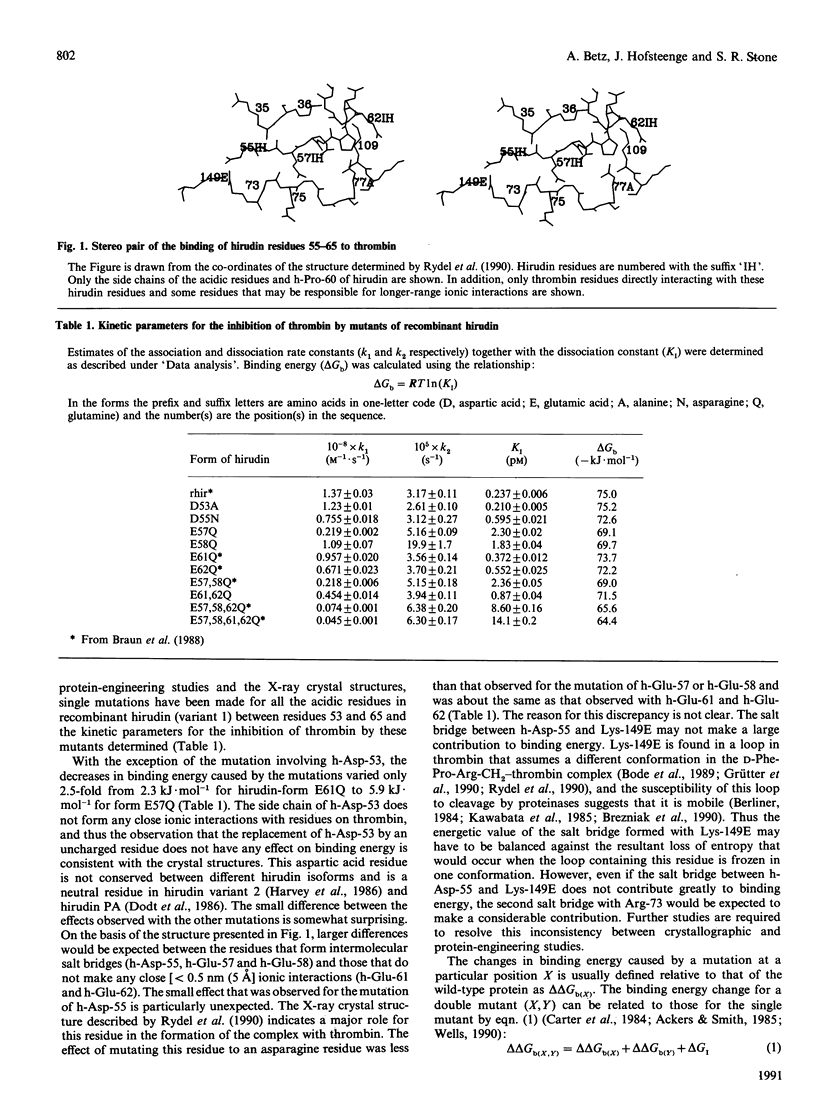
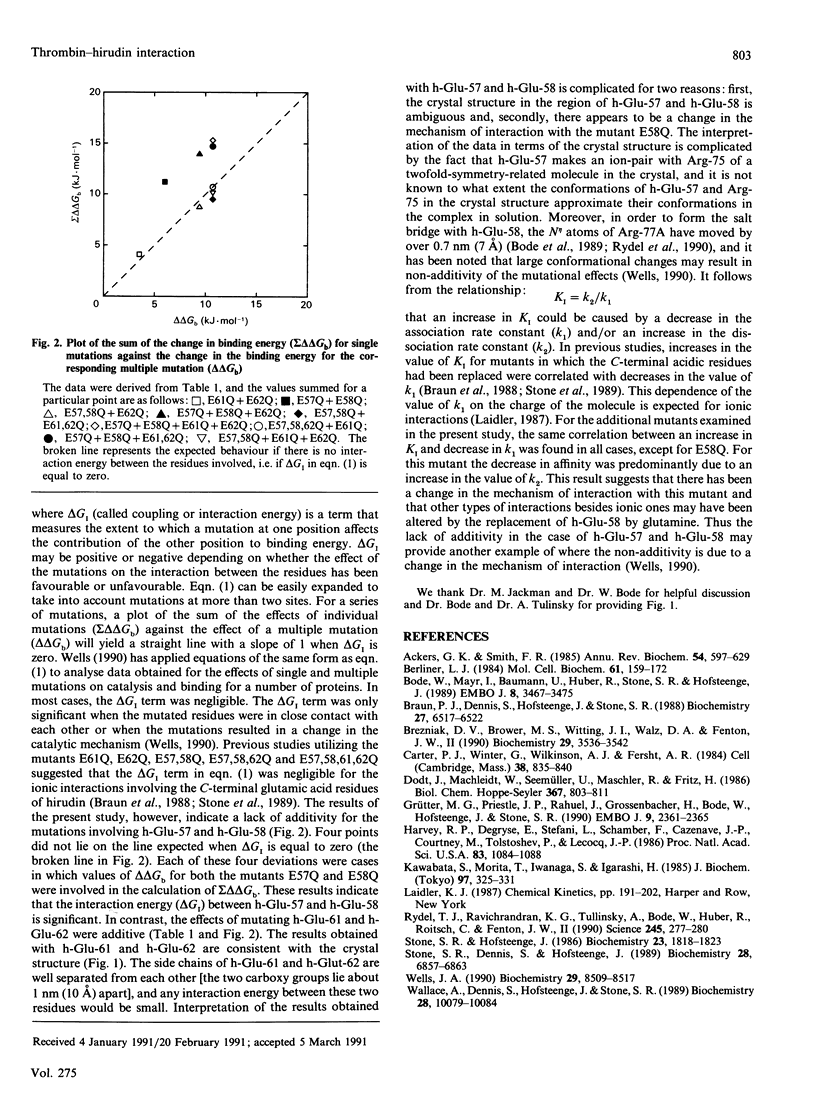
Site-directed mutagenesis has been used to examine the importance of each of the acidic C-terminal residues of hirudin in the formation of its complex with alpha-thrombin. The contribution to binding energy of acidic residues in the 11 C-terminal amino acids varied from 2.3 to 5.9 kJ.mol-1. The differences between the contributions of individual residues were smaller than would be expected from the crystal structures of the thrombin-hirudin complex. In particular, the small effect (2.4 kJ.mol-1) for the replacement of Asp-55 was surprising in view of the two salt bridges made by this residue. The results of studies involving multiple mutations indicated that the additivity of the effects varied with the position of the mutation. Whereas the effect of mutations involving the glutamic acid residues at positions 61 and 62 were additive, non-additivity was observed with the glutamic acid residues at positions 57 and 58.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackers G. K., Smith F. R. Effects of site-specific amino acid modification on protein interactions and biological function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:597–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner L. J. Structure-function relationships in human alpha- and gamma-thrombins. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;61(2):159–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00222493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Mayr I., Baumann U., Huber R., Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. The refined 1.9 A crystal structure of human alpha-thrombin: interaction with D-Phe-Pro-Arg chloromethylketone and significance of the Tyr-Pro-Pro-Trp insertion segment. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3467–3475. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun P. J., Dennis S., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. Use of site-directed mutagenesis to investigate the basis for the specificity of hirudin. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6517–6522. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezniak D. V., Brower M. S., Witting J. I., Walz D. A., Fenton J. W., 2nd Human alpha- to zeta-thrombin cleavage occurs with neutrophil cathepsin G or chymotrypsin while fibrinogen clotting activity is retained. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 10;29(14):3536–3542. doi: 10.1021/bi00466a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. J., Winter G., Wilkinson A. J., Fersht A. R. The use of double mutants to detect structural changes in the active site of the tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase (Bacillus stearothermophilus). Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):835–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodt J., Machleidt W., Seemüller U., Maschler R., Fritz H. Isolation and characterization of hirudin isoinhibitors and sequence analysis of hirudin PA. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Aug;367(8):803–811. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.2.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grütter M. G., Priestle J. P., Rahuel J., Grossenbacher H., Bode W., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. Crystal structure of the thrombin-hirudin complex: a novel mode of serine protease inhibition. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2361–2365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Degryse E., Stefani L., Schamber F., Cazenave J. P., Courtney M., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for the anticoagulant hirudin from the bloodsucking leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1084–1088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata S., Morita T., Iwanaga S., Igarashi H. Staphylocoagulase-binding region in human prothrombin. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):325–331. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel T. J., Ravichandran K. G., Tulinsky A., Bode W., Huber R., Roitsch C., Fenton J. W., 2nd The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human alpha-thrombin. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):277–280. doi: 10.1126/science.2374926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Dennis S., Hofsteenge J. Quantitative evaluation of the contribution of ionic interactions to the formation of the thrombin-hirudin complex. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 22;28(17):6857–6863. doi: 10.1021/bi00443a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace A., Dennis S., Hofsteenge J., Stone S. R. Contribution of the N-terminal region of hirudin to its interaction with thrombin. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):10079–10084. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A. Additivity of mutational effects in proteins. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8509–8517. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



