Abstract
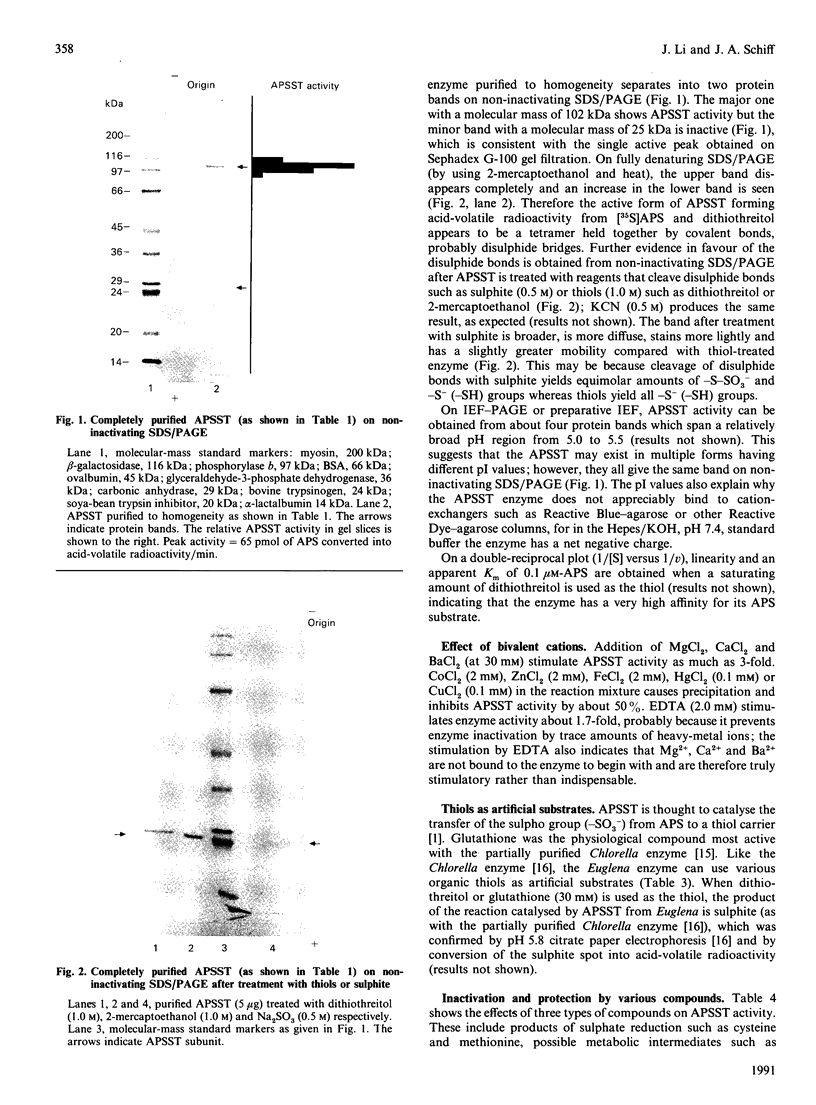
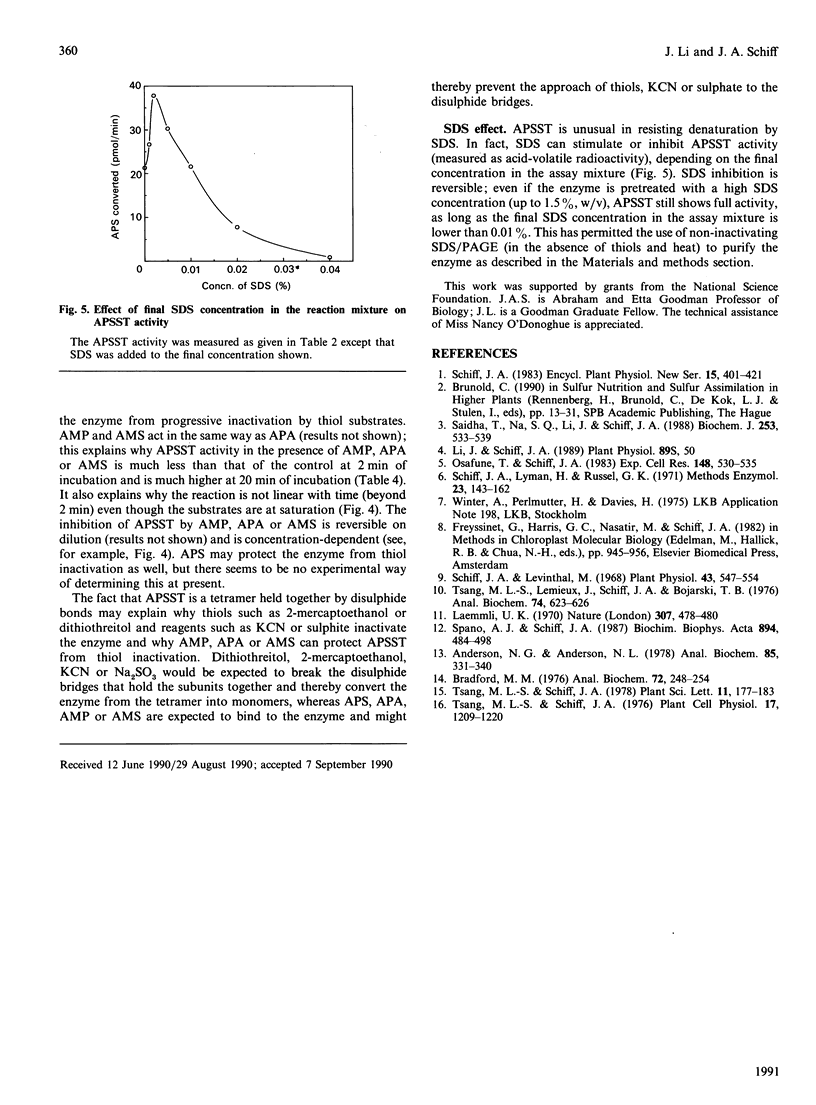
Adenosine 5'-phosphosulphate sulphotransferase (APSST) was extracted from Euglena gracilis Klebs var. bacillaris mutant W10BSmL by freezing and thawing and was purified about 10,000-fold (to homogeneity) with 10.5% recovery by (NH4)2SO4 precipitation, Sephadex G-100 chromatography, Reactive Blue-agarose, Reactive Dye-agarose, DEAE-cellulose, preparative isoelectric focusing and non-inactivating SDS/PAGE. The active APSST, with a molecular mass of 102 kDa and multiple forms from pI 5.0 to 5.5, is a tetramer held together by covalent (probably disulphide) bonds. An apparent Km of the purified enzyme for adenosine 5'-phosphosulphate (APS) of 0.1 microM is obtained when dithiothreitol is used as the thiol. The enzyme is stimulated by Mg2+, Ca2+ or Ba2+, and uses almost any thiol; dithiothreitol and dithioerythritol give the highest activity. In the absence of APS, the enzyme is inactivated (and is rendered monomeric) by thiols but is protected from thiol inactivation by AMP, adenosine 5'-phosphoramidate (APA) or adenosine 5'-monosulphate (AMS), which also inhibit APSST activity somewhat. The enzyme resists inactivation by SDS in the absence of thiols; SDS stimulates APSST activity at low concentration, but high concentrations are inhibitory.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Anderson N. L. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXI. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple isoelectric focusing. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osafune T., Schiff J. A. W10BSmL, a mutant of Euglena gracilis var. bacillaris lacking plastids. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Oct 15;148(2):530–535. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saidha T., Na S. Q., Li J. Y., Schiff J. A. A sulphate metabolizing centre in Euglena mitochondria. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 15;253(2):533–539. doi: 10.1042/bj2530533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff J. A., Levinthal M. Studies of sulfate utilization by algae. 4. Properties of a cell-free sulfate-reducing system from chlorella. Plant Physiol. 1968 Apr;43(4):547–554. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spano A. J., Schiff J. A. Purification, properties, and cellular localization of Euglena ferredoxin-NADP reductase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 17;894(3):484–498. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(87)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang M. L., Lemieux J., Schiff J. A., Bojarski T. B. Preparation of adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS) from adenosine 3'-phosphate 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) prepared by an improved procedure. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):623–626. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





