Abstract
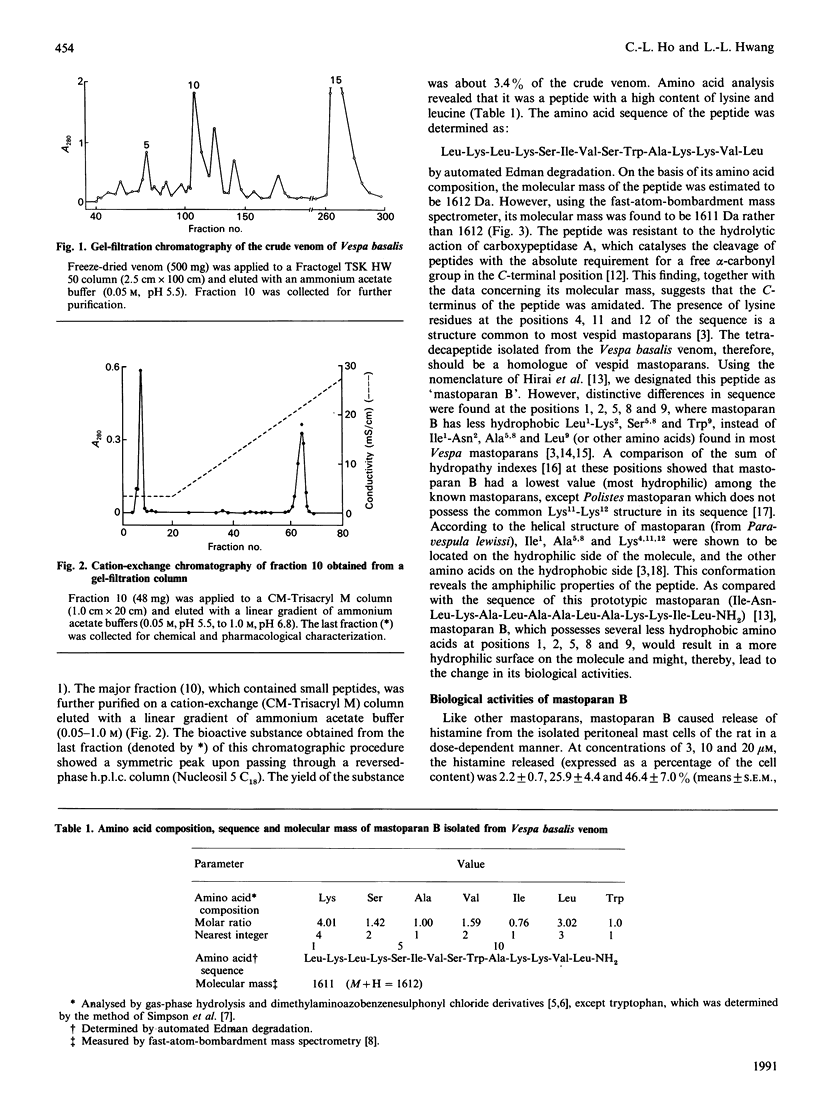
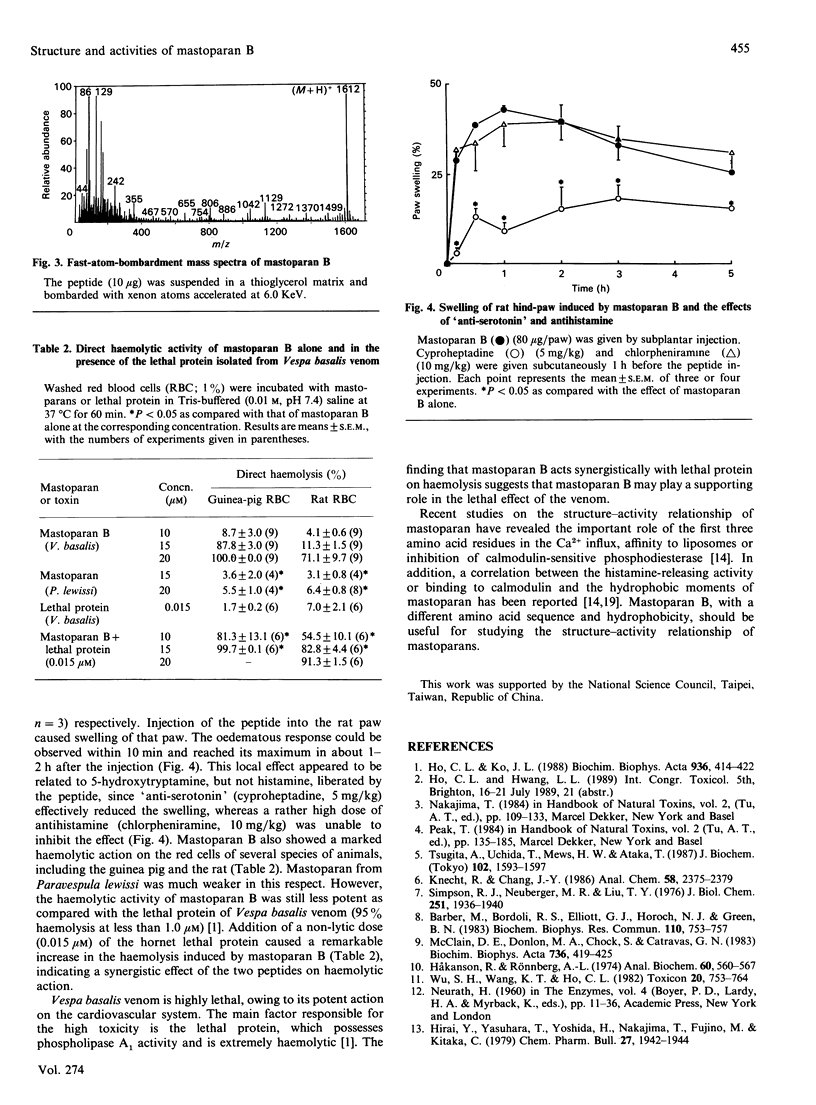
By gel filtration on a Fractogel TSK HW 50 column followed by cation-exchange chromatography on CM-Trisacryl M, a tetradecapeptide amide, designated 'mastoparan B', was purified from the venom of the hornet Vespa basalis. Its amino acid sequence was determined as: Leu-Lys-Leu-Lys-Ser-Ile-Val-Ser-Trp-Ala-Lys-Lys-Val-Leu-NH2 and its molecular mass was measured to be 1611 Da by fast-atom-bombardment mass spectrometry. In addition to having a common structure of vespid mastoparans, the peptide shows a less hydrophobic sequence at positions 1, 2, 5, 8 and 9. The peptide caused liberation of histamine from rat peritoneal mast cells and induced oedema in the rat paw. However, the latter effect was inhibited by 'anti-serotonin' (anti-5-hydroxytryptamine) (cyproheptadine), but not by antihistamine (chlorpheniramine). The peptide also possesses a potent haemolytic activity which acts in synergy with the lethal protein of the venom, suggesting the possible involvement of mastoparan B in the lethal effect of Vespa basalis venom.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber M., Bordoli R. S., Elliott G. J., Horoch N. J., Green B. N. Fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry of human proinsulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 10;110(3):753–757. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Wakamatsu K., Takemitsu M., Fujino M., Nakajima T., Miyazawa T. Conformational change of mastoparan from wasp venom on binding with phospholipid membrane. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 21;152(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80385-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai Y., Yasuhara T., Yoshida H., Nakajima T., Fujino M., Kitada C. A new mast cell degranulating peptide "mastoparan" in the venom of Vespula lewisii. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1979 Aug;27(8):1942–1944. doi: 10.1248/cpb.27.1942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C. L., Ko J. L. Purification and characterization of a lethal protein with phospholipase A1 activity from the hornet (Vespa basalis) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 16;963(3):414–422. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson R., Rönnberg A. L. Improved fluorometric assay of histamine: condensation with O-phthalaldehyde at -20 degrees C. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):560–567. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht R., Chang J. Y. Liquid chromatographic determination of amino acids after gas-phase hydrolysis and derivatization with (dimethylamino)azobenzenesulfonyl chloride. Anal Chem. 1986 Oct;58(12):2375–2379. doi: 10.1021/ac00125a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. E., Donlon M. A., Chock S., Catravas G. N. The effect of calmodulin on histamine release in the rat peritoneal mast cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell L., Sanyal G., Prendergast F. G. Probable role of amphiphilicity in the binding of mastoparan to calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):2979–2984. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Uzu S., Wakamatsu K., Saito K., Miyazawa T., Yasuhara T., Tsukamoto Y., Fujino M. Amphiphilic peptides in wasp venom. Biopolymers. 1986;25 (Suppl):S115–S121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Neuberger M. R., Liu T. Y. Complete amino acid analysis of proteins from a single hydrolysate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1936–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugita A., Uchida T., Mewes H. W., Ataka T. A rapid vapor-phase acid (hydrochloric acid and trifluoroacetic acid) hydrolysis of peptide and protein. J Biochem. 1987 Dec;102(6):1593–1597. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. H., Wang K. T., Ho C. L. Purification and pharmacological characterization of a cardiotoxin-like protein from Formosan banded krait (Bungarus multicinctus) venom. Toxicon. 1982;20(4):753–764. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


