Abstract
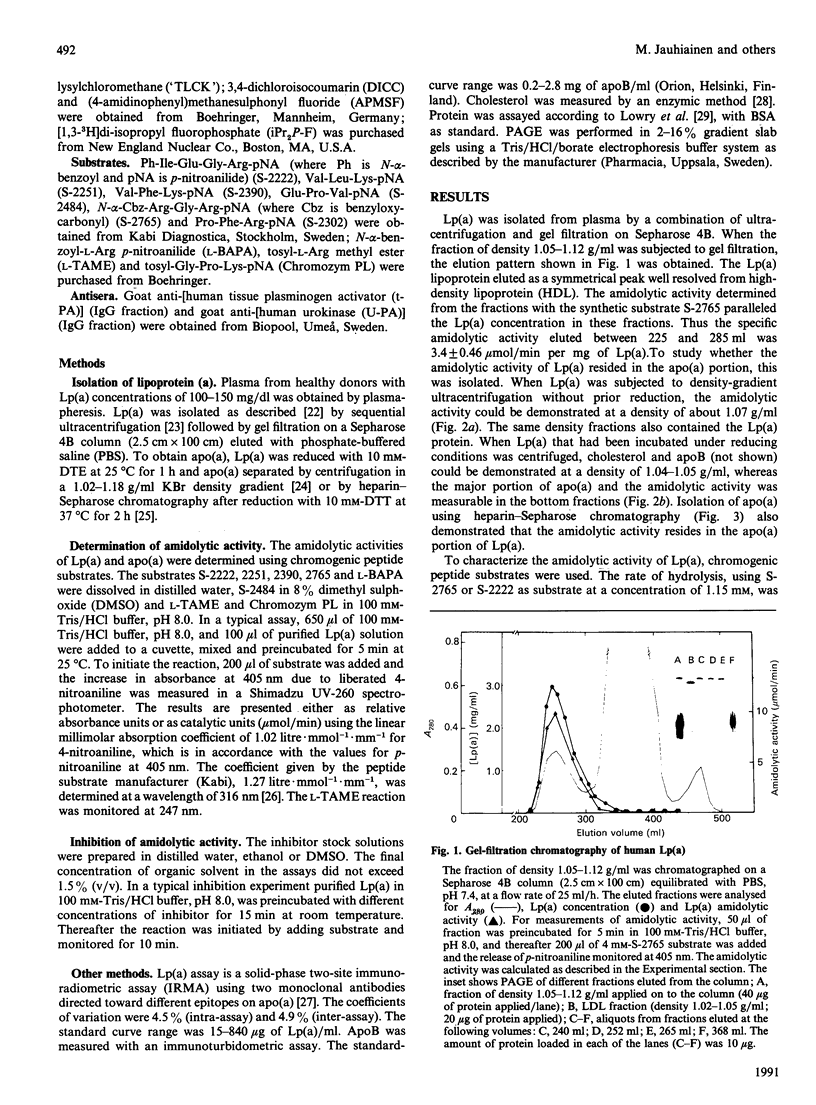
The plasma concentration of lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] is correlated with the risk of atherosclerosis. It is a lipoprotein particle consisting of apoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] is correlated with the risk of atherosclerosis. It is a lipoprotein particle consisting of apoprotein (a) [apo(a)], a protein showing considerable amino acid sequence identity with plasminogen. bound to low-density lipoprotein. The apo(a) portion of Lp(a) was recently shown to have serine-proteinase-type amidolytic activity and to be able to degrade the adhesive glycoprotein fibronectin. To characterize this enzyme activity further, we used chromogenic peptide substrates and inhibitors. Of the substrates tested, those with arginine at the scissile bond [N-alpha-benzoyl-L-Arg p-nitroanilide (pNA), N-alpha-benzoyl-Ile-Glu-Gly-Arg-pNA, N-alpha-benzyloxycarbonyl-Arg-Gly-Arg-pNA] gave the highest hydrolysis rates. Synthetic substrates with plasmin specificity (Val-Leu-L-Lys-pNA and Val-Phe-L-Lys-pNA) were not hydrolysed by Lp(a). Neither tissue plasminogen activator nor urokinase had any effect on the enzyme activity. The addition of antibodies to these plasminogen activators did not inhibit the enzyme activity of Lp(a). Inhibition experiments with phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride, carbodi-imide, dichloroisocoumarin and competitive peptide inhibitors demonstrated that Lp(a) has enzyme activity that closely resembles that of serine proteinases. Whether this serine-proteinase activity of Lp(a) plays any role in the genesis of atherosclerosis remains to be established.
Full text
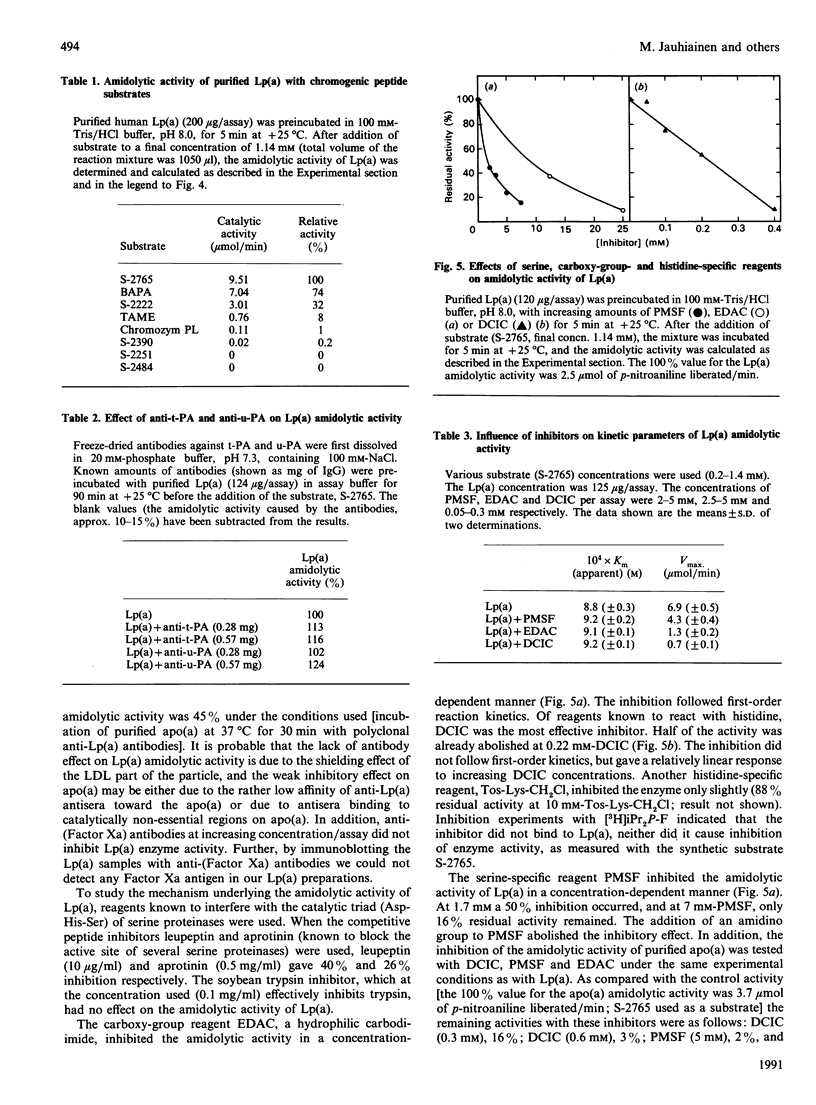
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong V. W., Cremer P., Eberle E., Manke A., Schulze F., Wieland H., Kreuzer H., Seidel D. The association between serum Lp(a) concentrations and angiographically assessed coronary atherosclerosis. Dependence on serum LDL levels. Atherosclerosis. 1986 Dec;62(3):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(86)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERG K. A NEW SERUM TYPE SYSTEM IN MAN--THE LP SYSTEM. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;59:369–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb01808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow D. M., Birktoft J. J., Hartley B. S. Role of a buried acid group in the mechanism of action of chymotrypsin. Nature. 1969 Jan 25;221(5178):337–340. doi: 10.1038/221337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D. On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Jun 18;43(2):77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Fless G. M., Kohr W. J., McLean J. W., Xu Q. T., Miller C. G., Lawn R. M., Scanu A. M. Partial amino acid sequence of apolipoprotein(a) shows that it is homologous to plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3224–3228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Garoff H., Renkonen O., Simons K. Protein and carbohydrate composition of Lp(a)lipoprotein from human plasma. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 15;11(17):3229–3232. doi: 10.1021/bi00767a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehnholm C., Garoff H., Simons K., Aro H. Purification and quantitation of the human plasma lipoprotein carrying the Lp(a) antigen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 25;236(2):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fless G. M., ZumMallen M. E., Scanu A. M. Isolation of apolipoprotein(a) from lipoprotein(a). J Lipid Res. 1985 Oct;26(10):1224–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S. L., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Mohandas T., Tomlinson J. E., McLean J. W., Lawn R. M., Lusis A. J. The apolipoprotein(a) gene resides on human chromosome 6q26-27, in close proximity to the homologous gene for plasminogen. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):352–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00282175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaubatz J. W., Heideman C., Gotto A. M., Jr, Morrisett J. D., Dahlen G. H. Human plasma lipoprotein [a]. Structural properties. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4582–4589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Gavish D., Breslow J. L., Nachman R. L. Lipoprotein(a) modulation of endothelial cell surface fibrinolysis and its potential role in atherosclerosis. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):303–305. doi: 10.1038/339303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Hemmi K., Powers J. C. Reaction of serine proteases with substituted isocoumarins: discovery of 3,4-dichloroisocoumarin, a new general mechanism based serine protease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1831–1841. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvie N. R., Schultz J. S. Studies of Lp-lipoprotein as a quantitative genetic trait. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):99–103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefler G., Harnoncourt F., Paschke E., Mirtl W., Pfeiffer K. H., Kostner G. M. Lipoprotein Lp(a). A risk factor for myocardial infarction. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):398–401. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.4.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Granzymes: a family of serine proteases in granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;140:33–47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-73911-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Avogaro P., Cazzolato G., Marth E., Bittolo-Bon G., Qunici G. B. Lipoprotein Lp(a) and the risk for myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jan-Feb;38(1-2):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzin H., Armstrong V. W., Niehaus M., Hilschmann N., Seidel D. Structural relationship of an apolipoprotein (a) phenotype (570 kDa) to plasminogen: homologous kringle domains are linked by carbohydrate-rich regions. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Dec;368(12):1533–1544. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraut J. Serine proteases: structure and mechanism of catalysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:331–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G., Gersdorf E., Menzel H. J., Duba C., Cleve H., Humphries S., Utermann G. The gene for the Lp(a)-specific glycoprotein is closely linked to the gene for plasminogen on chromosome 6. Hum Genet. 1989 Jan;81(2):149–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00293891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Tomlinson J. E., Kuang W. J., Eaton D. L., Chen E. Y., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Lawn R. M. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):132–137. doi: 10.1038/330132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath M., Niendorf A., Reblin T., Dietel M., Krebber H. J., Beisiegel U. Detection and quantification of lipoprotein(a) in the arterial wall of 107 coronary bypass patients. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(5):579–592. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Dahlen G., Berg K., Morton N. E., Dannenberg A. L. Lp(a) lipoprotein as a risk factor for myocardial infarction. JAMA. 1986 Nov 14;256(18):2540–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Summaria L., Wohl R. C. Human plasmin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):379–387. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Jauhiainen M., Zardi L., Vaheri A., Ehnholm C. Lipoprotein(a) binds to fibronectin and has serine proteinase activity capable of cleaving it. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4035–4040. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Ehnholm C., Renkonen O., Bloth B. Characterization of the Lp(a) lipoprotein in human plasma. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(4):459–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1970.tb04328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., Kay L. M., Dickerson R. E. The structure of bovine trypsin: electron density maps of the inhibited enzyme at 5 Angstrom and at 2-7 Angstron resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):185–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teger-Nilsson A. C., Friberger P., Gyzander E. Determination of a new rapid plasmin inhibitor in human blood by means of a plasmin specific tripeptide substrate. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson J. E., McLean J. W., Lawn R. M. Rhesus monkey apolipoprotein(a). Sequence, evolution, and sites of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5957–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H. Structures and activities of protease inhibitors of microbial origin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:678–695. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Kraft H. G., Menzel H. J., Hopferwieser T., Seitz C. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. I. Relation of LP(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to Lp(a) lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00291232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Duba H. C., Kemmler H. G., Seitz C. Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentrations in plasma. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):458–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Weber W. Protein composition of Lp(a) lipoprotein from human plasma. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 18;154(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. W., Hitchens J., Magnani H. N., Khan M. A study of methods of identification and estimation of Lp(a) lipoprotein and of its significance in health, hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1974 Sep-Oct;20(2):323–346. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(74)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Naray-Szabo G., Sussman F., Hwang J. K. How do serine proteases really work? Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3629–3637. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. S., Alden R. A., Kraut J. Structure of subtilisin BPN' at 2.5 angström resolution. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):235–242. doi: 10.1038/221235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




