Abstract
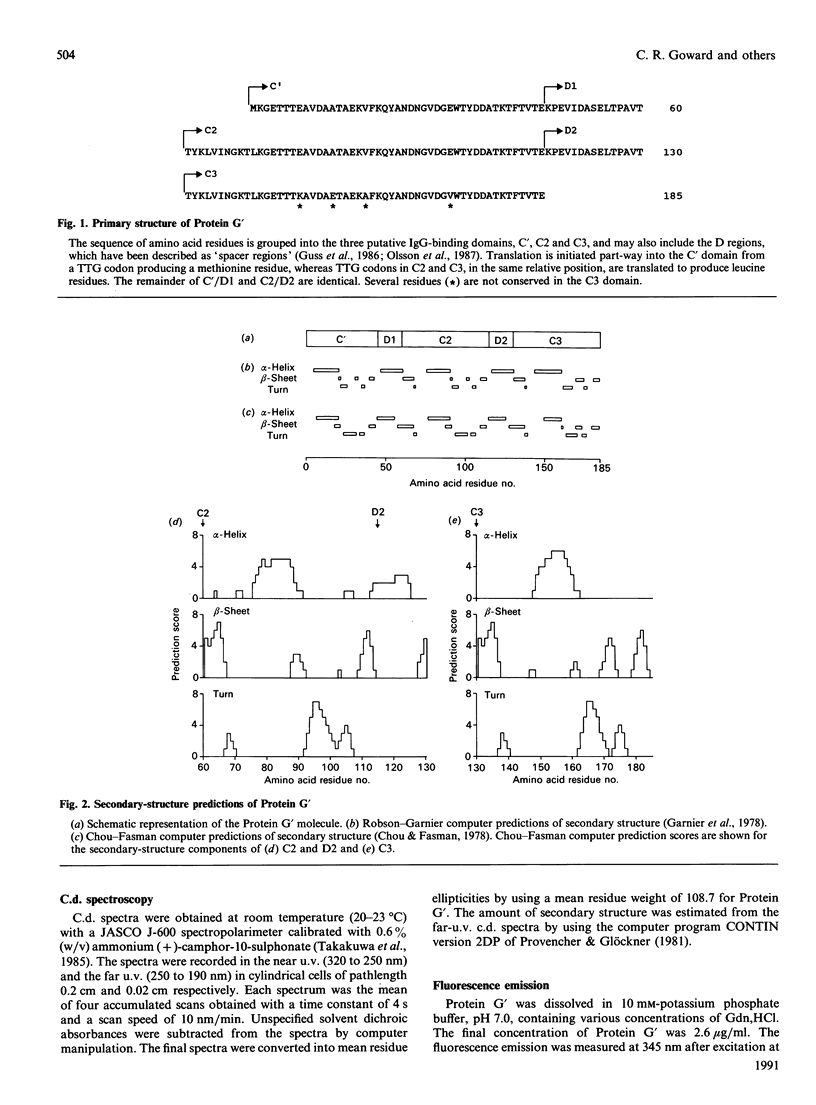
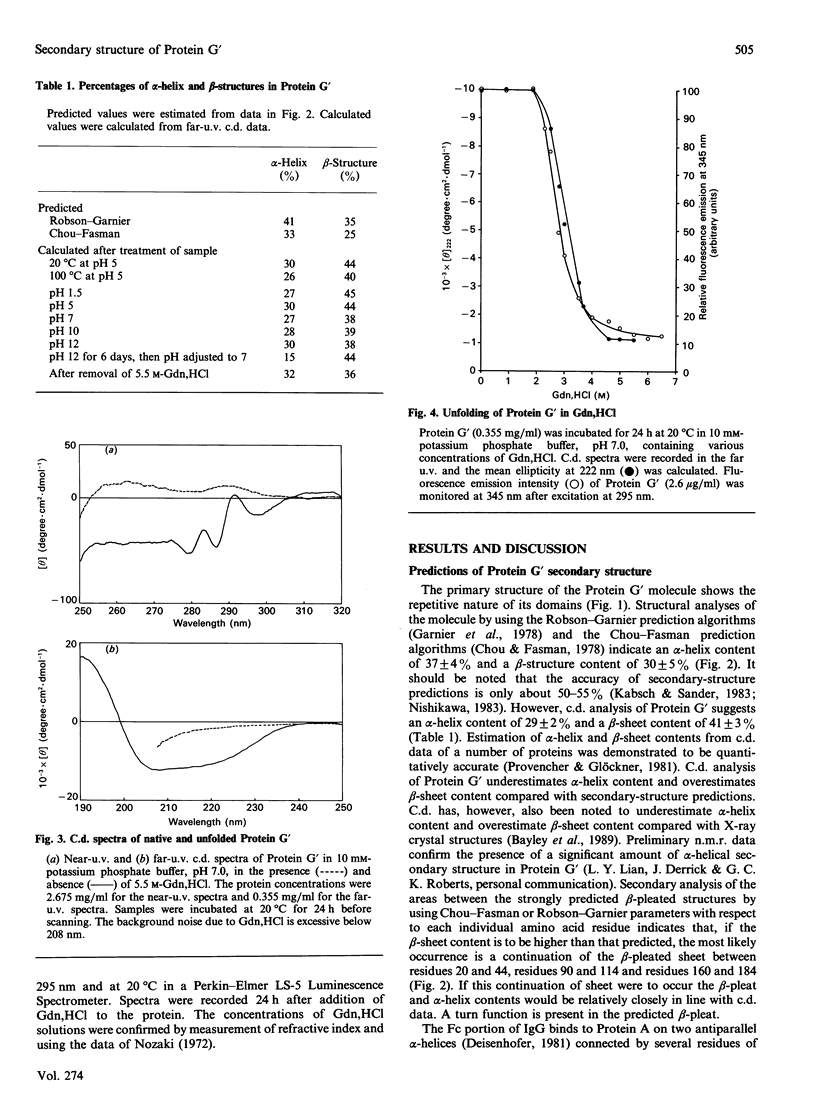
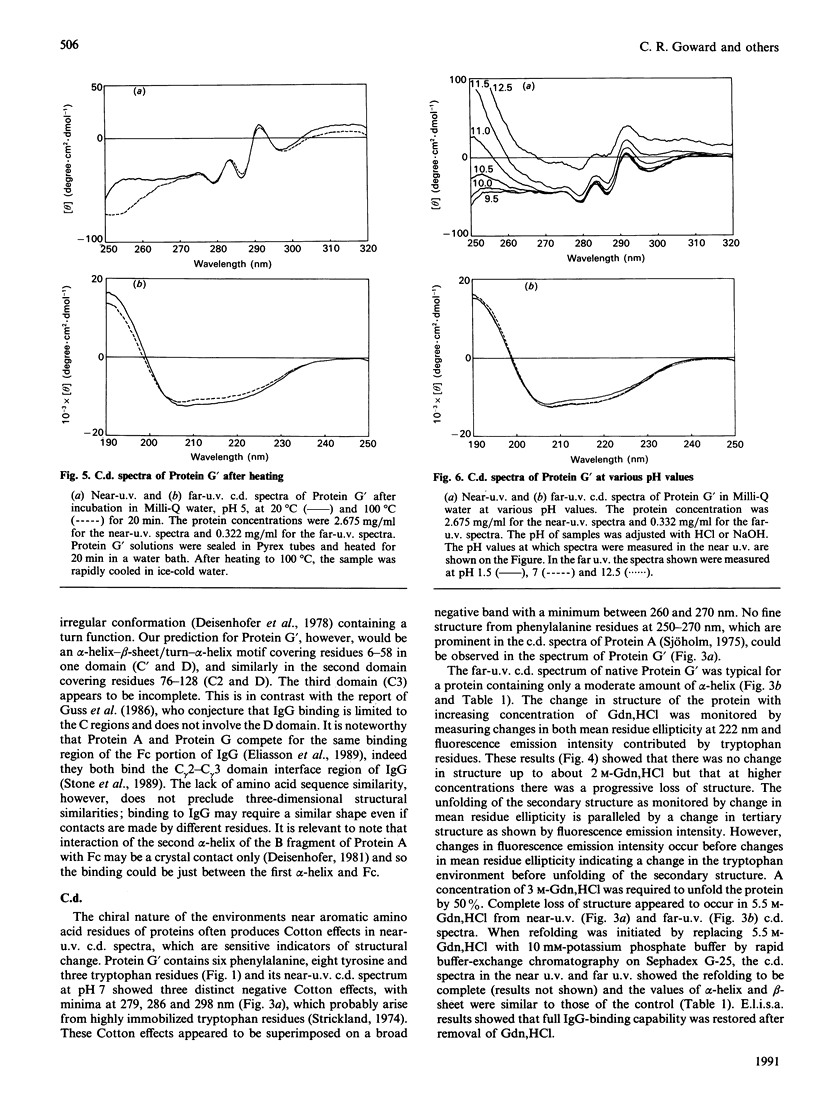
The secondary structure of recombinant streptococcal Protein G' was predicted and compared with spectropolarimetric data. The predicted secondary structure consisted of 37 +/- 4% alpha-helix and 30 +/- 5% beta-sheet, whereas the values obtained from c.d. data were 29 +/- 2% alpha-helix and 41 +/- 3% beta-sheet. An alpha-helix-beta-sheet/turn-alpha-helix motif is conjectured to comprise the Fc-binding unit. The c.d. spectra in the near u.v. and far u.v. show that the Protein G' molecule is stable to heating at 100 degrees C and to extremes of pH (pH 1.5 to 11.0). The protein retained biological activity at these extremes. The molecule uncoils above pH 11.5 in a time-dependent fashion. Unfolding of the molecule in guanidinium chloride was monitored by c.d. and fluorescence emission; 3 M-guanidinium chloride was required to unfold the protein by 50%. The protein was completely unfolded in 5.5 M-guanidinium chloride and fully refolded with restoration of activity after removal of guanidinium chloride.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerström B., Brodin T., Reis K., Björck L. Protein G: a powerful tool for binding and detection of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2589–2592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björck L., Kronvall G. Purification and some properties of streptococcal protein G, a novel IgG-binding reagent. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):969–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. K., Woody R. W. A theoretical study of the optical rotatory properties of poly-L-tyrosine. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 13;93(1):29–37. doi: 10.1021/ja00730a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of a human Fc fragment and its complex with fragment B of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus at 2.9- and 2.8-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2361–2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Jones T. A., Huber R., Sjödahl J., Sjöquist J. Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and atomic model of the complex formed by a human Fc fragment and fragment B of protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Aug;359(8):975–985. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson M., Andersson R., Olsson A., Wigzell H., Uhlén M. Differential IgG-binding characteristics of staphylococcal protein A, streptococcal protein G, and a chimeric protein AG. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erntell M., Myhre E. B., Sjöbring U., Björck L. Streptococcal protein G has affinity for both Fab- and Fc-fragments of human IgG. Mol Immunol. 1988 Feb;25(2):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goward C. R., Murphy J. P., Atkinson T., Barstow D. A. Expression and purification of a truncated recombinant streptococcal protein G. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):171–177. doi: 10.1042/bj2670171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss B., Eliasson M., Olsson A., Uhlén M., Frej A. K., Jörnvall H., Flock J. I., Lindberg M. Structure of the IgG-binding regions of streptococcal protein G. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1567–1575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C. How good are predictions of protein secondary structure? FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmark R. Estimation of the secondary structure of protein A from S. aureus by CD-spectroscopy. Mol Immunol. 1982 Jul;19(7):957–959. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K. Assessment of secondary-structure prediction of proteins. Comparison of computerized Chou-Fasman method with others. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 28;748(2):285–299. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y. The preparation of guanidine hydrochloride. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:43–50. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson A., Eliasson M., Guss B., Nilsson B., Hellman U., Lindberg M., Uhlén M. Structure and evolution of the repetitive gene encoding streptococcal protein G. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W., Glöckner J. Estimation of globular protein secondary structure from circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):33–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis K. J., Hansen H. F., Björck L. Extraction and characterization of IgG Fc receptors from group C and group G streptococci. Mol Immunol. 1986 Apr;23(4):425–431. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjodahl J. Repetitive sequences in protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Arrangement of five regions within the protein, four being highly homologous and Fc-binding. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):343–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm I. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Spectropolarimetric and Spectrophotometric studies. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):55–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone G. C., Sjöbring U., Björck L., Sjöquist J., Barber C. V., Nardella F. A. The Fc binding site for streptococcal protein G is in the C gamma 2-C gamma 3 interface region of IgG and is related to the sites that bind staphylococcal protein A and human rheumatoid factors. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H. Aromatic contributions to circular dichroism spectra of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):113–175. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



