Abstract
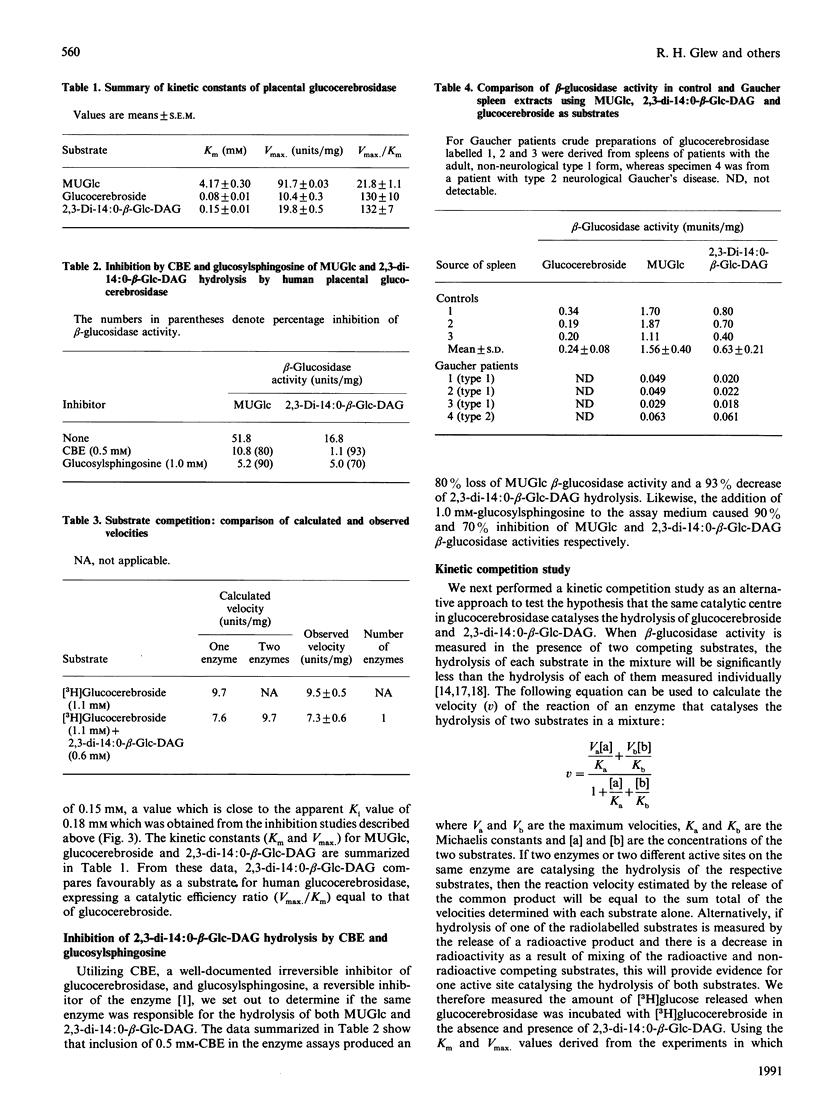
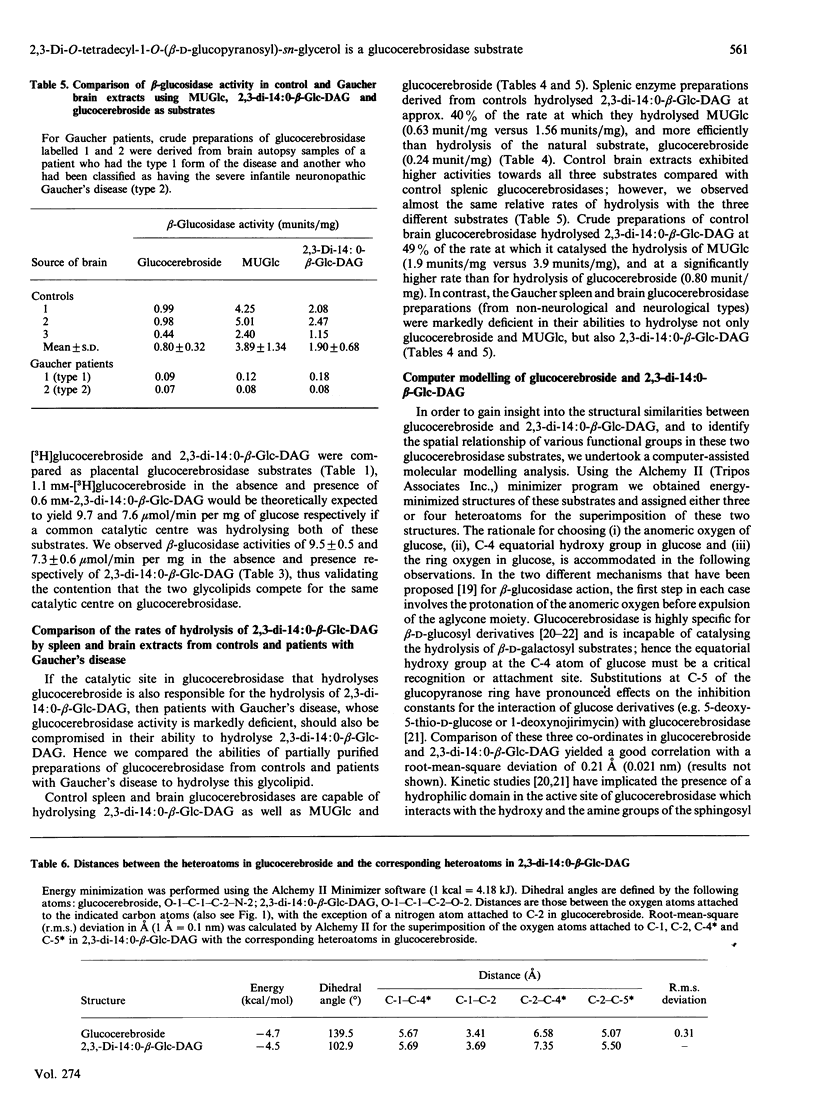
Glucocerebrosidase, the lysosomal enzyme that is deficient in patients with Gaucher's disease, hydrolyses non-physiological aryl beta-D-glucosides and glucocerebroside, its substrate in vivo. We document that 2,3,-di-O-tetradecyl-1-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (2,3,-di-14:0-beta-Glc-DAG) inhibits human placental glucocerebrosidase activity in vitro (Ki 0.18 mM), and the nature of inhibition is typical of a mixed-type pattern. Furthermore, 2,3-di-14:0-beta-Glc-DAG was shown to be an excellent substrate for the lysosomal beta-glucosidase (Km 0.15 mM; Vmax. 19.8 units/mg) when compared with the natural substrate glucocerebroside (Km 0.080 mM; Vmax. 10.4 units/mg). The observations that (i) glucocerebrosidase-catalysed hydrolysis of 2,3-di-14:0-beta-Glc-DAG is inhibited by conduritol B epoxide and glucosylsphingosine, and (ii) spleen and brain extracts from patients with Gaucher's disease are unable to hydrolyse 2,3-di-14:O-beta-Glc-DAG demonstrate that the same active site on the enzyme is responsible for catalysing the hydrolysis of 4-methylumbelliferyl beta-D-glucopyranoside, glucocerebroside and 2,3-di-14:O-beta-Glc-DAG. With the aid of computer modelling we have established that the oxygen atoms in 2,3-DAG-Glc at the C-1, C-4*, C-5* (the ring oxygen in glucose) and C-2 positions correspond topologically to the oxygens at C-1, C-4* and C-5* and the nitrogen atom attached to C-2 respectively in glucocerebroside (* signifies a carbon atom in glucose); furthermore, all of the distances with respect to overlap of corresponding heteroatoms range from 0.02 A to 0.77 A (0.002-0.077 nm). A root-mean-square deviation of 0.31 A (0.031 nm) was obtained when the energy-minimized structures of 2,3-di-14:O-beta-Glc-DAG and glucocerebroside were compared using the latter four heteroatom co-ordinates.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aerts J. M., Donker-Koopman W. E., Murray G. J., Barranger J. A., Tager J. M., Schram A. W. A procedure for the rapid purification in high yield of human glucocerebrosidase using immunoaffinity chromatography with monoclonal antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 1;154(2):655–663. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J. N., SHAPIRO D. METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. II. EVIDENCE OF AN ENZYMATIC DEFICIENCY IN GAUCHER'S DISEASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:221–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90743-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. Statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:103–138. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Basu A., LaMarco K. L., Prence E. M. Mammalian glucocerebrosidase: implications for Gaucher's disease. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):5–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., PASSONNEAU J. V., HASSELBERGER F. X., SCHULZ D. W. EFFECT OF ISCHEMIA ON KNOWN SUBSTRATES AND COFACTORS OF THE GLYCOLYTIC PATHWAY IN BRAIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:18–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMarco K. L., Glew R. H. Hydrolysis of a naturally occurring beta-glucoside by a broad-specificity beta-glucosidase from liver. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):469–476. doi: 10.1042/bj2370469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalégerie P., Legler G., Yon J. M. The use of inhibitors in the study of glycosidases. Biochimie. 1982 Nov-Dec;64(11-12):977–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osiecki-Newman K., Fabbro D., Legler G., Desnick R. J., Grabowski G. A. Human acid beta-glucosidase: use of inhibitors, alternative substrates and amphiphiles to investigate the properties of the normal and Gaucher disease active sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 2;915(1):87–100. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osiecki-Newman K., Legler G., Grace M., Dinur T., Gatt S., Desnick R. J., Grabowski G. A. Human acid beta-glucosidase: inhibition studies using glucose analogues and pH variation to characterize the normal and Gaucher disease glycon binding sites. Enzyme. 1988;40(4):173–188. doi: 10.1159/000469161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Brady R. O., Hibbert S. R., Gal A. E., Shapiro D. Isolation and characterization of glucocerebrosidase from human placental tissue. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5256–5261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S. P., Lee R. E., Glew R. H. A microassay for Gaucher's disease. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 May 1;60(3):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Choudary P. V., Martin B. M., Stubblefield B. K., Mayor J. A., Barranger J. A., Ginns E. I. A mutation in the human glucocerebrosidase gene in neuronopathic Gaucher's disease. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 5;316(10):570–575. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703053161002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Martin B. M., Barranger J. A., Stubblefield B. K., LaMarca M. E., Ginns E. I. Genetic heterogeneity in type 1 Gaucher disease: multiple genotypes in Ashkenazic and non-Ashkenazic individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2349–2352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger D. A., Satter M., Markey J. P. Deficiency of monogalactosyl diglycerid beta-B-galactosidase activity in krabbe's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 17;53(2):680–685. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90715-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimran A., Sorge J., Gross E., Kubitz M., West C., Beutler E. Prediction of severity of Gaucher's disease by identification of mutations at DNA level. Lancet. 1989 Aug 12;2(8659):349–352. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90536-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



