Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have immune regulatory properties that may ameliorate pathophysiological processes in sepsis. We determined the effect of allogeneic adipose-derived MSCs (Cx611) on the host response during sepsis due to community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP) by measuring 29 plasma biomarkers and blood transcriptomes at six time points in 82 patients randomised to two intravenous infusions of Cx611 or placebo. Cx611 treatment enhanced several endothelial cell and procoagulant response plasma biomarkers, and led to increased expression of pathways related to innate immunity, haemostasis and apoptosis. Cx611 infusion in sepsis due to CABP is associated with broad host response alterations.
Keywords: Pneumonia, Critical Care
Introduction
In spite of decades-long efforts, therapeutics capable of ameliorating disease pathophysiology and improving patient-important clinical outcomes in sepsis and pneumonia remain elusive. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)—multipotent cells that can contribute to tissue repair and modulate immune responses—exert a variety of effects on the pathophysiology of pneumonia and sepsis that have led to improved outcomes in preclinical models.1 Several small phase I and II clinical trials have demonstrated the safety of treatment with MSCs in critically ill patients with sepsis and/or acute respiratory distress syndrome.2 3 SEPCELL was a phase Ib/IIa clinical trial investigating the use of Cx611 (adipose-derived stem cells) in patients with severe community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CABP), and the largest study on the effects of MSCs in this population conducted thus far.4 5 We recently reported on the primary objective of SEPCELL—a favourable safety profile of Cx611 infusion in patients with severe CABP.5 In the current preplanned ancillary study,4 we aimed to assess the effect of Cx611 treatment on the host response by sequential measurements of plasma protein biomarkers—reflective of key pathophysiological processes—and blood transcriptomes.
Methods
Adult patients (≥18 and ≤80 years old) were eligible for the study if there was a clinical suspicion of severe CABP, and if they needed mechanical ventilation (including high-flow oxygen) and/or vasopressor treatment. Patients were randomised to receive either two intravenous administrations of Cx611 (160×106 cells) or placebo (Ringer’s lactate) at day 1 and day 3 of the study. We measured 29 protein biomarkers reflective of five pathophysiological domains (inflammation, inhibition of inflammation, apoptosis, endothelial cell responses and coagulation) before and at five time points after initiation of treatment (figure 1A, online supplemental table 1, online supplemental figure 1). We analysed the data using linear mixed models that adjusted for chance variation in baseline values between groups. Gene set enrichment analysis was done using the Reactome knowledgebase (reactome.org), focusing on predetermined pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of sepsis: immune system, apoptosis and haemostasis. Further details on study design, inclusion and exclusion criteria, sample collection and processing, and statistical analysis can be found in the online supplemental methods.
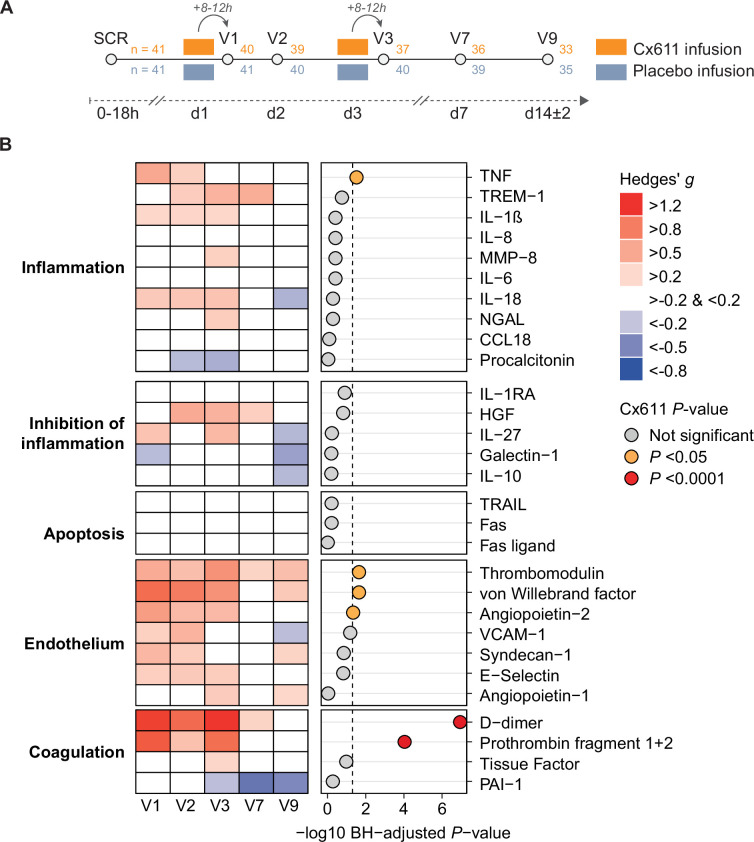
Figure 1. Overview of study design and effect of Cx611 treatment on plasma host response biomarkers stratified according to pathophysiological domains. (A) Overview of time points at which samples were collected for plasma protein and RNA biomarker analyses: within 18 hours of initiation of vasopressors and/or mechanical ventilation, prior to the initiation of treatment (screening/SCR), 8–12 hours following the initial infusion of Cx611 or placebo on day 1 (visit 1/V1), day 2 (V2), 8–12 hours following the second infusion of Cx611 or placebo on day 3 (V3), day 7 (V7) and day 14±2 (V9). Sample collection continued after intensive care unit (ICU) and hospital discharge. Number of samples available for plasma biomarker analyses listed to the right of each time point, Cx611-treated patients in orange, placebo-treated patients in blue/grey. (B) Heatmap showing the levels of each plasma protein host response biomarker, divided across five pathophysiological domains, for patients treated with Cx611 relative to patients treated with placebo at each time point after the initiation of treatment, expressed as an effect size (Hedges’ g, red indicates higher values and blue indicates lower values in Cx611-treated patients). For visual purposes, comparisons with a Hedges’ g >−0.2 and <0.2 (considered a negligible effect) are displayed as white tiles. To account for baseline variation in biomarker levels not attributable to treatment, we used the fold change from prior to treatment (screening/SCR time point) to each time point for each patient. The p values displayed to the right of heatmap are derived from a type II Wald test on linear mixed models for each individual biomarker (as described in the statistical analysis paragraph in the online supplemental methods), and indicate whether the overall effect of Cx611 on biomarker concentrations over all time points after initiation of treatment, adjusted for baseline variation in biomarker levels, is statistically significant. These p values were adjusted for multiple testing per domain using the Benjamini-Hochberg (BH) method. CCL, CC chemokine ligand; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IL-1RA, interleukin 1 receptor antagonist; MMP-8, matrix metalloproteinase 8; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; TREM-1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell 1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
Results
41 patients in both the Cx611 and placebo groups participated (online supplemental figure 2). Baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes were balanced between the groups (table 1, online supplemental table 2).5 Figure 1B provides an overview of the effect of Cx611 infusion (relative to placebo) on all biomarkers measured in plasma obtained at five time points after treatment initiation (overview of all measurements in online supplemental table 3). The proportion of patients still in the study at the V9 time point was high and comparable between study groups (35/41 (85.4%) for Cx611, 38/41 (92.7%); online supplemental table 1). Despite the anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects of MSCs reported in preclinical studies,1 we found few differences in biomarkers reflective of inflammation, inhibition of inflammation or apoptosis (online supplemental figures 3–5). Only tumour necrosis factor—a quintessential proinflammatory cytokine—was significantly higher in patients treated with Cx611 (p=0.030), driven by the time frame spanning stem cell infusion (V1–V3). With regard to endothelial cell biomarkers, the plasma concentrations of von Willebrand factor (reflecting endothelial cell activation), soluble thrombomodulin (endothelial cell injury) and angiopoietin-2 (disturbed barrier function) were higher in patients infused with Cx611 at time points up to V3 (ie, 8–12 hours after the second drug infusion; online supplemental figure 6). Moreover, Cx611 induced a procoagulant state in this time frame, as indicated by strong increases in the plasma levels of prothrombin fragment 1+2 (thrombin formation) and D-dimer (fibrin formation and fibrinolysis).
Table 1. Baseline characteristics and outcomes.
| Cx611 (n=41) | Placebo (n=41) | |
| Demographics | ||
| Age, years | 60.9 (11.3) | 63.4 (10.4) |
| Sex, male | 27 (65.9%) | 26 (63.4%) |
| Disease severity | ||
| Randomisation stratum | ||
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | 22 (53.7%) | 23 (56.1%) |
| Shock | 14 (34.1%) | 13 (31.7%) |
| Both | 5 (12.2%) | 5 (12.2%) |
| CURB-65 | 3 [2, 3] | 3 [2, 4] |
| APACHE II score | 20.2 (7.7) | 18.9 (6.2) |
| SOFA score* | 8 [7, 11] | 8 [7, 9] |
| Outcomes † | ||
| Any thromboembolic event‡ | 7 (17.1%) | 8 (19.5%) |
| Length of intensive care unit stay | 13 [6, 29] | 11 [6, 19] |
| Length of hospital stay | 20 [12, 44] | 19 [14, 36] |
| 28-day mortality | 8 (19.5%) | 6 (14.6%) |
Normally distributed continuous variables are listed as mean (SD); non-normally distributed continuous variables are listed as median [IQR]; categorical variables are listed as count (%).
All patients fulfilled the Sepsis-3 criteria (infection plus SOFA score of 2 or higher).
A full overview of adverse events and clinical outcomes can be found in the primary clinical report.5
Individual patients could have more than one thromboembolic event. For the Cx611 group, this included deep vein thrombosis (n=3), pulmonary embolism (n=1), cerebrovascular accident (n=2), device-related thrombosis (n=1), atrial thrombosis (n=1) and cerebral artery embolism (n=1). For the placebo group, this included deep vein thrombosis (n=5), pulmonary embolism (n=2), venous thrombosis (n=1), venous thrombosis of a limb (n=1) and jugular vein thrombosis (n=1).
APACHE-IIAcute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation IICURB-65confusion, blood urea nitrogen, respiratory rate, blood pressure, age 65 or olderSOFASequential Organ Failure Assessment
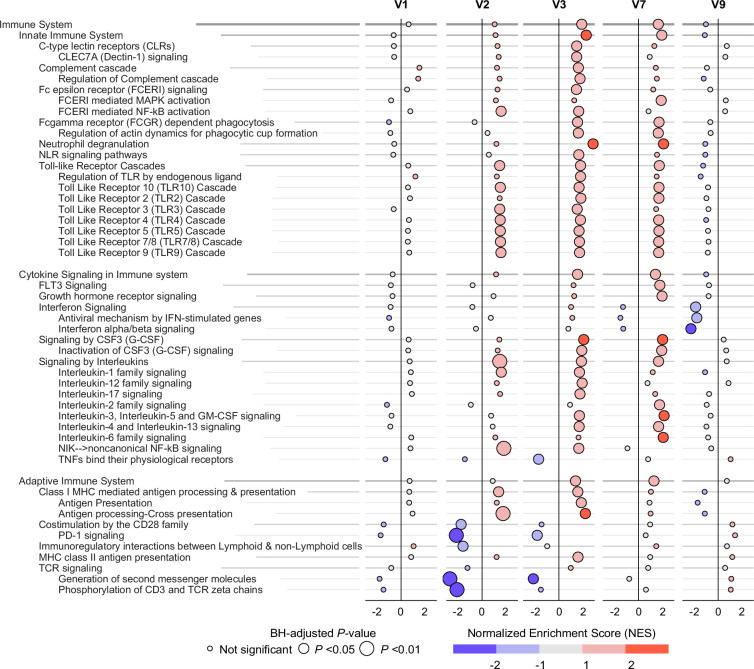
Analysis of blood transcriptome data revealed that Cx611 induced a predominantly proinflammatory state, detectable from day 2 after the initiation of treatment (V2) up to 4 days after the second treatment (V7; figure 2, online supplemental figure 7, online supplemental table 4). In the innate immune system pathways, we found upregulation of pattern recognition receptor pathways such as toll-like receptors, accompanied by upregulation of pathways related to innate immune effector functions, such as neutrophil degranulation (online supplemental figure 8). Innate immune activation was further corroborated by upregulation of pathways related to key growth factors involved in emergency myelopoiesis (granulocyte and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors, and interleukin 3) and proinflammatory cytokine signalling (figure 2). In the adaptive immune system, Cx611-treated patients exhibited upregulation of pathways related to major histocompatibility complex class I antigen presentation, suggesting activation of cellular immunity, specifically cytotoxic CD8 T cells (figure 2, online supplemental figure 8), while downregulation of pathways related to T cell receptor signalling and reduced CD28 costimulation pointed at impaired T cell activation. However, downregulation of signalling through the inhibitory immune checkpoint programmed death 1 in Cx611-treated patients argued against adaptive immunosuppression. A more detailed overview of the plasma biomarker and transcriptomic results—including the modest upregulation of pathways related to apoptosis, endothelial cell surface interactions and haemostasis—can be found in online supplemental figures 9 and 10.
Figure 2. Significant immune system pathways from gene set enrichment analysis of the blood transcriptome. Bubble plot displaying the effect of Cx611 treatment on transcriptional pathways related to the immune system (as obtained from the Reactome knowledgebase) for each time point after the initiation of treatment with Cx611 or placebo. To adjust for chance variation in baseline gene expression between groups, the differences in gene expression at each time point are derived from the interaction terms between Cx611 and time point in linear mixed models that included the SCR time point (prior to initiation as treatment) as the reference category, and can therefore be interpreted as the difference in gene expression levels between groups at each time point relative to the gene expression levels prior to initiation of treatment. The differences in expression of genes in the listed pathways are quantified as NES and reflected in the intensity of the colour: a red bubble means higher in the Cx611-treated group, a blue bubble means lower in the Cx611-treated group and a grey bubble indicates a negligible difference. The size of the bubble is proportional to the Benjamini-Hochberg (BH)-adjusted p value for that pathway. This figure only includes pathways in which a significant difference between groups was found at one or more time points; the full version of the figure including non-significant pathways can be found in online supplemental figure 7. CLEC7A, C-type lectin domain family 7 member A; Fc, fragment crystallisable region (of an antibody); FLT3, fms-related receptor tyrosine kinase 3; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN, interferon; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NIK, NF-κB-inducing kinase; NLR, nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat containing receptor; PD-1, programmed death 1; TCR, T cell receptor; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.
Discussion
We report the largest and most comprehensive study on the effect of MSCs on the immune response in critically ill patients, but there are limitations to consider. The study was exploratory in nature and the total intended sample size was not calculated specifically to detect differences in biomarker levels. While the risk of attrition bias is low, informative censoring due to death or withdrawal from the study may have resulted in some residual bias not fully addressed by linear mixed models. A replication cohort in this patient population did not exist at time of analysis, and the results could therefore not be validated externally.
While there were no adverse events related to Cx611 infusion,5 Cx611 treatment resulted in transient proinflammatory effects mainly relating to enhanced activation of the endothelium and coagulation system, and increased expression of gene pathways involved in pattern recognition receptor and cytokine signalling, haemostasis and apoptosis. Our results may in part be indicative of recognition of intravenously introduced MSCs by the host immune system. The proinflammatory effects reported here contrast with the anti-inflammatory effects reported in the preponderance of preclinical studies.1 However, previous clinical studies that reported biological outcomes were small and have not conclusively demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects of MSCs in critically ill humans.6,8 The adipose origin of Cx611 may play a part, but clear evidence that the immune regulatory properties of adipose-derived MSCs are different from those of MSCs of other origins is not available. Although a higher expression of tissue factor on adipose-derived MSCs9 could indicate a higher procoagulant potential, procoagulant responses have also been reported for MSCs of other origins.10 It remains to be established which effects of MSCs on the host response in patients with sepsis due to CABP would be beneficial for clinical outcomes, and which could potentially do harm.
supplementary material
Acknowledgements
We thank Desirée Perlee, PhD, for her role in the initial phases of the biomarker studies. We thank Augustijn M Klarenbeek, Jacky de Leeuw, Fayola de Lange, Barbara Dierdorp, and Tamara Dekker and the Amsterdam UMC Core Facility Genomics for their invaluable support in the laboratory and for providing HPC Genomics as high-performance compute resource. The SEPCELL study consortium is coordinated by Takeda Pharmaceuticals. The authors acknowledge the valued contribution of the investigators to the SEPCELL study.
Footnotes
Funding: This study was supported by a grant from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program (agreement number 681031) and sponsored by TiGenix SAU (a wholly owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceuticals). TDYR is supported by the research programme 'NACTAR', project ‘MDR-phage’ (grant number 16447), which is financed by the Dutch Research Council (NWO).
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Patient consent for publication: Not applicable.
Ethics approval: This study involves human participants and was approved by the independent ethics committees of the participating hospitals: Comite de Protection des Personnes Sud-Ouest et Outre-Mer II, Agence Régionale de Santé Occitanie (Dossier 2-18-08); Comité d’Éthique Hospitalo Facultaire, Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc, Université catholique de Louvain (2015/13NOV/618); Comité Etica Regional de la Comunidad de Madrid (Cx611-0204/2015-002994-39). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients, their legal representative or next of kin. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
Collaborators: SEPCELL study group: Dr Christine Colienne, Dr Diego Castanares Zapatero, Dr Ludovic Gerard, Dr Philippe Hantson and Dr Virginie Montiel; Dr Jean-Pierre Pelgrim, Dr Marco Vinetti, Dr Nicolas De Schryver and Dr Sophie Terneu; Dr Bernard Lambermont and Dr Philippe Morimont; Dr Elisabeth De Waele, Dr Joris Bart Troubleyn, Dr Jouke De Regt and Dr Patrick M Honore; Dr Manuel Álvarez González, Dr Mercedes Nieto Cabrera and Dr Ma José Jiménez; Dr Antoni-Jordi Betbesé Roig, Dr Maria Torrents Sonet, Dr Mario Antonio Alfaro Farias, Dr Miguel Ovejero Gordillo, Dr Mireia Cuartero Sala, Dr Nuria Rodriguez Farre and Dr Jaume Baldirà Martinez; Dr Cristina Pinilla, Dr Ma Asunción Romero, Dr Noemí Paredes and Dr Rosario Cuadra; Dr Adrian Ceccato, Dr Antoni Torres Marti, Dr Catia Cilloniz, Dr Cristina Dominedò and Dr Gianluigi Li Bass; Dr Adolfo Ruiz Sanmartín, Dr Alejandro Cortes Herrera, Dr Jaume Baldirà Martinez, Dr Juan Carlos Ruiz Rodriguez and Dr Sofía Contreras Medina; Dr Juan Carlos Montejo, Dr Helena Marín, Dr Ignacio Saez, Dr Silvia Chacón and Dr Zaida Molina; Dr Rafael Máñez Mendiluce, Dr Gabriel Moreno González and Dr Juan Carlos López Delgado; Dr Jordi Codina Calero, Dr Maria Begoña Balsera Garrido, Dr Mar Miralbés Torner, Dr Mercedes Palomar Martínez and Dr Montserrat Vallverdú Vidal; Dr Baltasar Sánchez González, Dr Carles Ferrer i Peretó and Dr Josep Trenado Álvarez; Dr Gerard Moreno Muñoz, Dr Gonzalo Sirgo Rodríguez, Dr Maria A Bodí and Dr Mònica Marget Iglesias; Dr Borja Suberviola Cañas, Dr Alejandro Gonzalez-Castro, Dr Andrés Jiménez and Dr Maite Arlabán Carpintero; Dr José Manuel Añón, Dr Alexander Agrifoglio, Dr Lucía Cachafeiro and Dr Manuel Quintana; Dr Gadea Alonso, Dr Ma Concepción García and Dr Ma Luisa Rodríguez; Dr Esther Villareal and Dr Mónica Gordon; Dr Ana Maria Navas Pérez, Dr Emilio Diaz Santos and Dr Jordi Vallés Daunis; Dr Diana Noreikiene, Dr Sandra Mazeikiene and Dr Vitalija Nausediene; Dr Pål Klepstad, Dr Hege-Merete Krabseth and Dr Johan-Arnt Hegvik; Dr Roberto Alberto De Blasi, Dr Livia Errico and Dr Maria Teresa Cirasa; Dr Anne Laure Fedou, Dr Arnaud Desachy, Dr Bruno Evrard, Dr Guillaume Gilbert, Dr Julien Vaidie, Dr Marine Goudelin, Dr Philippe Vignon and Dr Thomas Daix; Dr David Schnell, Dr Charles Lafon, Dr Christophe Cracco, Dr Gilles Lardillon, Dr Olivier Longuet, Dr Olivier Thierry Baudin, Dr Stephane Rouleau and Dr Sylvie Nicole Calvat; Dr Brian Emonet, Dr Caroline Pouplet, Dr Christine Lebert, Dr Gwenhael Colin, Dr Isabelle Vinatier, Dr Jean-Claude Lacherade and Dr Konstantinos Bachoumas; Dr Laurent Camous, Dr Laurent Martin-Lefevre, Dr Marie-Ange Azais, Dr Matthieu Henry-Lagarrigue and Dr Maud Fiancette; Dr Anne Bretagnol, Dr Armelle Mathonnet, Dr Dalila Benzekri Lefèvre, Dr François Barbier, Dr Grégoire Muller, Dr Isabelle Runge, Dr Marie Skarzynski and Dr Sophie Jacquier; Professor Bertrand Souweine, Dr Armelle Gilard, Dr Claire Bachelier, Dr Elisabeth Coupez, Dr François Thouy, Dr Jean Mathias Liteaudon, Dr Marjolaine Borel and Dr Laure Calvet; Dr Charlotte Garret, Dr Jean-Baptiste Lascarrou, Dr Maëlle Martin, Dr Noëlle Brulé and Dr Laura Crosby; Dr Emmanuelle Mercier, Dr Annick Legras, Dr Antoine Guillon, Dr Charlotte Salmon-Gandonniere, Dr Denis Garrot, Dr Laetitia Bodet-Contentin, Dr Marlène Morisseau, Dr Pierre-François Dequin, Dr Stephan Ehrmann and Dr Yonatan Perez; Dr Alexandra Monnier, Dr Christine Kummerlen, Dr Hamid Merdji, Dr Hassene Rahmani, Dr Julie Helms, Dr Laure Stiel, Dr Raphael Clere-Jehl and Dr Yannick Rabouel; Dr Jean-Pierre Quenot, Dr Audrey Large, Dr Auguste Dargent and Dr Pascal Andreu; Dr Damien Contou, Dr Elsa Logre, Dr Hervé Mentec, Dr Jean-Pierre Laforet, Dr Olivier Pajot and Dr Radj Cally; Dr Saadalla Nseir, Dr Anne Sophie Moreau, Dr Geoffrey Ledoux, Dr Julien Poissy, Dr Laurent Robriquet, Dr Marion Houard, Dr Olivier Pouly, Dr Raphael Favory, Dr Sophie Six and Dr Thibault Duburcq.
Correction notice: This article has been corrected since it was published Online First. A collaborator name has been corrected.
Contributor Information
Tom D Y Reijnders, Email: t.d.reijnders@amsterdamumc.nl.
Pierre-François Laterre, Email: pierrefrancoislaterre@gmail.com.
Bruno François, Email: bruno.francois@chu-limoges.fr.
Miguel Sánchez García, Email: miguelsanchez.hcsc@gmail.com.
Tjitske S R van Engelen, Email: t.s.vanengelen@amsterdamumc.nl.
Daoud Sie, Email: d.sie@amsterdamumc.nl.
Brendon P Scicluna, Email: brendon.scicluna@um.edu.mt.
Dmitry V Ostanin, Email: dmitry.ostanin@takeda.com.
Kevin J Galinsky, Email: kevin.galinsky@takeda.com.
Joe M Butler, Email: j.m.butler@amsterdamumc.nl.
Eleuterio Lombardo, Email: eleuterio.lombardo@takeda.com.
Tom van der Poll, Email: t.vanderpoll@amsterdamumc.nl.
SEPCELL study group:
Christine Colienne, Diego Castanares Zapatero, Ludovic Gerard, Philippe Hantson, Virginie Montiel, Jean-Pierre Pelgrim, Marco Vinetti, Nicolas De Schryver, Sophie Terneu, Bernard Lambermont, Philippe Morimont, Elisabeth De Waele, Joris Bart Troubleyn, Jouke De Regt, Patrick M Honore, Manuel Álvarez González, Mercedes Nieto Cabrera, Ma José Jiménez, Antoni-Jordi Betbesé Roig, Maria Torrents Sonet, Mario Antonio Alfaro Farias, Miguel Ovejero Gordillo, Mireia Cuartero Sala, Nuria Rodriguez Farre, Jaume Baldirà Martinez, Cristina Pinilla, Ma Asunción Romero, Noemí Paredes, Rosario Cuadra, Adrian Ceccato, Antoni Torres Marti, Catia Cilloniz, Cristina Dominedò, Gianluigi Li Bass, Adolfo Ruiz Sanmartín, Alejandro Cortes Herrera, Jaume Baldirà Martinez, Juan Carlos Ruiz Rodriguez, Sofía Contreras Medina, Juan Carlos Montejo, Helena Marín, Ignacio Saez, Silvia Chacón, Zaida Molina, Rafael Máñez Mendiluce, Gabriel Moreno González, Juan Carlos López Delgado, Jordi Codina Calero, Maria Begoña Balsera Garrido, Mar Miralbés Torner, Mercedes Palomar Martínez, Montserrat Vallverdú Vidal, Baltasar Sánchez González, Carles Ferrer i Peretó, Josep Trenado Álvarez, Gerard Moreno Muñoz, Gonzalo Sirgo Rodríguez, Maria A Bodí, Mònica Marget Iglesias, Borja Suberviola Cañas, Alejandro Gonzalez-Castro, Andrés Jiménez, Maite Arlabán Carpintero, José Manuel Añón, Alexander Agrifoglio, Lucía Cachafeiro, Manuel Quintana, Gadea Alonso, Ma Concepción García, Ma Luisa Rodríguez, Esther Villareal, Mónica Gordon, Ana Maria Navas Pérez, Emilio Diaz Santos, Jordi Vallés Daunis, Diana Noreikiene, Sandra Mazeikiene, Vitalija Nausediene, Pål Klepstad, Hege-Merete Krabseth, Johan-Arnt Hegvik, Roberto Alberto De Blasi, Livia Errico, Maria Teresa Cirasa, Anne Laure Fedou, Arnaud Desachy, Bruno Evrard, Guillaume Gilbert, Julien Vaidie, Marine Goudelin, Philippe Vignon, Thomas Daix, David Schnell, Charles Lafon, Christophe Cracco, Gilles Lardillon, Olivier Longuet, Olivier Thierry Baudin, Stephane Rouleau, Sylvie Nicole Calvat, Brian Emonet, Caroline Pouplet, Christine Lebert, Gwenhael Colin, Isabelle Vinatier, Jean-Claude Lacherade, Konstantinos Bachoumas, Laurent Camous, Laurent Martin-Lefevre, Marie-Ange Azais, Matthieu Henry-Lagarrigue, Maud Fiancette, Anne Bretagnol, Armelle Mathonnet, Dalila Benzekri Lefèvre, François Barbier, Grégoire Muller, Isabelle Runge, Marie Skarzynski, Sophie Jacquier, Bertrand Souweine, Armelle Gilard, Claire Bachelier, Elisabeth Coupez, François Thouy, Jean Mathias Liteaudon, Marjolaine Borel, Laure Calvet, Charlotte Garret, Jean-Baptiste Lascarrou, Maëlle Martin, Noëlle Brulé, Laura Crosby, Emmanuelle Mercier, Annick Legras, Antoine Guillon, Charlotte Salmon-Gandonniere, Denis Garrot, Laetitia Bodet-Contentin, Marlène Morisseau, Pierre-François Dequin, Stephan Ehrmann, Yonatan Perez, Alexandra Monnier, Christine Kummerlen, Hamid Merdji, Hassene Rahmani, Julie Helms, Laure Stiel, Raphael Clere-Jehl, Yannick Rabouel, Jean-Pierre Quenot, Audrey Large, Auguste Dargent, Pascal Andreu, Damien Contou, Elsa Logre, Hervé Mentec, Jean-Pierre Laforet, Olivier Pajot, Radj Cally, Saadalla Nseir, Anne Sophie Moreau, Geoffrey Ledoux, Julien Poissy, Laurent Robriquet, Marion Houard, Olivier Pouly, Raphael Favory, Sophie Six, and Thibault Duburcq
Data availability statement
RNAseq data are available from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the BioProject accession PRJNA1097551. Other data generated and/or analysed during the current study are available on reasonable request.
References
- 1.Shaw TD, Krasnodembskaya AD, Schroeder GN, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: an Antimicrobial and Host-Directed Therapy for Complex Infectious Diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021;34:e00064-21. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00064-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang F, Li Y, Wang B, et al. The safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cells in ARDS: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit Care. 2023;27:1–11. doi: 10.1186/S13054-022-04287-4/FIGURES/4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sun J, Ding X, Sun T. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Sepsis: From Basic Research to Clinical Application. ICRES. 2021;1:2. doi: 10.2991/icres.k.210622.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Laterre P-F, Sánchez-García M, van der Poll T, et al. A phase Ib/IIa, randomised, double-blind, multicentre trial to assess the safety and efficacy of expanded Cx611 allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells (eASCs) for the treatment of patients with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia admitted to the intensive care unit. BMC Pulm Med. 2020;20:309. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-01324-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Laterre P-F, Sánchez García M, van der Poll T, et al. The safety and efficacy of stem cells for the treatment of severe community-acquired bacterial pneumonia: A randomized clinical trial. J Crit Care. 2024;79:154446. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2023.154446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schlosser K, Wang J-P, Dos Santos C, et al. Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment on Systemic Cytokine Levels in a Phase 1 Dose Escalation Safety Trial of Septic Shock Patients. Crit Care Med. 2019;47:918–25. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kaffash Farkhad N, Sedaghat A, Reihani H, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for COVID-19-induced ARDS patients: a successful phase 1, control-placebo group, clinical trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13:1–13. doi: 10.1186/S13287-022-02920-1/FIGURES/6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Matthay MA, Calfee CS, Zhuo H, et al. Treatment with allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells for moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (START study): a randomised phase 2a safety trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7:154–62. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30418-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Christy BA, Herzig MC, Montgomery RK, et al. Procoagulant activity of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017;83:S164–9. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yang B, Long Y, Zhang A, et al. Procoagulant Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles: a Novel Aspect of Thrombosis Pathogenesis. Stem Cells. 2024;42:98–106. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxad087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
RNAseq data are available from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the BioProject accession PRJNA1097551. Other data generated and/or analysed during the current study are available on reasonable request.