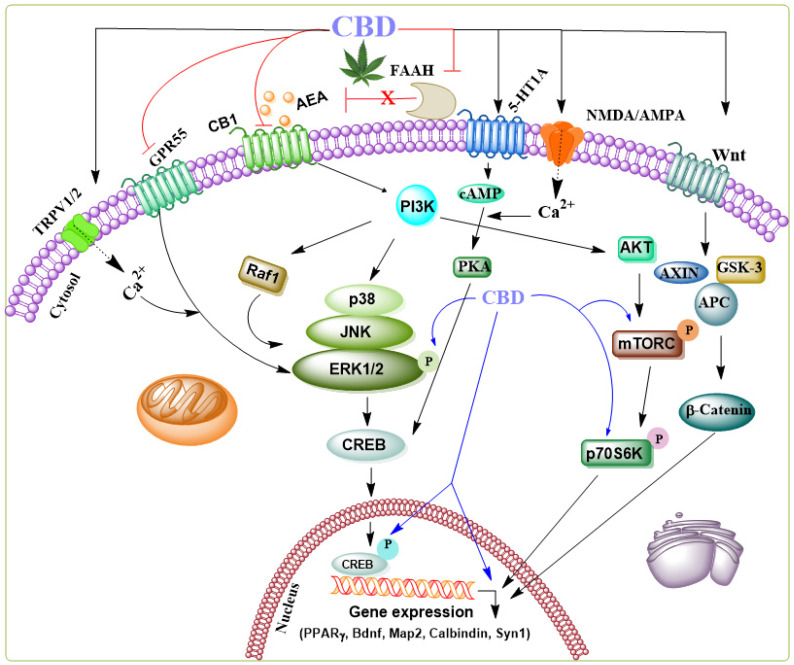
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the signaling pathways modulated by CBD through various receptors in the brain. CBD acts as an agonist, activating several receptors such as 5-HT1A, NMDA/AMPA, Wnt-Frizzled (Fz) family receptors, and TRPV1/2—additionally, CBD functions as a negative allosteric modulator of CB1 and an inhibitor of FAAH, an enzyme involved in the degradation of anandamide (AEA) and an antagonist of GPR55. While the precise mechanisms of action in specific neurodegenerative diseases remain unclear, the collective synergistic effects of CBD have been shown to contribute to its neuroprotective role in several neurological disorder models. CBD’s influence on the ERK1/2 [52], PI3K/AKT [53], and pCREB [60] pathways, which are critical for regulating genes required for cell death, survival, neurogenesis, and synaptic plasticity, including BDNF, MAP-2, synapsin 1, calbindin, and PPARγ, suggests its potential to elicit neuroprotective effects.