Abstract
Quilombola communities play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity through traditional management models. The use of medicinal plants within these communities reflects a deep reservoir of knowledge, passed down through generations. The objective of this study was to conduct a scoping review to systematically analyze and synthesize the existing literature on the medicinal plants used by Quilombola communities in Brazil, with a focus on their therapeutic applications and cultural significance. The Population, Concept, and Context (PCC) strategy was utilized, where the population refers to the Quilombolas, the concept pertains to medicinal plants, and the context involves illness. A total of 888 studies were initially identified, but only 10 met the inclusion criteria, covering 297 plant species from 80 different families. These plants are employed in a wide range of therapeutic applications, with decoction, alcohol maceration, and infusion being the most common methods of preparation. The study highlights the rich ethnopharmacological knowledge held by Quilombola communities and underscores the need for greater recognition and integration of this traditional knowledge into public health practices. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of preserving and validating the use of medicinal plants by these communities, which could serve as a foundation for future pharmacological discoveries and the development of culturally appropriate health interventions.
Keywords: ethnopharmacological knowledge, natural products, therapeutic uses, public health
1. Introduction
Brazil is recognized as the most biodiverse country in the world, containing six biomes that highlight its rich and varied flora [1]. The Ministry of the Environment reports that 46,355 plant species have been documented across the nation [2]. However, Brazil has experienced ongoing environmental degradation, largely due to economic activities that began during the colonial period. This has led to a significant loss of many species, including those with important therapeutic properties [3].
The knowledge of medicinal plant use for therapeutic purposes is deeply rooted in traditional populations, particularly among Quilombola and indigenous communities [4]. Quilombola communities, in particular, play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity through their traditional management practices [5]. Understanding the interactions within these traditional communities is vital for developing public policies that aim to preserve their cultural heritage and support the continuation of their knowledge and practices [6].
For two centuries, Brazil was a major participant in the transatlantic slave trade, standing out for both the large number of enslaved Africans it trafficked and the prolonged duration of this practice within its borders [7]. Enslaved Africans were subjected to various forms of physical, social, and psychological violence, leading many to flee in search of safer spaces, which resulted in the creation of quilombos—fortresses of resistance and cultural preservation [8]. These communities became sanctuaries where the African identity, culture, and knowledge, both ancestral and gained in Brazil, were maintained and reinvented [9]. The intimate connection with nature in these territories ensured the perpetuation of their way of life [10]. However, the lack of legal recognition for Quilombola territories has led to ongoing disputes that expose these communities to social vulnerabilities, such as rural violence and inequities in accessing health services [11]. Stigmatized and marginalized, many Quilombolas feel alienated from broader society and often turn to traditional healers instead of utilizing the limited services available to them [12].
The use of medicinal plants reflects the accumulated knowledge of traditional communities, passed down through generations, primarily through oral tradition. This empirical knowledge is deeply rooted in the lived experiences of these communities [13].
Medicinal plant species hold great significance in these communities, particularly as they emphasize sustainable development [14]. This emphasis on sustainability enhances the living conditions of these populations, as they possess extensive knowledge of plants and methods for treating various ailments. It is, therefore, crucial to integrate scientific and traditional knowledge to strengthen plant conservation practices [14].
Ethnobotanical surveys are conducted to underscore the importance of these plants in the discovery of new medicines and to deepen our understanding of the intricate relationships between communities and their local flora. These surveys also explore the cultural practices and beliefs associated with different plant uses [15,16]. Research on the use of medicinal plants by Quilombola communities is not only relevant but also vital for advancing scientific knowledge, preserving cultural heritage, and promoting sustainable development at both national and international levels.
Recognizing the importance of preserving cultural traditions alongside therapeutic practices involving medicinal plants, it is essential to review the existing literature. This will help systematize knowledge and expand scientific research on the subject. Thus, the objective of this study was to conduct a scoping review on the use of medicinal plants by Quilombola communities in Brazil.
2. Materials and Methods
This study followed a combination of two contemporary protocols for conducting scoping reviews: the PRISMA-ScR guidelines [17] and the Joanna Briggs Institute [18]. The final protocol has been registered with the Open Science Framework (osf.io/h4u82). To be included in the study, publications had to meet the following criteria: (i) they must be peer-reviewed; (ii) they must identify, through herbarium specimens, which plants Quilombola communities use to treat health problems; and (iii) they must be written in Portuguese, English, or Spanish. There were no restrictions on the publication date. Excluded materials included reviews, book chapters, books, theses, dissertations, monographs, letters to the editor, and case reports. These eligibility criteria are consistent with the “Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual” [18].
The Population, Concept, and Context (PCC) strategy was employed to determine the key topics [18]. In this framework, “population” referred to the Quilombolas, “concept” to medicinal plants, and “context” to health-related issues. Studies that did not explicitly identify their samples as Quilombolas were excluded, given that public health policies for Quilombolas are based on official recognition of individuals or communities as such.
The bibliographic databases selected for the search were as follows: the Virtual Health Library (VHL), PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, Web of Science, Science Direct, and SciELO. Additionally, a manual search was conducted using reference lists from Google Scholar to include gray literature and extend the search scope. Metadata from the search databases were exported to the Rayyan QCRI online platform (RRID:SCR_017584) for analysis.
The search algorithm was tailored to each database, using the following Mesh Terms combined with the Boolean operators “OR” and “AND”: (i) “Ethnic Groups” OR “Quilombolas” AND “Plants, medicinal” OR “Phytotherapy” OR “Medicine, traditional” OR “Ethnobotany”; (ii) “Surveys” OR “questionnaires” OR “Ethnic groups” OR “Quilombolas” AND “Medicinal plants” OR “Phytotherapy” OR “Traditional medicine” OR “Ethnobotany”. The search was conducted in both Portuguese and English to maximize the search scope. There was no limitation on the study period, and the geographical scope covered the entire country, as Quilombola communities are found exclusively in Brazil.
Two reviewers independently and blindly assessed all the identified papers. The Rayyan platform was used for this selection process. Initially, duplicates were removed, followed by incomplete abstracts. The remaining papers were then evaluated based on their titles and abstracts, according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. In cases of a discrepancy, a third reviewer (A.L.V.C.) was consulted. Researchers underwent prior calibration using 177 studies, and the intra-examiner agreement was verified (100% agreement; kappa 1.00, 95% CI; 95.74% agreement; kappa 0.91, 95% CI; 100% agreement; kappa 1.00, 95% CI, for examiners 1, 2, and 3, respectively) as well as inter-observer agreement (96.25% agreement; kappa 0.93, 95% CI).
The extracted information included the study’s characteristics (the authors, year of publication, and objective), research specifics (the location, design, and sample), and details on the plants used (their scientific name, preparation method, and the health condition treated). The main findings were synthesized following the “JBI Evidence Synthesis Manual” guidelines [19].
The results were organized and presented according to the medicinal applications of the plants. All the plants are listed in Table 1, categorized by the cited literature, year of publication, Quilombola community location, plant family, species, common name, part used, and therapeutic indications. After organizing the data, the scientific names of each plant were verified using the Tropicos platform (https://www.tropicos.org/home—accessed on 27 August 2024), and their conservation status was assessed through the Flora and Funga of Brazil 2020 platform (https://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br—accessed on 27 August 2024).
In the synthesis of the results, we used the International Classification of Primary Care—ICPC-2 [20] to identify the bodily systems most frequently targeted by medicinal plants in Quilombola communities.
Table 1.
Summary of ethnopharmacological data on medicinal plants used by Brazilian Quilombola Communities. NR = Not Reported.
| Authors | Year of Publication | Localization | Family | Species | Local Name | Used Part | Preparation | Therapeutic Indications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Adoxaceae | Sambucus sp. | Sabugueiro | Leaves; Flower | Decoction; Infusion | Headache; Fever; Inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Amaranthaceae | Alternanthera brasiliana (L.) Kuntze | Anador/bezetacil | Leaves | Infusion | Urine inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Amaranthaceae | Celosia sp. | Crista do galo | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion; Juice | Trauma; Helminthiasis; Chest pain; Toothache; Pereba; Women’s pain; Women’s inflammation; Gastritis; Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Amaranthaceae | Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakij and Clemants | Mastruz | Whole plant | Decoction; Maceration in Alcohol | Flu; Cough; Bellyache; Inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Amaryllidaceae | Allium ascalonicum L. | Cebola-branca | Bulb | Decoction; Maceration in Alcohol | To avoid stroke; Epilepsy; Cough; Flu; Constipation; Stomach; Throat; Fortification |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Amaryllidaceae | Allium cepa L. | Cebola | Bulb | Decoction; Juice; Maceration | Fortification; Flu; Pressure; Amebiasis |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Amaryllidaceae | Allium sativum L. | Alho | Bulb | Infusion | Urethra; Bellyache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Anacardiaceae | Anacardium occidentale L. | Caju branco | Leaves | Decoction | Flu; Fever; Women’s disease; Cough |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Anacardiaceae | Astronium urundeuva (M.Allemão) Engl. | Aroeira | Leaves | Infusion; Decoction; Maceration | Wound healing; Ulcer; Toothache; Postpartum cleansing; Women’s inflammation; Chest pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Anacardiaceae | Mangifera indica L. | Manga espada | Leaves | Infusion; Decoction | Blood pressure; Dysentery |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Anacardiaceae | Spondias purpurea L. | Seringuela | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion | Cancer; Diabetes; High blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Annonaceae | Annona muricata L. | Graviola | Leaves; Bark; Fruit | Decoction; Infusion | Stomach pain; Gasses; Dysentery |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Apiaceae | Foeniculum vulgare Mill. | Erva doce | Leaves; Fruit | Others | Rheumatism |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Araceae | Philodendron sp. | Imbí, imbé | Leaves | Infusion; Decoction | Stomachache; Bellyache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Acanthospermum glabratum (DC.) Wild. | Carrapicho roxo | Whole plant | Maceration in Alcohol; Infusion; In Natura | Headache; Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Achillea millefolium L. | Arcanfor | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion | Flu; Dysentery |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Achyrocline satureioides (Lam.) DC. | Macela do campo | Leaves; Flower | Decoction; Infusion | Body aches; Sight; Hoarseness; Flu; Phlegm |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Ageratum conyzoides L. | Mentrasto | Whole plant | Decoction; Infusion; Maceration in Alcohol | Menstrual cramps; Inflammation; Heart; Stomach; Throat; Fortification |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Artemisia sp. | Losna | Leaves | Juice; Infusion; Maceration in Alcohol | Sight; Postpartum cleansing |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Artemisia vulgaris L. | Artemijo | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion; Maceration in Alcohol | Blood pressure; Urethra pain; Kidney inflammation; Postpartum cleansing; Diabetes |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Bidens pilosa L. | Carrapicho | Seeds; Leaves | Decoction | Back pain; Women’s inflammation; High blood pressure; Kidney |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Chamaecrista blanchetti (Benth.) Conc., L.P. Queiroz and G.P. Lewis | Rompe gibão | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion; Maceration in Alcohol | Bellyache; Fever; Phlegm; Flu; Menstrual cramps; Nausea; Postpartum cleansing |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Gymnanthemum amygdalium (Delile) Sch.Bip. ex Walp. | Aluão | Leaves | Others | To avoid stroke; Headache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Helianthus annuus L. | Girassol | Seeds | Others | Wounds |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Lactuca sativa L. | Alface | Leaves | Decoction | Insomnia |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Matricaria chamomilla L. | Camomila | Leaves | Decoction | Women’s inflammation; Flu; Urine inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Pluchea sagittalis (Lam.) Cabrera | Quitoco | Root; Leaves | Decoction; Infusion; Maceration in Alcohol | Urethra pain; Women’s inflammation; Contusion; Leg pain; Menstrual cramps; Stomachache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Sphagneticola trilobata (L.) Pruski | Calêndula | Whole plant | Maceration; Decoction | Inflammation; |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Spondias tuberosa Arruda | Umbú | Bark | Decoction | Whooping cough |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Tagetes patula L. | Cravo de defunto | Flower | Decoction; Infusion | To avoid dysentery; Stomach pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Asteraceae | Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Sch. Bip. | Macela/ macela galega | Leaves; Flower | Maceration | Cancer; Women’s inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Bignoniaceae | Handroanthus impetiginosus (Mart. ex DC.) Mattos | Pau d’arco roxo | Bark | Others | Evil eye; Back; Contusion forte; Wound healing; Joint pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Bignoniaceae | Tabebuia aurea (Silva Manso) Benth. and Hook.f. ex S.Moore | Caraíba | Bark | Maceration; Infusion | Inflammation; Contusion; Menstrual cramps; Ovaries pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Bixaceae | Bixa orellana L. | Urucum | Seeds; Leaves | Infusion | Walking aid |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Boraginaceae | Cordia sp. | Moleque duro | Leaves | Infusion | Cancer |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Boraginaceae | Symphytum officinale L. | Confrei | Leaves | Infusion | Improves memory |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Brassicaceae | Lepidium ruderale L. | Morfina | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion | Cough; Phlegm; Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Brassicaceae | Rorippa nasturtium-aquaticum (L.) Hayek | Agrião | Leaves | Decoction; Juice | Cholesterol |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Bromeliaceae | Ananas comosus (L.) Merril | Abacaxi | Bark | Syrup | Kidney; Back |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Cactaceae | Melocactus bahiensis (Britton and Rose) Luetzelb. | Cabeça de frade | Whole plant | Others | Headache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Cactaceae | Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Mill. | Palma | Others | Decoction; Infusion | Fever; Flu; Cough |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Caricaceae | Carica papaya L. | Mamão | Fruit | Maceration; Infusion | Amebiasis; Flu; Phlegm; Pressure; Worms; Diabetes |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Celastraceae | Monteverdia rigida (Mart.) Biral | Pau-de-colher | Bark | Maceration in Alcohol; Decoction | Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Commelinaceae | Murdannia nudiflora (L.) Brenan | Marianinha | Leaves | Juice | Sight |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Convolvulaceae | Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. | Batata doce | Leaves | Decoction | Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Convolvulaceae | Operculina macrocarpa (L.) Urb. | Purga de batata | Bark | Decoction | Worms; Hemorrhoids |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Crassulaceae | Bryophyllum pinnatum (Lam.) Oken | Folha da costa | Leaves | Decoction | Inflammation; Contusion |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Crassulaceae | Sedum dendroideum DC | Bálsamo | Leaves | Juice | Inflammation; Eye pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Cucurbitaceae | Cucurbita sp. | Abóbora | Seeds | Infusion | Worms |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Cucurbitaceae | Momordica charantia L. | São caetano | Leaves | Decoction | Women’s inflammation; Leg pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Cucurbitaceae | Sicyos edulis Jacq. | Chuchu | Leaves | Decoction | To decrease blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Dioscoriaceae | Dioscorea villosa L. | Inhame | Root | Decoction | Aphrodisiac |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Erythroxylaceae | Erythroxylum vacciniifolium Mart. | Catuaba | Bark | Others | Aphrodisiac |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Euphorbiaceae | Croton antisyphiliticus Mart. | Enxerto de passarinho | Bark | Decoction | Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Euphorbiaceae | Croton campestris A. St.-Hil. | Velame | Leaves | Decoction | Stroke; Sight; Mouth wound |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Euphorbiaceae | Dalechampia sp. | Urtiga | Root | Decoction | Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Euphorbiaceae | Jatropha gossypiifolia L. | Pinhão roxo | Leaves | Others | Pork allergy |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Euphorbiaceae | Phyllanthus flaviflorus (K.Schum. and Lauterb.) Airy Shaw | Quebra pedra | Whole plant | Decoction; Infusion | Kidney pain; Women’s inflammation; Blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Euphorbiaceae | Ricinus communis L. | Mamona | Others | Others | Helps with childbirth |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Abarema cochliacarpos (Gomes) Barneby and J.W. Grimes | Barbatimão | Bark | Maceration; Maceration in Alcohol; Decoction | Inflammation; Wound healing; Ulcer |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Amburana cearensis (Allem.) A.C. Sm. | Imburana/emburana/umburana | Bark; Leaves; Seeds | Decoction; Infusion | Stomach; Inflammation; Menstrual cramps |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Anadenanthera colubrina (Vell.) Brenan | Angico | Bark | Decoction | Flu; Phlegm |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Cajanus cajan (L.) Huth | Andú branco | Leaves; Flower | Decoction; Infusion | Amebiasis; Stomach pain; |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Cenostigma pyramidale (Tul.) Gagnon and G.P.Lewis | Catinga de porco/pau de rato/manevintura | Leaves | Decoction | Flu; Cough; Sinusitis |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Copaifera lucens Dwyer | Copaiba/ pau de óleo | Others | Others | Stroke; Sight; Throat; Wound healing |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Erythrina sp. | Mulungú | Bark | Decoction | Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Hymenaea stigonocarpa Mart. ex Hayane var. stigonocarpa | Jatobá | Bark | Decoction; Infusion; Maceration in Alcohol | Liver, Kidney; Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Libidibia ferrea (Mart. ex Tul.) L.P. Queiroz | Pau—ferro | Bark | Maceration in Alcohol; Decoction | Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Mimosa sp. | Jurema | Bark | Decoction | Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Peltophorum sp. | Farinha seca | Bark | Infusion | Dysentery |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Periandra mediterranea (Vell.) Taub. | Arcaçus | Root | Decoction; In Natura; Maceration in Alcohol | Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Senna occidentalis (L.) Link | Fedegoso | Leaves; Root; Flower | Infusion; Decoction | Flu; Postpartum; Child’s tooth |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Fabaceae | Tephrosia pupurea (L.) Pers. | Sena | Leaves | Infusion | Phlegm |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Mentha gentilis L. | Alevante miúdo | Leaves | Infusion | Blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Mentha pulegium L. | Peijo (poeijo) | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion; Maceration in Alcohol | Bellyache; Fungal infection; Flu; Cough; Postpartum cleansing; Stomach; Throat; Fortification |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Mentha spicata L. | Hortelã miúdo | Leaves | Juice; Decoction | Amebiasis; Uterus; Stomach; Throat; Fortification; Flu; Worms; To sleep |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Ocimum basilicum L. | Manjericão | Leaves | Infusion; Decoction | Soothing; Blood pressure; Flu; Cough |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Ocimum carnosum (Spreng.) Link and Otto ex Benth. | Alfavaca | Whole plant | Infusion; Decoction | Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Ocimum sp. | Basilicão | Leaves | Decoction | Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng. | Hortelã grosso/graúdo | Leaves | Juice; Decoction | Dysentery; Stomachache; Women’s inflammation; Vaginal discharge |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Plectranthus barbatus Andr. | Boldo/sete dores | Leaves | Infusion; Decoction | Dysentery; Stomach pain; Menstrual cramps |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Plectranthus ornatus Codd | Boldo de quintal | Leaves | Juice; Infusion; Decoction | Stomach; Kidney; Headache; Fever; Dysentery |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Rosmarinus officinalis L. | Alecrim de quintal | Whole plant | Decoction; Infusion | Sinusitis; Calmative; Flu, Sore throat |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lamiaceae | Salvia officinalis L. | Salva | Leaves | Infusion; Decoction | Sight; Flu; Headache; Body aches |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lauraceae | Cinnamomum verum J.Presl | Canela | Bark | Decoction; Maceration | Cough, Flu; Uterus; Stomach; Throat; Fortification; Women’s inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lauraceae | Persea americana Mill. | Abacate | Leaves; Seeds | Decoction; Maceration in Alcohol | Kidney |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Liliaceae | Nothoscordum sp. | Alho bravo | Root | Maceration; Maceration in Alcohol; Decoction | Rheumatism |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Lythraceae | Punica granatum L. | Romã | Fruit | Decoction | Sore throat |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Malpighiaceae | Malpighia glabra L. | Acerola | Leaves; Fruit | Decoction; Infusion; Juice | Bronchitis; Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Malvaceae | Gossypium herbaceum L. | Algodão | Fruit; Leaves | Juice; Decoction | Flu; Expectorant; Cough; Pain; Women’s inflammation; Contusion |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Malvaceae | Luehea grandiflora Mart | Cedro | Bark | Decoction | Bellyache; Fungal infection; Constipation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Malvaceae | Sida cordifolia L. | Malva—branca | Leaves; Root | Decoction | Blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Malvaceae | Sidastrum micranthum (A.St.-Hil.) Fryxell | Malva—preta/ malva de sebo | Root | Maceration in Alcohol | Hair loss |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Malvaceae | Guazuma ulmifolia Lam. | Mutamba | Bark | Infusion; Decoction | Pain; Flu; Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Moraceae | Dorstenia sp. | Carapuá/carapiá | Root | Decoction | Blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Moraceae | Ficus carica L. | Figo | Leaves | Decoction | Cough; Blood pressure; Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Musaceae | Musa sapientum L. | Banana | Inflorescence | Infusion; Maceration in Alcohol; Decoction | Menstrual cramps; Stroke; Uterus; Stomach; Throat; Fortification |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Myristicaceae | Myristica fragrans Houtt. | Noz-moscada/manuscada | Seeds | Infusion; Decoction | Fever; Flu; Sinusitis; Phlegm |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Myrtaceae | Eucalyptus globulus Labill. | Eucalipto | Leaves; Seeds | Decoction | Amebiasis; Fever; Flu; Cough |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Myrtaceae | Eugenia uniflora L. | Pitanga | Leaves | Decoction | Dysentery |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Myrtaceae | Plinia peruviana (Poir.) Govaerts | Jabuticaba | Bark | Decoction | Bellyache; Women’s inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Myrtaceae | Psidium guajava L. | Goiabeira | Bark; Leaves | In Natura; Decoction | Headache; Dysentery |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Myrtaceae | Psidium guineense Sw. | Araçá | Leaves | Decoction | Cough, Flu, Whooping cough |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Myrtaceae | Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merr. and L.M.Perry | Cravo da índia | Flower | Decoction; Infusion; In Natura | Cholesterol; High blood pressure; Ulcer; Diabetes; Heart; Women’s inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Myrtaceae | Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels | Janelão/jamelão | Leaves; Fruit | Maceration in Alcohol | Postpartum cleansing; |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Nyctaginaceae | Boerhaavia coccinea Willd. | Pega pinto | Whole plant | Decoction | To decrease blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Orchidaceae | Vanilla sp. | Baunilha | Leaves | Infusion | Stroke; Epilepsy |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Papaveraceae | Argemone mexicana L. | Carro santo | Leaves | Infusion; Juice; Decoction | To sleep; Blood pressure; Soothing; Hemorrhoids |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Passifloraceae | Passiflora cincinnata Mart. | Maracujá do mato | Flower; Fruit; Root | Infusion | Blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Passifloraceae | Passiflora edulis Sims | Maracujá | Flower; Leaves | Others | Joint pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Pedaliaceae | Sesamum indicum L. | Gergelin | Seeds | Decoction | Fortification |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Piperaceae | Piper nigrum L. | Pimenta do reino | Seeds | Decoction; Infusion; In Natura; Maceration in Alcohol | Urine inflammation; Sore throat; Toothache; Women’s inflammation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Plantaginaceae | Plantago major L. | Trançagem | Whole plant | Decoction; Juice | Kidney pain; Back pain; Liver; Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Poaceae | Bambusa bambos (L.) Voss | Bambu | Flower; Fruit | Decoction; Infusion | Soothing; Diabetes; High blood pressure; Flu; Release more urine |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Poaceae | Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf. | Capim-santo | Leaves; Root | Decoction; Infusion; Juice | Headache; Healing |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Poaceae | Digitaria insularis (L.) Fedde | Capim açú | Leaves | Decoction | Blood circulation aid |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Poaceae | INDET | Capim lanceta | Aerial part of the plant | Decoction; Infusion | Cough, Flu; Soothing |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Poaceae | INDET | Capim nagô | Aerial part of the plant | Decoction; Infusion | High blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Poaceae | Saccharum officinarum L. | Cana caiana | Leaves | Others | Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Poaceae | Zea mays L. | Milho | Leaves | Infusion | Heart |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Rosaceae | Rosa sp. | Rosa branca ou branca de neve | Flower | Decoction | Stroke |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Rubiaceae | Coffea sp. | Café | Seeds | Decoction; maceration in alcohol; In natura | Abortive; Bellyache; Kidney; Liver |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Rubiaceae | Coutarea hexandra (Jacq.) K. Schum. | Quina | Bark | Infusion | Pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Rubiaceae | Palicourea coriacea (Cham.) K. Schum. | Gemedeira | Root | Decoction | Soothing; High blood pressure; Fever; Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Rutaceae | Citrus aurantium L. | Laranja | Leaves | Juice; Decoction; Infusion | Cholesterol; High blood pressure; Flu; Skin wound |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Rutaceae | Citrus x limon (L.) Osbeck | Limão | Fruit; Leaves | Decoction; Maceration in Alcohol | Phlegm; Flu; Postpartum cleansing; Throat; Fortification |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Rutaceae | Ruta graveolens L. | Arruda | Leaves | Maceration; Decoction; Maceration in Alcohol; in natura; Infusion | Stomach pain; Dysentery; Vomit; Back pain; Blood pressure |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Smilacaceae | Smilax hilariana A.DC. | Jacaré/ catana de jacaré | Root | Decoction | Toothache |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Solanaceae | Capsicum sp. | Pimenta | Fruit; Leaves | Decoction | Vaginal discharge; Cystitis |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Solanaceae | Solanum ambrosiacum Vell. | Melancia da praia | Whole plant | Decoction | Diarrhea; Worms; Vaginal discharge |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Solanaceae | Solanum erianthum D. Don. | Caiçara | Root | Decoction; infusion | To vomit; To stomach pain |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Solanaceae | Solanum sp. | Cassutinga | Bark; Leaves | Decoction | Child’s colic |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Sterculiaceae | Helicteres macropetala A.St.-Hil. | Rosca | Fruit | Decoction | Stroke |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Verbenaceae | Aloysia gratíssima (Gillies and Hook.) Tronc. | Alfazema | Whole plant | Decoction; infusion | Urine inflammation; Flu; Soothing |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Verbenaceae | Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E.Br. | Erva cidreira | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion; In Natura | To stomach pain; Dysentery; Barriga fofa; Headache; Pressure; Soothing; Diabetes; Calmative |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Verbenaceae | Lippia grata Schauer | Alecrim de vaqueiro | Leaves | Decoction; Infusion | Blood pressure; Flu |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Violaceae | Pombalia calceolaria (L.) Paula-Souza | Papaconha | Root | Decoction | Stroke; Amebiasis; Purgative |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Vitaceae | Vitis aestivalis Michx. | Uva | Leaves | Decoction | To decrease menstruation |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Xanthorrhoeaceae (Liliaceae) | Aloe vera (L.) Burm.f. | Babosa | Leaves | Juice; Decoction | Cancer; Stroke; Worms; |
| Barboza da Silva et al. [21] | 2012 | Barra II, Bahia | Zingiberaceae | Alpinia zerumbet (Pers.) B.L.Burtt and R.M.Sm. | Alevante vermelho | Root | Infusion | Blood pressure |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Acanthaceae | Justicia pectoralis Jacq. | Xaxaba | Leaves | NR | Flu; Fever; Phlegm; Cough |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Adoxaceae | Sambucus australis Cham. and Schltdl. | Sabugueiro | Leaves; Flower | NR | Flu; Fever; Phlegm; Cough; Hypertension |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Amaranthaceae | Alternanthera aff. philoxeroides (Mart.) Griseb. | Acônico | Leaves | NR | Stomachache; Headache; Fever |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Amaranthaceae | Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin and Clemants | Mastruz | Leaves | NR | Anemia; Inflammation; Bronchitis; High cholesterol; Colic; Diabetes; Diarrhea; Phlegm; Gastritis; Flu; Cough; Trauma; Worms |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Anacardiaceae | Anacardium occidentale L. | Cajueiro roxo | Bark | NR | Inflammation; Trauma; Worms; Contusion; Wounds; Stomachache |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Anacardiaceae | Schinus terebinthifolia Raddi | Aroeira | Bark | NR | Inflammation; Sore throat; Trauma; Wounds; Allergies |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Annonaceae | Annona muricata L. | Graviola | Leaves; Fruit | NR | Cancer; Diabetes; Hypertension |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Apiaceae | Eryngium foetidum L. | Coentro maranhão | Leaves | NR | Heart attack |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Apiaceae | Pimpinella anisum L. | Erva-doce | Seeds | NR | Bellyache; Hypertension; Detox; Indigestion |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Apocynaceae | Catharanthus roseus (L.) Don | Boa noite branca | Root | NR | Flu |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Apocynaceae | Hancornia speciosa Gomes | Mangaba | Latex | NR | Gastritis; Ulcer |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Asteraceae | Acanthospermum hispidum DC. | Espinho de cigano | Leaves; Root | NR | Flu; Phlegm; Cough |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Asparagaceae | Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. | Babosa | Pulp | NR | Flu; Headache; Bellyache |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Asteraceae | Bidens sp. | Camomila | Flower | NR | Sedative; Headache |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Asteraceae | Conyza bonariensis (L.) Cronquist | Rabo de raposa | Leaves | NR | Ringworm |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Asteraceae | Gymnanthemum amygdalinum (Delile) Sch.Bip. ex Walp. | Alcachofra | Leaves | NR | High cholesterol; Diabetes; Liver; Kidney pain; Indigestion; Gallbladder pain |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Asteraceae | Solidago chilensis Meyen | Arnica brasileira | Leaves | NR | Contusion |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Bignoniaceae | Handroanthus impetiginosus (Mart. ex DC.) Mattos | Pau D’arco roxo | Bark | NR | Inflammation; Anemia; Cancer; Wounds; Trauma |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Costaceae | Costus lasius Loes. | Cana da índia | Leaves | NR | Diabetes; Kidney stone |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Crassulaceae | Kalanchoe crenata (Andrews) Haw. | Saião | Leaves | NR | Gastritis; Flu; Ulcer; Phlegm; Worms |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Cucurbitaceae | Cucurbita pepo L. | Jerimum | Flower | NR | Earache; Hemorrhoids; Worms |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Cucurbitaceae | Momordica charantia L. | Melão São Caetano | Leaves | NR | Sight |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Euphorbiaceae | Cnidoscolus urens (L.) Arthur | Urtiga branca | Root | NR | Inflammation |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Euphorbiaceae | Jatropha mollissima (Pohl) Baill. | Pinhão branco | Latex | NR | Hemorrhage |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Euphorbiaceae | Pedilanthus tithymaloides (L.) Poit. | Beladona | Leaves | NR | Fever; Bellyache; Flu; Headache |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Euphorbiaceae | Ricinus communis L. | Carrapateira | Leaves | NR | Fever; Bellyache; Flu; Headache |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Fabaceae (Caesalpinoideae) | Senna occidentalis (L.) Link | Manjirioba | Leaves | NR | Diabetes; Flu |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Fabaceae (Cercidoideae) | Bauhinia monandra Kurz | Pata de vaca | Leaves | NR | Diabetes |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Fabaceae (Mimosoideae) | Stryphnodendron pulcherrimum (Willd.) Hochr. | Babatenom | Bark | NR | Inflammation; Wounds; Trauma; Contusion |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Geraniaceae | Pelargonium graveolens L’Hér. | Malva-rosa | Whole plant | NR | Fever; Flu; Hemorrhoid; Phlegm |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Aeollanthus suaveolens Mart. ex Spreng. | Macaça | Leaves | NR | Heart attack; Earache; Hypertension |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Callicarpa sp. | Vick | Leaves | NR | Inflammation; Headache; Phlegm; Flu; Fever; Cough |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Leonotis nepetifolia (L.) R.Br. | Cordão de São Francisco | Leaves; Flower | NR | Heart attack |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Mentha sp | Hortelã miúda | Leaves | NR | Heart attack; Worms; Cough; Amebiasis; Bellyache; Earache; Flu; Hemorrhoid; Sinusitis; Worms; Cough |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Ocimum basilicum L | Manjerona | Leaves | NR | Depression |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Ocimum gratissimum L. | Louro do mato | Leaves | NR | Diarrhea; Bellyache; Stomachache |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng. | Hortelã grande | Leaves | NR | Asthma; Bronchitis; Headache; Headache; Sore throat; Phlegm; Flu; Hypertension; Cough; Sinusitis |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Rosmarinus officinalis L. | Alecrim | Leaves | NR | Heart attack; Headache; Fever; Hypertension; Thrombosis; Bellyache; Diarrhea |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lamiaceae | Vitex agnus-castus L. | Liamba | Leaves | NR | Bellyache; Rhinitis |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lauraceae | Cinnamomum verum J. Presl | Canela | Leaves; Bark | NR | Diarrhea; Stomachache; Vomit |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lauraceae | Persea americana Mill. | Abacate | Leaves | NR | Bellyache; Kidney pain; Liver; Urinary tract infection; Prostate |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Lythraceae | Punica granatum L. | Romã | Bark; Seeds | NR | Conjunctivitis; Sore throat; Cough |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Malpighiaceae | Malpighia glabra L. | Acerola | Fruit | NR | Flu; Cough |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Malvaceae | Guazuma ulmifolia Lam. | Mutamba | Bark | NR | Dandruff; Diarrhea; Hemorrhoid |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Meliaceae | Azadirachta indica A.Juss. | Nim | Leaves | NR | Ringworm |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Moraceae | Morus alba L. | Amora | Leaves; Fruit | NR | Cramp; High cholesterol; Diabetes; Fever; Gastritis; To lose weight |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Musaceae | Musa x paradisiaca L. | Banana | Latex | NR | Wounds |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Myrtaceae | Eugenia uniflora L. | Pitanga | Leaves; Fruit | NR | Bellyache; Diarrhea; Flu |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Myrtaceae | Psidium guajava L. | Goiaba | Leaves | NR | Bellyache; Diarrhea |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Myrtaceae | Psidium guineense Sw. | Araça | Leaves | NR | Bellyache; Diarrhea |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Myrtaceae | Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels | Oliveira | Leaves | NR | Diabetes |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Passifloraceae | Passiflora edulis Sims | Maracujá | Leaves; Flower | NR | Sedative |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Phyllanthaceae | Phyllanthus niruri L. | Quebra-pedra | Root | NR | Kidney stone |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Phytolaccaceae | Petiveria alliacea L. | Tipi | Leaves | NR | Wounds; Wounds; Pain |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Piperaceae | Piper nigrum L. | Pimenta do reino | Seeds | NR | Sore throat; Stomachache |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Plantaginaceae | Plantago major L. | Transagem | Leaves | NR | Sore throat |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Plantaginaceae | Scoparia dulcis L. | Vassourinha | Leaves; Flower; Root | NR | Diarrhea; Inflammation; Contusion |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Poaceae | Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf | Capim santo | Leaves | NR | Anemia; Bellyache; Diarrhea; Diabetes; Stomachache; Flu; Hypertension; Worms; Vomit; Indigestion |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Rubiaceae | Borreria verticillata (L.) G.Mey. | Vassoura de botão | Root; Flower | NR | Bellyache; Diarrhea; Contusion; Constipation; Cough |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Rubiaceae | Morinda citrifolia L. | Noni | Fruit | NR | Heart attack; Cancer; High cholesterol; Diabetes |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Rubiaceae | Tocoyena sellowiana (Cham. and Schltdl.) K.Schum. | Jenipapo bravo | Bark | NR | Contusion; Cough; Inflammation; Wounds; Wounds |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Rutaceae | Citrus limon (L.) Osbeck | Limão | Fruit | NR | Cough; Flu |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Rutaceae | Citrus x aurantium L. | Laranja | Leaves | NR | Sedative; Bellyache; Toothache; Fever |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Rutaceae | Ruta graveolens L. | Arruda | Leaves; Flower | NR | Menstrual cramps; Conjunctivitis; Earache; Fever |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Solanaceae | Solanum americanum Mill. | Erva moura | Leaves; Seeds | NR | Wounds; Contusion |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Verbanaceae | Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E.Br. ex P. Wilson | Cidreira | Leaves | NR | Abortive; Anemia; Sedative; Menstrual cramps; Diarrhea; Stomachache; Fever; Flu; Indigestion; Cough |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Verbanaceae | Lippia grata Schauer | Alecrim de tabuleiro | Leaves | NR | Flu |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Vitaceae | Cissus verticillata (L.) Nicolson and C.E.Jarvis | Insulina | Leaves | NR | Diabetes |
| Beltreschi et al. [22] | 2018 | Ipiranga, Paraíba | Zingiberaceae | Alpinia zerumbet (Pers.) B.L. Burtt and R.M. Sm. | Colônia | Leaves; Flower | NR | Cancer; Acidity; Dandruff; Wounds; Furuncle; Gastritis; Ulcer; Contusion; Hemorrhoids; Worms |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Acanthaceae | Ruellia sp. | Solda-osso | Whole plant | NR | Bronchitis; Phlegm; Headache; Fever; Flu; Sinusitis; Cough |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Adoxaceae | Sambucus nigra L. | Sabugueira | Flower | Infusion | Broken bone |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Amaranthaceae | Alternanthera tenella Colla | Meracilina | Leaves | Boiled | Fever; Sore throat |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Amaranthaceae | Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin and Clemants | Mentruz | Leaves; Stem | NR | Pain; Inflammation |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Apiaceae | Apium graveolens L. | Endro | Leaves; Bark | NR | Worms; Cough |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Asparagaceae | Asparagus densiflorus (Kunth) Jessop | Alfinete/agulha | Leaves; Stem | NR | Anemia; Inflammation |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Asparagaceae | Dracaena trifasciata (Prain) Mabb. | Espada-de-são-jorge | Leaves | Boiled | To avoid stroke |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Asteraceae | Solidago chilensis Meyen | Arnica | Leaves; Stem; Flower | NR | Energetic |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Cactaceae | Pereskia grandifolia Haw. | Orai-por- nove | Leaves; Flower; Fruit | NR | Back pain; Pain; Muscle torsion |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Euphorbiaceae | Croton heliotropiifolius Kunth | Velande | Leaves | NR | Pain |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Euphorbiaceae | Jatropha gossypiifolia L. | Pião-roxo | Leaves; Stem | NR | Diabetes; Inflammation |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Euphorbiaceae | Jatropha multifida L. | Metiolate | Leaves | NR | Wound healing; Muscle relaxant; Kills insects |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Fabaceae | Cajanus cajan (L.) Huth | Feijão-andu | Leaves; Seeds | NR | Wound healing |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Fabaceae | Senna macranthera (DC.) H.S.Irwin and Barneby | Fedegoso | Seeds | NR | Headache; Labyrinthitis; Depression; High blood pressure |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Lamiaceae | Melissa officinalis L. | Erva-cidreira | Leaves | NR | Labyrinthitis; High blood pressure |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Lamiaceae | Mentha arvensis L. | Vick | Leaves | NR | Cramp; Depression |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Lamiaceae | Mentha suaveolens Ehrh | Hortelã-da-folha-miúda | Leaves | NR | Cramp; Inflammation; Stomachache |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Lamiaceae | Mesosphaerum pectinatum (L.) Kuntze | Favaca-pequena | Leaves; Stem | NR | Cramp; Flu; Ingestion; Inflammation |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Lamiaceae | Ocimum basilicum L. | Sambacaitá | Leaves | NR | Cramp |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Lamiaceae | Ocimum sp. | Favaca-de-vaqueiro | Leaves; Root | NR | Inflammation |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Lamiaceae | Salvia rosmarinoides A.St.-Hil. | Alecrim | Leaves; Stem | NR | Cramp; Depression; Ingestion |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Lamiaceae | Vitex sp. | Jurema-de-cabloco | Leaves; Seeds | Infusion | To prevent heart attack; Hoarseness |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Malpighiaceae | Byrsonima stipulacea A.Juss | Murici | Leaves; Fruit | NR | Headache; Infertility; To control menstrual period; To relieve menopausal heat; To reduce male libido |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Phyllantaceae | Phyllanthus niruri L. | Quebra-pedra | Leaves; Root | NR | Fever; Inflammation; Cancer |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Phytolaccaceae | Petiveria alliacea L. | Tipi | Leaves | NR | Kidney stone; Diabetes |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Plantaginaceae | Plantago major L. | Transagem | Leaves | NR | Energetic; Joint pain |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Polygalaceae | Polygala microphylla L. | Zezinho | Leaves; Stem | NR | Urinary tract infection; Ovarian infection; Cancer |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Pteridaceae | Adiantium capillus-veneri L. | Avenca | Leaves; Stem | Infusion | Swelling; Postpartum |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Rubiaceae | Morinda citrifolia L. | Noni | Fruit | NR | Cancer; Diabetes; Hypertension |
| Magalhães et al. [23] | 2022 | Pau D’arco, Alagoas | Verbenaceae | Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E.Br. ex Britton and P.Wilson | Beladona | Leaves; Stem | NR | Pneumonia; Diabetes; Kidney stone |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Anacardiaceae | Mangifera indica L. | manga- grande, mangueira | Bark | NR | Depression; Diabetes |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Apocynaceae | Aspidosperma excelsum Benth. | Carapanaúba | Bark | NR | Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Apocynaceae | Geissospermum argenteum Woodson | Quinarana | Bark | NR | Malaria; Fever; Liver; Body aches, Migraine |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Apocynaceae | Himatanthus articulates (Vahl) Woodson | Sucuuba | Latex | NR | Liver; Malaria; Hepatitis |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Arecaceae | Euterpe ptrvstoria Mart. | Açaí | Root | NR | Malaria; Fortification |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Asteraceae | Artemisia vulgaris L. | Anador | Aerial part of the plant | NR | Anemia; Hepatitis; Jaundice; Liver; Fatigue; Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Asteraceae | Bidens bipinnata L. | Picão/carrapicho | Root | NR | Headache; Malaria; Fever; Body aches |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Asteraceae | Blainvillea acmella (L.) Philipson | Jambu, jambuí | Aerial part of the plant | NR | Malaria, Liver |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Asteraceae | Gymnanthemum amygdalinum (Delile) Sch.Bip. ex Walp | Figatil | Leaves | NR | Liver; Malaria; Migraine |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Caricaceae | Carica papaya L. | Mamão- macho | Leaves | NR | Liver; Malaria; Restlessness; Nausea; Fever; Hepatitis |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Convolvulaceae | Operculina hamiltonii (G.Don) D.F. Austin and Staples | Batatão, batata-depurga | Tuber | NR | Malaria; Liver; Nausea; Anemia, Laxative; Vomit; Spleen cleansing, Restlessness |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Curcubitaceae | Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. and Nakai | Melancia | Seeds | NR | Laxative; Clearance; Malaria; Hepatitis |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Curcubitaceae | Luffa operculata (L.) Cogn | Cabacinha | Fruit | NR | Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Euphorbiaceae | Croton cajucara Benth. | Sacaca | Bark | NR | Emetic; Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Euphorbiaceae | Croton sacaquinha Croizat | Sacaquinha, piaçoca | Bark | NR | Liver, Malaria, Hepatitis |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Euphorbiaceae | Jatropha curcas L. | Peão-branco | Seeds | NR | Liver; Malaria; Migraine |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Euphorbiaceae | Meororis stipulate Raf. | Quebra-pedra | Whole plant | NR | Laxative; Malaria; Loss of appetite |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Fabaceae | Dalbergia riedelii (Benth.) Sandwith | Verônica | Bark | NR | Malaria; Jaundice |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Fabaceae | Machaerium ferox (Benth.) Ducke | Saratudo | Trunk | NR | Anemia; Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Fabaceae | Senna occidentalis Link. | Paramagioba | Root | NR | Malaria; Jaundice |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Humiriaceae | Endopleura uchi (Huber) Cuatrec | Uxi-liso | Bark | NR | Malaria; Anemia |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Lamiaceae | Plectranthus barbatus Andr. | Melhoral, boldo | Leaves | NR | Malaria; Liver; Anemia |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Lauraceae | Cinnamomum verum J.Presl | Canela | Leaves | NR | Liver; Hangover; Malaria; Migraine; Anemia |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Lecythidaceae | Bertholletia excelsa Bonpl. | Castanheira | Fruit | NR | Fatigue; Headache; Migraine; Liver; Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Malvaceae | Quararibea guianensis Aubl. | Inajarana | Bark | NR | Malaria; Jaundice |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Meliaceae | Carapa guianensis Aubl. | Andiroba | Seeds | NR | Anemia; Hepatitis; Malaria; Liver |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Meliaceae | Cedrela odorata L. | Cedro | Bark | NR | Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Moraceae | Parahancornia fasciculata (Poir.) Benoist | Amapá- amargo | Latex | NR | Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Pedaliaceae | Sesamum indicum L. | Gergelim | Seeds | NR | To prevent malaria; Improves blood circulation |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Rhamnaceae | Ampelozizyphus amazonicus Ducke | Saracuramirá | Bark | NR | Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Rubiaceae | Uncaria guianensis (Aubl.) J.F.Gmel. | Unha-de-gato | Bark | NR | Malaria; Liver; Clearance; Anemia; Loss of appetite |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Rutaceae | Citrus x aurantium L. | Laranja-daterra, laranjeira | Fruit | NR | Anemia; Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Rutaceae | Ruta graveolens L. | Arruda | Aerial part of the plant | NR | Liver; Malaria; Anemia; Fatigue; Headache; Migraine |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Simaroubaceae | Homololepis cedron (Planch.) Devecchi and Pirani | Pau-paratudo | Bark | NR | Fever; Malaria; Headache; Body aches; Fatigue; To prevent diseases |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2015 | Oriximiná, Pará | Solanaceae | Physalis angulata L. | Gamapu, camapu | Root | NR | Malaria |
| Oliveira et al. [24] | 2014 | Oriximiná, Pará | Verbenaceae | Lippia origanoides Kunth | Salva-de-marajó | Leaves; Aerial part of the plant | NR | Liver; Anemia; Hepatitis; Malaria |
| Rodrigues [25] | 2007 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Arecaceae | Syagrus petraea (Mart.) Becc | Açaí-bravo | Fruit | NR | Menstrual cramps, Stomachache; Baby colic; Postpartum. |
| Rodrigues [25] | 2007 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Lamiaceae | Hyptidendron canum (Pohl ex Benth.) Harley | Hortela-da-várzea | Leaves | In Natura | Contraceptive |
| Rodrigues [25] | 2007 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Loganiaceae | Strychnos pseudoquina A. St.-Hil | Quina | Leaves; Bark | Decoction | Abortive |
| Rodrigues [25] | 2007 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Oxalidaceae | Oxalis physocalyx Zucc. ex Progel | Azedinha | Whole plant | Decoction | Abortive |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2004 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Asteraceae | Conyza bonariensis (L.) Cronquist | NI | NI | Juice | Abortive |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2006 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Bignoniaceae | Cybistax antisyphilitica (Mart.) Mart | NI | NI | NR | Mental alteration |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2004 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Fabaceae | Senna occidentalis (L.) Link | NI | NI | NR | Headache |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2004 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Flacourtiaceae | Casearia sylvestris Sw. | NI | NI | NR | Mental alteration |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2004 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Lythraceae | Lafoensia pacari A. St.-Hil. | NI | NI | NR | Mental alteration |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2006 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Malpighiaceae | Heteropterys tomentosa A.Juss. | Nó-de-Cachorro | NI | NR | Mental alteration |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2004 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Malvaceae (Sterculiaceae) | Guazuma ulmifolia Lam. | NI | NI | NR | Rejuvenating |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2004 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Moraceae | Brosimum gaudichaudii Trécul. | Algodaozinho | NI | NR | Mental alteration |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2006 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Phytolaccaceae | Petiveria alliacea L. | NI | NI | Decoction | Mental alteration |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2006 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Poaceae | Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf | NI | NI | NR | Mental alteration |
| Rodrigues and Carlini [26] | 2004 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Rutaceae | Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck | NI | NI | NR | Soothing; To decrease blood pressure |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Amaryllidaceae | Allium sativum L. | Alho | Bulb | NR | Mental alteration |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Bignoniaceae | Anemopaegma arvense (Vell.) Stellfeld ex de Souza | Alecrim-do-norte | Leaves | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Lamiaceae | Hyptidendron canum (Pohl ex Benth.) Harley | hortelã-da-várzea | Leaves | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Moraceae | Dorstenia asaroides Gardner | Caiá-piá | Rhizome | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Myrtaceae | Eucalyptus globulus Labill | Eucalipto | Leaves | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Myrtaceae | Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merr. and L.M.Perry | Cravo-da-Índia | Flower | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Phytolaccaceae | Petiveria alliacea L. | Guiné | Leaves | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Rutaceae | Ruta graveolens L. | Arruda | Leaves | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Rodrigues et al. [27] | 2008 | Sesmaria Mata-Cavalos, Mato Grosso | Siparunaceae | Siparuna guianensis Aubl. | Negramina | Leaves | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Acanthaceae | Justicia pectoralis Jacq. | Doril | Whole plant | NR | To improve learning; Nervous breakdown |
| Yazbek et al. [28]. | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Adoxaceae | Sambucus cf. canadensis L. | Sabugueiro | Leaves; Flower | Decoction | Flu; Headache |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Alismataceae | Echinodorus grandiflorus (Cham. and Schltr.) Micheli | Chapéu-de-couro | Leaves | Decoction/Syrup | Fever; Measles |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Amaranthaceae | Alternanthera brasiliana (L.) Kuntze | Terramicina | Leaves | Decoction | Kidney stone; Diabetes |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Amaranthaceae | Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin and Clemants | Erva-de-Santa Maria | Leaves | Decoction | Flu; Headache; Urinary tract infection |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Amaranthaceae | Pfaffia glomerata (Spreng.) Pedersen | Novalgina | Leaves | Infusion | Wounds; Bone trauma; To prevent worms |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Anacardiaceae | Anacardium occidentale L. | Cajueiro | Bark | Decoction | Flu; Headache; Fever |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Annonaceae | Annona muricata L. | Graviola | Leaves | Decoction | Swelling; Hemorrhoid; Bone trauma |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Apiaceae | Eryngium foetidum L. | Coentro-natural | Whole plant | Decoction | Diabetes |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Apiaceae | Foeniculum vulgare Mill. | Erva-doce | Whole plant | Decoction | Snakebite |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Apocynaceae | Tabernaemontana laeta Mart. | Guaraná | Exudate | Decoction | Cold; Soothing |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Araceae | Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott | Inhame | Root | In Natura | Myiasis |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Araceae | Philodendron martianum Engl. | Banana-do-mato | Exudate | Cooked | Anemia |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asparagaceae | Furcraea foetida (L.) Haw | Pita | Leaves | In Natura | Dandruff |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Achillea millefolium L. | Camomila | Whole plant | Maceration | Scabies |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Acmella ciliata (Kunth) Cass. | Anestesia | Bark | Decoction | Expectorant; Helminthiasis |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Ageratum conyzoides L. | Erva-de-São-João | Leaves | Decoction | Headache |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Baccharis sp. | Carqueja | Leaves | Maceration | Bruises; Cold; Bone trauma; Menstrual regulation |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Bidens pilosa L. | Picão | Whole plant | Maceration | Diarrhea |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Conyza cf. canadensis (L.) Cronquist | Taporava | Leaves | Decoction | Anemia; Hepatitis |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Emilia sonchifolia (L.) DC | Serralha | Leaves | Heated | Antifungal |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Erechtites valerianifolius (Wolf) DC | Gondó | Whole plant | Decoction | Gastritis |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Gamochaeta pensylvanica (Willd.) Cabrera | Macelinha | Whole plant | In natura | Clearance; Anemia |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Gymnanthemum amygdalinum (Delile) Sch.Bip. ex Walp. | Boldo-sem-pêlo | Leaves | Decoction | Constipation |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Mikania laevigata Sch.Bip. ex Bake | Guaco | Leaves | Decoction | Digestive |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Montanoa bipinnatifida (Kunth) K.Koch | Flor-de-maio | Leaves | Decoction | Cough; Sore throat |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Asteraceae | Vernonanthura beyrichii (Less.) H.Rob. | Cambará-preto/Cambará-roxo | Leaves | Decoction | Ulcer |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Bignoniaceae | Handroanthus impetiginosus (Mart. ex DC.) Mattos | Ipê-roxo | Bark | Decoction | Bruises; Pneumonia; Bone trauma |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Bignoniaceae | Jacaranda puberula Cham. | Carobinha | Leaves | Decoction | Clearance; Anemia |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Bignoniaceae | Varronia curassavica Jacq. | Erva-baleeira | Leaves | Decoction | Coagulant |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Bromeliaceae | Bromelia antiacantha Bertol. | Picova-amarelo | Fruit | Maceration | Bruises; Bone trauma; Back pain; Myoma |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Caricaceae | Carica papaya L. | Mamão | Flower | Decoction | Flu; Bronchitis |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Celastraceae | Monteverdia ilicifolia (Mart. ex Reissek) Biral | Espinheira-Santa | Leaves | In natura | Cough |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Clusiaceae | Garcinia gardneriana (Planch. and Triana) Zappi | Bacupari | Bark | Decoction | Stomachache |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Convolvulaceae | Cuscuta obtusiflora Kunth | Cipó-chumbo | Whole plant | Decoction | Gastritis |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Convolvulaceae | Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam | Batata | Leaves | Decoction | Scabies |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Costaceae | Costus arabicus L. | Caninha-do-brejo | Whole plant | Heated | Toothache |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Crassulaceae | Kalanchoe pinnata (Lam.) Pers | Saião-roxo | Leaves | Decoction | Urinary tract infection |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Crassulaceae | Kalanchoe pinnata (Lam.) Pers | Saião-branco | Leaves | Maceration | Ulcer |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Crassulaceae | Sedum cf. dendroideum Moc. and Sessé ex DC. | Bálsamo | Leaves | Heated | Antifungal |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Cucurbitaceae | Cucurbita cf. maxima Duchesne | Abóbora | Flower; Seeds | Raw, unprocessed | Digestion |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Cucurbitaceae | Momordica charantia L. | Malãozinho-do-mato | Leaves | Heated | Earache |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Dilleniaceae | Davilla rugosa Poir | Cipó-caboclo | Exudate | Decoction | Ulcer |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Euphorbiaceae | Euphorbia thymifolia L. | Quebra-pedra-roxo | Whole plant | Maceration | Scabies |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Euphorbiaceae | Manihot esculenta Crantz | Mandioca-doce | Leaves | In natura | Cataract |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Fabaceae | Bauhinia forficata Link | Pata-de-vaca | Leaves | Decoction | To prevent kidney stone |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Fabaceae | Hymenaea altissima Ducke | Jatobá/Jataí | Bark; Exudate | Cooked | Fortification |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Fabaceae | Mimosa pudica L. | Dormideira | Leaves | Decoction | Diabetes |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Fabaceae | Swartzia oblata R.S.Cowan. | Barbatimão | Bark; Leaves | Decoction | Coagulant; Anemia; Digestion; Diabetes; Fortification |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Hypoxidaceae | Hypoxis decumbens L. | Cebolinha-do-mato | Bulb | Infusion | Sore throat; To sleep better |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lamiaceae | Mentha pulegium L. | Poejo | Leaves | Decoction | Coagulant; Anti-inflammatory; Back pain; Scabies |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lamiaceae | Mentha sp. | Hortelã-de-bicha | Leaves | Decoction | Diabetes |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lamiaceae | Ocimum gratissimum L. | Favacão | Leaves | Decoction | Expectorant; Sore throat |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lamiaceae | Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng | Hortelã-castelo/Hortelã-de-carne | Leaves | Decoction | Flu; Soothing; Helminthiasis |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lamiaceae | Plectranthus barbatus Andrews | boldo-com-pelo | Leaves | Syrup | Cough |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lauraceae | Cryptocarya mandioccana Meisn. | Noz-moscada | Seeds | Decoction | Flu |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lauraceae | Cryptocarya saligna Mez | Canela-sassafraize | Bark | Decoction | Hangover |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lauraceae | Persea americana Mill. | Abacate-roxo | Leaves | Decoction; Maceration | Bruises; Ulcer; Bronchitis; Bone trauma |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Loranthaceae | Struthanthus marginatus (Desr.) G.Don | Erva-de-passarinho | Leaves | Maceration | Purification; Measles |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lythraceae | Cuphea carthagenensis (Jacq.) J.F.Macbr. | Sete-sangria | Whole plant | Decoction | Kidney stone |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Lythraceae | Psidium cattleianum Sabine | Araçá | Leaves | Maceration | Coagulant; Sore throat; Bone trauma |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Malvaceae | Sida planicaulis Cav. | Vassoura-guanxuma | Leaves | Maceration | Digestion |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Meliaceae | Cedrela fissilis Vell. | Cedro-rosa | Bark | Decoction | Antihypertensive; Hepatitis; To prevent kidney stone |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Musaceae | Musa x paradisiaca L. | Banana | Exudate | Decoction | Diarrhea |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Myrtaceae | Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston | Jambo/jambolão | Leaves | Heated | Furuncle |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Myrtaceae (Lythraceae) | Eugenia uniflora L. | Pitanga | Leaves; Fruit | Decoction | Bruises |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Myrtaceae (Lythraceae) | Psidium guajava L. | Goiaba-branca | Leaves | In natura | Coagulant |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Nyctaginaceae | Mirabilis jalapa L. | Maravilha | Leaves | Decoction | Diabetes |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Phyllanthaceae | Phyllanthus niruri L. | Quebra-pedra-branca | Whole plant | Decoction | Diarrhea; Cough; Sore throat |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Piperaceae | Piper mollicomum Kunth | Perta-ruão | Leaves | Decoction | Diarrhea |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Piperaceae | Piper scutatum Yunck | Jaborandi | Root | Heated | Furuncle |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Plantaginaceae | Plantago australis Lam. | Trançagem/tanchagem | Leaves | Infusion | To prevent kidney stone |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Poaceae | Coix lacryma-jobi L. | Capiá | Leaves | Maceration | Coagulant; Joint dislocation |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Poaceae | Cymbopogon nardus (L.) Rendle | Citronela | Leaves | Maceration | Anesthetic |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Poaceae | Saccharum officinarum L. | Cana | Leaves | Maceration | Coagulant; Diarrhea; Sore throat; Urinary tract infection; To lose weight |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Polygonaceae | Polygonum sp. | Erva-fogo | Leaves | Decoction | Helps with childbirth |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Polygalaceae | Senega paniculata (L.) J.F.B.Pastore and J.R.Abbott | Gelol | Whole plant | Maceration | Insect repellent |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Rutaceae | Citrus reticulata Blanco | Laranja-mixirica | Leaves | Decoction | Antihypertensive |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Rutaceae | Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck | Laranja | Leaves | Maceration | Toothache; Headache |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Rutaceae | Citrus x limon (L.) Osbeck | Limão | Bark | Decoction | Burning |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Rutaceae | Zanthoxylum rhoifolium Lam. | Mamica-de-porca | Bark | Decoction | Flu |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Solanaceae | Solanum capsicoides All. | Arrebenta-cavalo | Fruit | Decoction | Flu |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Urticaceae | Boehmeria caudata Sw. | Urtiga-branca | Leaves | Decoction | Cough; Sore throat |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Urticaceae | Cecropia glaziovii Snethl. | Embaúba / Bauibeira | Leaves | Decoction | Clearance; Diabetes |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Urticaceae | Urera baccifera (L.) Gaudich. ex Wedd. | Urtiga-roxa | Leaves | In natura | Furuncle |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Verbenaceae | Lippia alba (Mill.) N.E.Br. ex P.Wilson | Melissa, ponta-livre | Leaves | Decoction | Sore throat; Furuncle |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Verbenaceae | Stachytarpheta cayennensis (Rich.) Vahl | Gervão | Leaves | Decoction; Syrup | Bronchitis |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Zingiberaceae | Curcuma sp. | Açafrão | Root | In natura | Anemia; Bone trauma; Prostate cancer; Scabies |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Zingiberaceae | Hedychium coronarium J.Koenig | Angélica | Leaves | In natura | Antihypertensive; Soothing |
| Yazbek et al. [28] | 2019 | Quilombo da Fazenda, São Paulo | Zingiberaceae | Renealmia petasites Gagnep. | Picova | Seeds | Infusion | Digestion |
3. Results
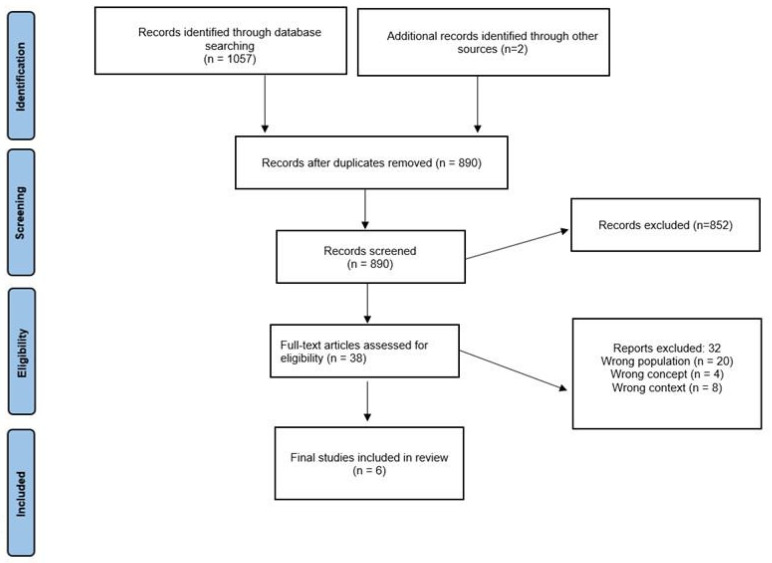
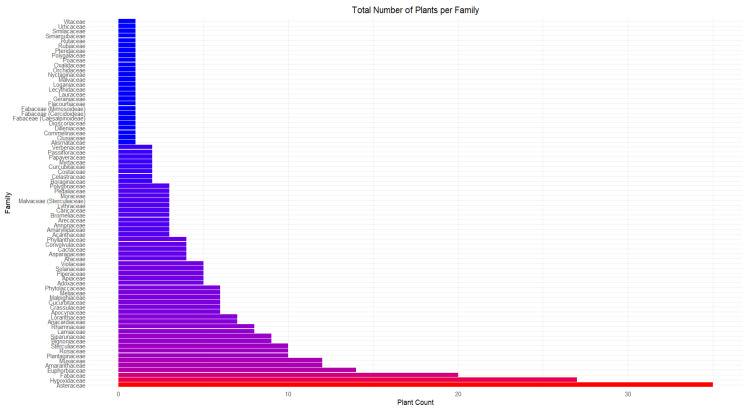
Using the search criteria, 888 articles were identified. After reviewing the titles and abstracts, 38 studies were selected for further evaluation. Of these, 30 were excluded following a full-text review for not meeting the inclusion criteria, leaving eight studies that were included in the final analysis. An additional two studies were included after a manual search. The details of the research process are illustrated in Flowchart 1 (Figure 1). Across all the selected studies, 297 plants from 80 different families were identified (Figure 2). These plants were used for a wide range of therapeutic purposes. Moreover, the plants were known by various common names, which differed depending on the region where each study was conducted. The most frequently mentioned methods for preparing the harvested plant parts were decoction, alcohol maceration, maceration, and infusion (Table 1).
Figure 1.
Flowchart detailing the research steps (Source: Authors).
Figure 2.
Distribution of plant families in ethnobotanical practices among Quilombola communities.
The most frequently cited families were Asteraceae Bercht. and J. Presl, with 42 citations [21,22,23,24,26,28], followed by Lamiaceae Martinov [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28], and Euphorbiaceae Juss [21,22,23,24,28].
The most commonly cited species in the selected articles were Lippia alba (Mill.) Britton and P. Wilson [21,22,23,28], Petiveria alliacea L. [22,23,26,27], Momordica charantia L. [21,22,28], Ocimum basilicum L. [21,22,23], Ruta graveolens L. [21,22,24,27], and Senna occidentalis (L.) Link [21,22,24,26].
The studies included in this research were conducted in communities located in the states of Paraíba, Bahia, Alagoas, Mato Grosso, São Paulo, and Pará. Of the 297 cited species, only 35 are listed in the Brazilian Phytotherapeutic Formulary, a platform that provides information on the correct methods of preparation, indication, and restrictions for the use of medicinal plants in pharmacies, authorized by the National Health Surveillance System [29]. This highlights the importance of research on the medicinal plants used by Quilombola communities, as it contributes to the broader adoption of integrative and complementary health practices.
Table 2 highlights the diverse therapeutic applications of medicinal plants used by Quilombola communities, categorized according to the CIAP-2 system. The most cited usage categories include the digestive system (213 mentions), with common conditions like abdominal pain and liver issues; the respiratory system (179 mentions), dominated by treatments for flu and cough; and general and non-specific conditions (157 mentions), such as malaria, fever, and inflammation. Other significant categories include the nervous system (84 mentions) and the circulatory system (66 mentions), reflecting the communities’ focus on managing headaches, mental health, and cardiovascular conditions. These data underscore the comprehensive knowledge and varied use of medicinal plants across different health-related issues in these communities.
Table 2.
Therapeutic Usage Categories, Based on CIAP-2.
| Usage Category (CIAP-2) | Most Cited Therapeutic Indications | Total |
|---|---|---|
| A: General and Non-Specific | Malaria (37); Fever (33); Inflammation (23); Cancer (12); Pain (7); | 157 |
| D: Digestive System | Abdominal pain (30); Liver (22); Toothache (20); Diarrhea (16); Stomach (15) | 213 |
| F: Eyes | Eye inflammation (3); Vision (3); Cataract (1); Conjunctivitis (1); Eye inflammation or pain (1) | 10 |
| H: Ears | Ear pain (5) | 5 |
| K: Circulatory System | Blood pressure (26); Hypertension (12); High cholesterol (5); Heart attack (5); Antihypertensive (4) | 66 |
| L: Musculoskeletal System | Back pain (5); Rheumatism (3); Body pain (2); Leg pain (2); Joint pain (2) | 32 |
| N: Nervous System | Headache (42); Mental alteration (10); Migraine (8); Improve learning / nervous breakdown (7); Stroke (6) | 84 |
| P: Psychological | Calming (6); Depression (5); Restlessness (3); Sedative (2); To calm (1) | 17 |
| R: Respiratory System | Flu (84); Cough (25); Phlegm (13); Sore throat (12); Throat (12) | 179 |
| S: Skin | Healing (8); Cuts (7); Bruises (5); Scabies (5); Wounds (4) | 44 |
| T: Endocrine, Metabolic, and Nutritional | Diabetes (26); Anemia (22); Detoxifying (5); Anti-inflammatory (1); Lack of appetite (1) | 55 |
| U: Urinary System | Kidney stones (7); Kidneys (7); Kidney pain (4); Prevent kidney stones (3); Urethra pain (2); Painful urination (1) | 27 |
| W: Pregnancy and Family Planning | Abortifacient (3); Increase contraction (2); Contraceptive/Abortifacient (1) | 6 |
| Y: Male Genital System | Prostate cancer (1); Prostate (1) | 2 |
| X: Female Genital System (including breast) | Women’s inflammation (13); Menstrual cramps (9); Uterus (7); Ovarian infection (5); Discharge (4) | 61 |
| Z: Social Issues | - | 0 |
According to the flora and fauna of Brazil, the species Amburana cearensis (Allem.) A.C. Smith, Handroanthus impetiginosus (Mart. ex DC.) Mattos, Cuscuta obtusiflora Kunth, Piper scutatum Yunck, and Handroanthus impetiginosus (Mart. ex DC.) Mattos are classified as “near threatened”. All other species are classified as “Least Concern” (LC) or have no estimated risk, according to the flora and fauna of Brazil.
4. Discussion
For Quilombola communities, the concept of health extends beyond the biological dimension to encompass social, psychological, and political factors. Health is closely tied to their way of life, their connection with nature, and their experiences within their territories. The relationship between the community and nature is therefore a crucial element for the well-being of these populations. This highlights the importance of caring for nature, maintaining direct contact with it, and understanding the interconnectedness between the health of the land and the health of the people [30].
When it comes to accessing health services, it is evident that the basic care available to the Quilombola population, which still heavily relies on the biomedical model focused on curing and medicalization, fails to fully address the specific needs of these communities. Fragmented health care remains prevalent [31]. The use of natural resources for treating illnesses and caring for ecosystems are longstanding traditions among Quilombola communities [23]. These traditions are passed down through generations, though each new generation may introduce new practices and uses. Within the broad ethnobotanical knowledge of these communities, medicinal plants play a key role in the treatment of various diseases, contributing to both environmental conservation and community health [32].
The transmission of knowledge about the use of medicinal plants helps to preserve and strengthen tradition, ensuring it remains alive and contributing to the cultivation of these plants [23]. In this study, it was observed that the same plant species were used for different purposes, depending on the Quilombola community. For instance, in the northeast of Brazil, Eryngium foetidum L. and Foeniculum vulgare Mill. are used to treat heart attacks and colds, respectively, whereas in the southeast, they are used for snakebites and dysentery. As knowledge is passed down through generations, interpretations of this information and external factors can influence how the therapeutic properties of plants are applied in each region [23].
Alternanthera brasiliana (L.) Kuntze was used for treating headaches, while Annona muricata L. was indicated for cancer and diabetes in different regions. The use of the same plant species for treating the same disease in various locations suggests their wide distribution across territories and their effectiveness in treating specific conditions [33]. Lippia alba is utilized across four different communities with varying therapeutic applications, highlighting the diversity of traditional knowledge, even when the same species is involved. Interestingly, Momordica charantia exhibits different applications in geographically distant communities, while its use converges when the communities are in closer proximity. This pattern underscores how both cultural and environmental factors, such as local ecosystems and cultural traditions, influence the choice and preparation of medicinal plants. These findings emphasize the dynamic nature of traditional knowledge, shaped by both shared heritage and local adaptations.
This study, while comprehensive, has some limitations, such as the lack of specific scientific data on the biological and pharmacological properties of many of the plants mentioned by Quilombola communities. Additionally, the variability in documentation and methodologies across the studies reviewed may have limited the comparability of the data. However, this study’s main strength lies in its ability to gather and organize a wide range of traditional knowledge, providing a solid foundation for future ethnopharmacological research and the integration of this knowledge into public health practices. For readers, the study offers the opportunity to appreciate traditional knowledge and understand the connections between culture, health, and biodiversity, while also highlighting the urgent need for further scientific research to deepen our understanding of the plants used by these communities and their potential therapeutic applications.
In our study, the most commonly used plant parts by the surveyed communities were the leaves. Leaves are preferred for therapeutic preparations because they are easier to collect and more readily available compared to flowers, fruits, and seeds, which may not be accessible year-round [34]. Additionally, traditional communities favor leaves because they believe these parts accumulate active components through photosynthetic pigments, such as alkaloids and tannins [35,36]. Decoction and infusion were the most frequently cited preparation methods in the studies, likely due to the simplicity of using water for preparation [36]. Preparing teas aids in the extraction of active compounds from the plant and helps preserve the solution for longer periods [37].
The study of plants that are endangered or near threatened is crucial for the preservation of native flora, especially in the context of climate change. As ecosystems face increasing pressure from rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and habitat destruction, understanding the status and conservation needs of these species becomes imperative. Protecting these plants not only helps maintain biodiversity but also ensures the survival of traditional knowledge and practices that rely on these species, particularly within communities that have historically depended on them for their health and well-being.
On the other hand, the use of plants based on traditional knowledge holds scientific significance, as it provides direction for research, saving both time and resources [37]. Traditional knowledge helps in selecting plants with potential applications in medicine production. In this context, the discovery of new active molecules often involves a combination of traditional and scientific knowledge [38]. Therefore, the use of medicinal plants by these communities may contribute valuable evidence for the development of pharmaceuticals [39].
5. Conclusions
This study highlights the importance of traditional knowledge in the use of medicinal plants among Quilombola communities in Brazil. The diversity of plant species used and the variations in therapeutic applications across different regions demonstrate the richness and adaptability of this knowledge over time. Additionally, the predominant use of leaves in therapeutic preparations and methods such as decoction and infusion reflect the practical wisdom of these communities in extracting active compounds. Preserving and recognizing this knowledge not only contributes to the health and well-being of these communities but also provides a valuable resource for scientific research and the development of integrative health practices. Consequently, this work serves as a foundation for future studies that seek to deepen the understanding and application of Quilombola ethnopharmacological knowledge, fostering cultural conservation and scientific innovation. To achieve this, future research should aim to integrate other disciplines, such as pharmacology, anthropology, environmental science, and history, in an interdisciplinary effort to better understand the evolution of plant use and uncover how traditional knowledge can contribute to sustainable development. Furthermore, it is crucial to ensure the active participation of Quilombola communities in future research, safeguarding their knowledge and ensuring that they directly benefit from any research based on their traditional practices.
Author Contributions
L.F.S.R. and P.H.S.-d.-S.—contribution to the conception. A.G.d.S., M.J.F.C., M.B.M. and P.H.S.-d.-S.—analyzed the data and interpreted the result. A.G.d.S., L.F.S.R. and R.d.S.A.—performed the literature review and the design of the work. A.d.A.R. and M.E.d.S.—helped with the taxonomy of the groups. I.L.D.C.—tables and figures. A.L.V.d.C., M.B.M. and L.R.A.d.L.—the interpretation of the data. M.J.F.C.—data interpretation and design. P.H.S.-d.-S.—supervised the data collection and reviewed the manuscript. M.E.d.S., M.B.M., L.R.A.d.L., M.J.F.C. and P.H.S.-d.-S.—wrote the manuscript’s draft and final version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
The authors are grateful for the support of the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES)—Financing Code 001, as well as the agency for promoting processes 88881.692858/2022-01 and 88887.798320/2022-00 of the PDPG-POSDOC (PDPG—Strategic Post-Doctoral Program). The authors also are grateful to Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco—FACEPE (IBPG-1888-4.00/22).
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
References
- 1.Valli M., Russo H.M., Bolzani V.S. The potential contribution of the natural products from Brazilian biodiversity to bioeconomy. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências. 2018;90:763–778. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765201820170653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.BRASIL Ministério do Meio Ambiente. [(accessed on 15 November 2023)]; Available online: https://www.gov.br/mma/pt-br.
- 3.Castro M.R., Figueiredo F.F. Saberes tradicionais, biodiversidade, práticas integrativas e complementares: O uso de plantas medicinais no SUS. Rev. Bras. Geo. Méd. Saúde. 2019;15:56–70. doi: 10.14393/Hygeia153146605. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ferreira L.R., Soares da Silva T.L., Silva M.F.O., Ferreira Batista R., Pina Montão D. Conhecimentos sobre plantas medicinais de comunidades tradicionais em Viseu/PA. Rev. Bras. Agroec. 2019;14:72–83. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Santos D.L., Moraes J.S., Araújo Z.T.S., Silva I.R. Vista do Saberes tradicionais sobre plantas medicinais na conservação da biodiversidade amazônica. Ciênc. Foco. 2019;12:86–96. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gadelha C.S., Pinto Junior V.M., Bezerra K.K.S., Pereira B.B.M., Maracajá P.B. Estudo bibliográfico sobre o uso das plantas medicinais e fitoterápicos no Brasil. Revista Verde. 2013;8:208–2012. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Silva G.B. Comunidades quilombolas: O reconhecimento e a autoindentificação frente ao processo de globalização e a massificação cultural. EDUFBA. 2013;5:1–175. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sousa C. Estratégias discursivas e retórica colonial na narrativa jornalística do conflito entre quilombolas e cla. Humanidade Inovação. 2021;7:198–211. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Silva G.M. Por outras epistemologias: Os quilombos como espaços de construção de conhecimentos. Interethnic@. 2022;23:100–127. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Santos G.B. Os processos de negação da memória e da identidade negra em “a máscara” de grada kilomba. REASE. 2020;6:475–484. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ribeiro R.F., Pirani D. As Áfricas Brasileiras: As políticas públicas em torno dos territórios quilombolas. Conecte-se! 2019;3:24–44. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pinto F.R.S. Populações quilombolas e sua luta pelo direito integral à saúde: O alcance do SUS na comunidade de remanescentes de quilombo Alto Alegre—Ceará. Cad. Humanidades Perspect. 2021;5:18–31. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pereira A.C.S., Cunha M.G.C. Medicina Popular E Saberes Tradicionais Sobre As Propriedades Medicinais Da Flora Cerradeira. Hygeia Rev. Bras. Geo. Méd. Saúde. 2015;11:126–137. doi: 10.14393/Hygeia1132443. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Oliveira A., Oliveira N., Resende U., Martins P. Ethnobotany and traditional medicine of the inhabitants of the Pantanal Negro sub-region and the raizeiros of Miranda and Aquidauna, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2011;71:283–289. doi: 10.1590/S1519-69842011000200007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Arshad M., Ahmad M., Ahmed E., Saboor A., Abbas A., Sadiq S. An ethnobiological study in Kala Chitta hills of Pothwar region, Pakistan: Multinomial logit specification. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2014;10:13. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-10-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Silva F.S., Ramos M.A., Hanazaki N., Albuquerque U.P. Dynamics of traditional knowledge of medicinal plants in a rural community in the Brazilian semi-arid region. Rev. Bras. Farmacog. 2011;21:382–391. doi: 10.1590/S0102-695X2011005000054. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tricco A.C., Lillie E., Zarin W., O’Brien K.K., Colquhoun H., Levac D., Moher D., Peters M.D.J., Horsley T., Weeks L., et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018;169:467–473. doi: 10.7326/M18-0850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Peters M.D.J., Godfrey C.M., Khalil H., McInerney P., Parker D., Soares C.B. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015;13:141–146. doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Aromataris E., Munn Z. JBI Manuals for Evidence Synthesis. Joana Briggs Institute; Adelaide, Australia: 2020. Introduction to Scoping reviews; pp. 2018–2021. [Google Scholar]
- 20.WONCA. International Classification Committee . International Classification of Primary Care (ICPC-2-R) Volume 2 Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barboza da Silva N.C., Delfino Regis A.C., Esquibel M.A., Espírito Santo Santos J., de Almeida M.Z. Medicinal plants use in Barra II quilombola community—Bahia, Brazil. Bol. Latinoam. Caribe Plantas Med. Aromat. 2012;11:435–453. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Beltreschi L., de Lima R.B., da Cruz D.D. Traditional botanical knowledge of medicinal plants in a “quilombola” community in the Atlantic Forest of northeastern Brazil. Environ. Develop. Sustain. 2019;21:1185–1203. doi: 10.1007/s10668-017-0079-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Magalhães P.K.A., Araujo E.N., Santos A.M., Vanderlei M.B., Souza C.C.L., Correia M.S., Fonseca S.A., Pavão J.M.J.S., Souza M.A., Costa J.G., et al. Ethnobotanical and ethnopharmacological study of medicinal plants used by a traditional community in Brazil’s northeastern. Braz. J. Biol. 2022;82:e237642. doi: 10.1590/1519-6984.237642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Oliveira D.R., Krettli A.U., Aguiar A.C.C., Leitão G.G., Vieira M.N., Martins K.S., Leitão S.G. Ethnopharmacological evaluation of medicinal plants used against malaria by quilombola communities from Oriximiná, Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015;173:424–434. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rodrigues E. Plants of restricted use indicated by three cultures in Brazil (Caboclo-river dweller, Indian and Quilombola) J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007;111:295–302. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.11.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rodrigues E., Carlini E.A. A comparison of plants utilized in ritual healing by two Brazilian cultures: Quilombolas and Kraho. J. Psych. Drugs. 2011;38:37–41. doi: 10.1080/02791072.2006.10399854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rodrigues E., Gianfratti B., Tabach R., Negri G., Mendes F.R. Preliminary investigation of the central nervous system effects of “Tira-capeta” (Removing the Devil), a cigarette used by some Quilombolas living in Pantanal Wetlands of Brazil. Phytother. Res. 2008;22:1248–1255. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yazbek P.B., Matta P., Passero L.F., Santos G.D., Braga S., Assunção L., Sauini T., Cassas F., Garcia R.J.F., Honda S., et al. Plants utilized as medicines by residents of Quilombo da Fazenda, Núcleo Picinguaba, Ubatuba, São Paulo, Brazil: A participatory survey. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019;244:112123. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária . Orientações Sobre o Uso de Fitoterápicos e Plantas Medicinais. Anvisa; Brasilia, Brasil: 2022. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Silva G.W., Dantas I.G., Fernandes S.L. Quilombola’s health: Health perceptions in a quilombo in the Agreste of Pernambuco/Brazil. Saúd. Socied. 2021;30:e190624. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cardoso C.S., Melo L.O., Freitas D.A. Health conditions in quilombola communities. J. Nurs. UFPE. 2018;12:10737–10745. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Modro A.F.H., Meneguelli A.Z., Ribeiro S.B., Maia E., Lima-Júnior G.A. Importância do conhecimento tradicional de plantas medicinais para a conservação da Amazônia. J. Chem. Infor. Model. 2019;53:1689–1699. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tugume P., Nyakoojo C. Ethno-pharmacological survey of herbal remedies used in the treatment of pediatric diseases in Buhunga parish, Rukungiri District, Uganda. BMC Comp. Altern. Med. 2019;19:353. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2763-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cajaiba R.L., Silva W.B., Sousa R.D.N., Sousa A.S. Levantamento etnobotânico de plantas medicinais comercializadas no município de Uruará, Pará, Brasil. Biotemas. 2016;29:115–131. doi: 10.5007/2175-7925.2016v29n1p115. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fortini P., Di Marzio P., Guarrera P.M., Iorizzi M. Ethnobotanical study on the medicinal plants in the Mainarde Mountains (central-southern Apennine, Italy) J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016;184:208–218. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mbuni Y.M., Wang S., Mwangi B.N., Mbari N.J., Musili P.M., Walter N.O., Hu G., Zhou Y., Wang Q. Medicinal plants and their traditional uses in local communities around cherangani hills, western Kenya. Plants. 2020;9:331. doi: 10.3390/plants9030331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mukherjee P.K., Harwansh R.K., Bahadur S., Banerjee S., Kar A., Chanda J., Biswas S., Ahmmed S.M., Katiyar C.K. Development of Ayurveda—Tradition to trend. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017;197:10–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Süntar I. Importance of ethnopharmacological studies in drug discovery: Role of medicinal plants. Phytochem. Rev. 2020;19:1199–1209. doi: 10.1007/s11101-019-09629-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Passero L.F.D., Brunelli E.S., Sauini T., Amorim Pavani T.F., Jesus J.Á., Rodrigues E. The potential of traditional knowledge to develop effective medicines for the treatment of leishmaniasis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021;12:690432. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.690432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.