Abstract
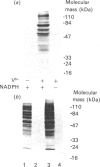
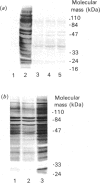
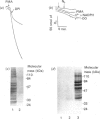
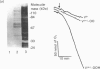
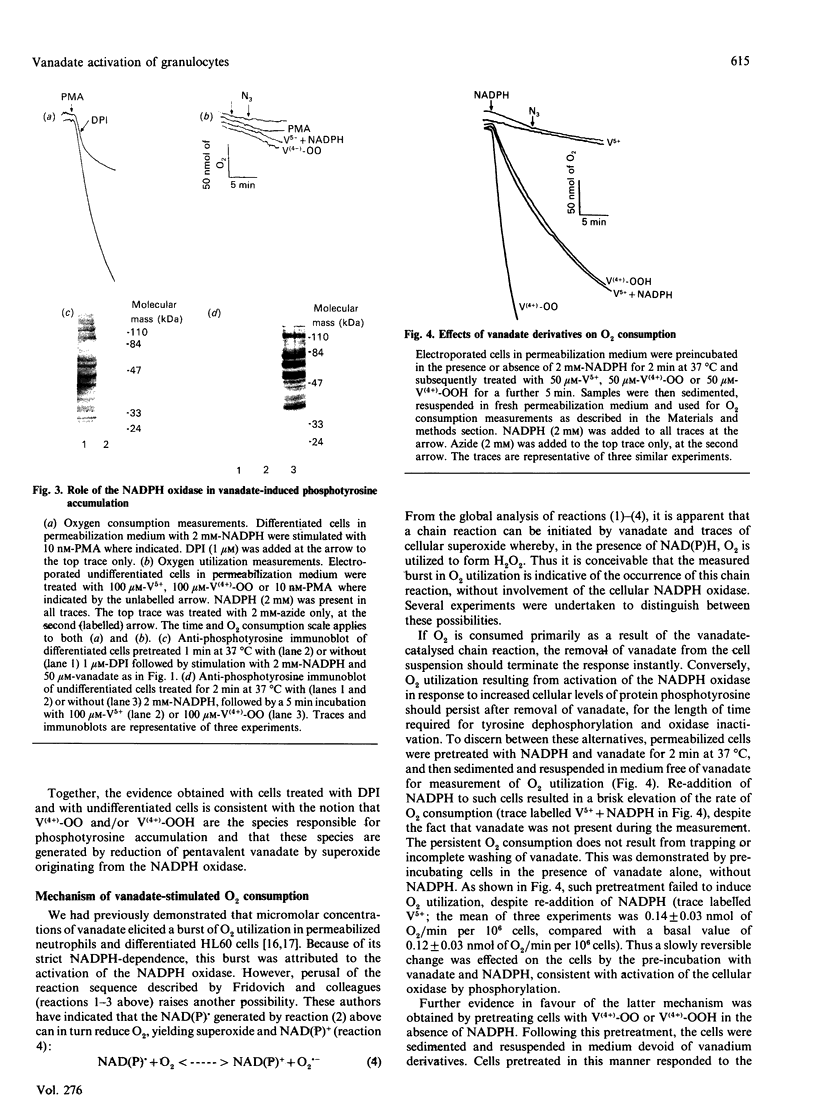
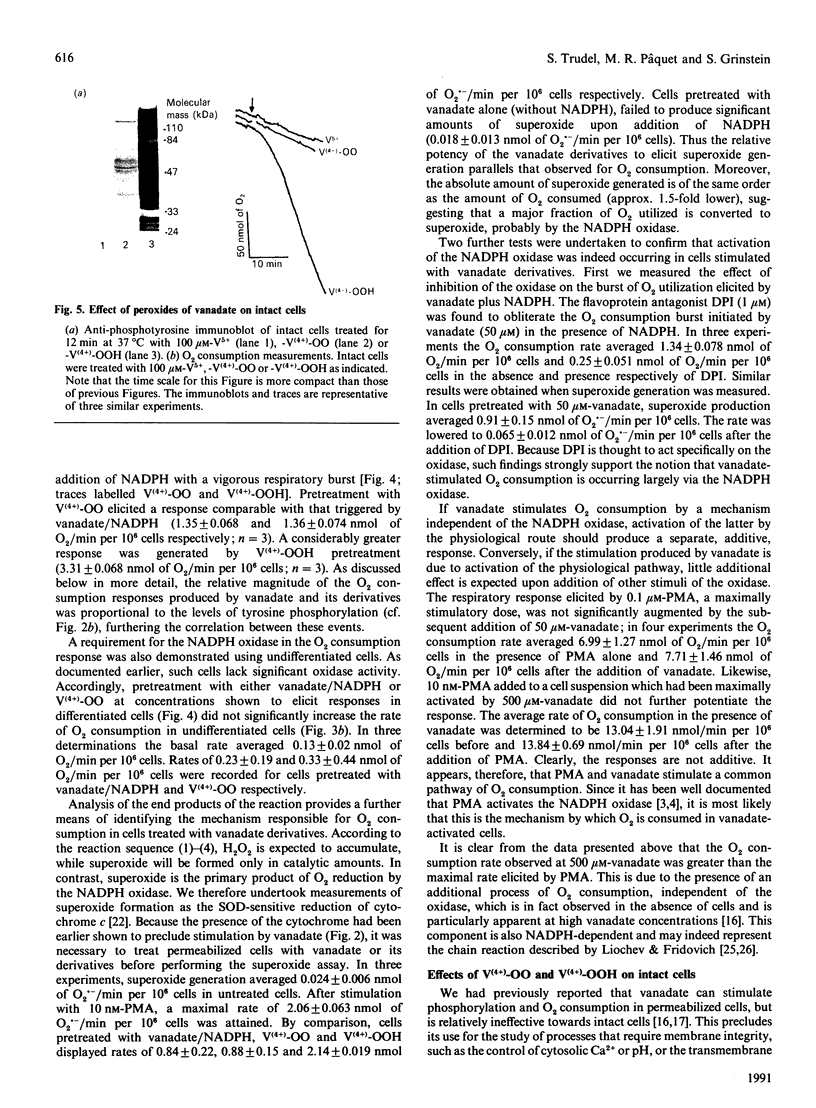
Vanadate induces phosphotyrosine accumulation and activates O2 consumption in permeabilized differentiated HL60 cells. NADPH, the substrate of the respiratory burst oxidase, was found to be necessary not only for the increased O2 consumption, but also for tyrosine phosphorylation. The effect of NADPH was not due to reduction of vanadate to vanadyl. Instead, NADPH was required for the synthesis of superoxide, which triggered the formation of peroxovanadyl [V(4+)-OO] and vanadyl hydroperoxide [V(4+)-OOH]. One or both of these species, rather than vanadate itself, appears to be responsible for phosphotyrosine accumulation and activation of the respiratory burst. Accordingly, the stimulatory effects of vanadate and NADPH were abrogated by superoxide dismutase. Moreover, phosphorylation was activated in the absence of NADPH by treatment with V(4+)-OO and/or V(4+)-OOH, generated by treatment of orthovanadate with KO2 or H2O2 respectively. The main source of the superoxide involved in the formation of V(4+)-OO and V(4+)-OOH is the NADPH oxidase. This was shown by the inhibitory effects of diphenylene iodonium and by the failure of undifferentiated cells, which lack oxidase activity, to undergo tyrosine phosphorylation when treated with vanadate and NADPH. By contrast, exogenously generated V(4+)-OO induced marked phosphorylation in the undifferentiated cells, demonstrating the presence of the appropriate tyrosine kinases and phosphatases. A good correlation was found to exist between induction of tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the respiratory burst, suggesting a causal relationship. Therefore an amplification cycle appears to exist in cells treated with vanadate, whereby trace amounts of superoxide initiate the formation of V(4+)-OO and/or V(4+)-OOH. These peroxides promote phosphotyrosine formation, most likely by inhibition of tyrosine phosphatases. Accumulation of critical tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins then initiates a respiratory burst, with abundant production of superoxide. The newly formed superoxide catalyses the formation of additional V(4+)-OO and/or V(4+)-OOH, thereby magnifying the response. Since vanadium derivatives are ubiquitous in animal tissues, V(4+)-OO and/or V(4+)-OOH could be formed in vivo by reduced O2 metabolites, becoming potential endogenous tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors. Because of their potency, peroxides of vanadate may be useful as probes for the study of protein phosphotyrosine turnover.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehner R. L., Boxer L. A., Allen J. M., Davis J. Autooxidation as a basis for altered function by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1977 Aug;50(2):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Dodson R. W., Kraft A. S. Human neutrophils contain distinct cytosolic and particulate tyrosine kinase activities: possible role in neutrophil activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 31;997(3):292–301. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkow R. L., Dodson R. W. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation during activation of human neutrophils. Blood. 1990 Jun 15;75(12):2445–2452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Chovaniec M. E. Superoxide production by digitonin-stimulated guinea pig granulocytes. The effects of N-ethyl maleimide, divalent cations; and glycolytic and mitochondrial inhibitors on the activation of the superoxide generating system. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):1088–1096. doi: 10.1172/JCI109008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Babior B. M. Effects of anaerobiosis and inhibitors on O2-production by human granulocytes. Blood. 1975 Jun;45(6):851–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. A., Mayer S. J., Jones O. T. The effect of the NADPH oxidase inhibitor diphenyleneiodonium on aerobic and anaerobic microbicidal activities of human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1988 May 1;251(3):887–891. doi: 10.1042/bj2510887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantus I. G., Kadota S., Deragon G., Foster B., Posner B. I. Pervanadate [peroxide(s) of vanadate] mimics insulin action in rat adipocytes via activation of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 31;28(22):8864–8871. doi: 10.1021/bi00448a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases. An adaptation to a paramagnetic gas. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7761–7764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I. Leukocyte chemotaxis. Fed Proc. 1983 Aug;42(11):2851–2862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Bonak V. A., Wang E., Casnellie J. E., Shiraishi T., Sha'afi R. I. Tyrosine phosphorylation in human neutrophil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1478–1485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90841-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Cambronero J., Yamazaki M., Metwally F., Molski T. F., Bonak V. A., Huang C. K., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and human neutrophils: role of guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W., Lu D. J., Mills G. B. Vanadate stimulates oxygen consumption and tyrosine phosphorylation in electropermeabilized human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):318–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W. Receptor-mediated activation of electropermeabilized neutrophils. Evidence for a Ca2+- and protein kinase C-independent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1779–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Hill M., Furuya W. Activation of electropermeabilized neutrophils by adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (ATP[S]). Role of phosphatases in stimulus-response coupling. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):755–759. doi: 10.1042/bj2610755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffetz D., Bushkin I., Dror R., Zick Y. The insulinomimetic agents H2O2 and vanadate stimulate protein tyrosine phosphorylation in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2896–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Laramee G. R., Casnellie J. E. Chemotactic factor induced tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane associated proteins in rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):794–801. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K. Protein kinases in neutrophils: a review. Membr Biochem. 1989;8(2):61–79. doi: 10.3109/09687688909082261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadota S., Fantus I. G., Deragon G., Guyda H. J., Hersh B., Posner B. I. Peroxide(s) of vanadium: a novel and potent insulin-mimetic agent which activates the insulin receptor kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):259–266. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liochev S. I., Fridovich I. Vanadate-stimulated oxidation of NAD(P)H in the presence of biological membranes and other sources of O2-. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 May 15;279(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90454-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Kustin K., Cantley L. C., Jr Glutathione reduces cytoplasmic vanadate. Mechanism and physiological implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 17;629(1):95–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90268-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmith P. E., Mills G. B., Grinstein S. Guanine nucleotides induce tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the respiratory burst in neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):893–897. doi: 10.1042/bj2570893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nechay B. R. Mechanisms of action of vanadium. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984;24:501–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.24.040184.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Chovaniec M. E., Greenberger J. S., Cohen H. J. Functional changes in human leukemic cell line HL-60. A model for myeloid differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):315–322. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F. The O2- -forming NADPH oxidase of the phagocytes: nature, mechanisms of activation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 4;853(1):65–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(86)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'afi R. I., Molski T. F. Activation of the neutrophil. Prog Allergy. 1988;42:1–64. doi: 10.1159/000318681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Brettler D. B., Kennington E. A., Blumberg P. M. Relation of human neutrophil phorbol ester receptor occupancy and NADPH-oxidase activity. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):333–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I. Protein kinase C and the activation of the human neutrophil NADPH-oxidase. Blood. 1987 Mar;69(3):711–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel S., Downey G. P., Grinstein S., Pâquet M. R. Activation of permeabilized HL60 cells by vanadate. Evidence for divergent signalling pathways. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):127–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2690127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]