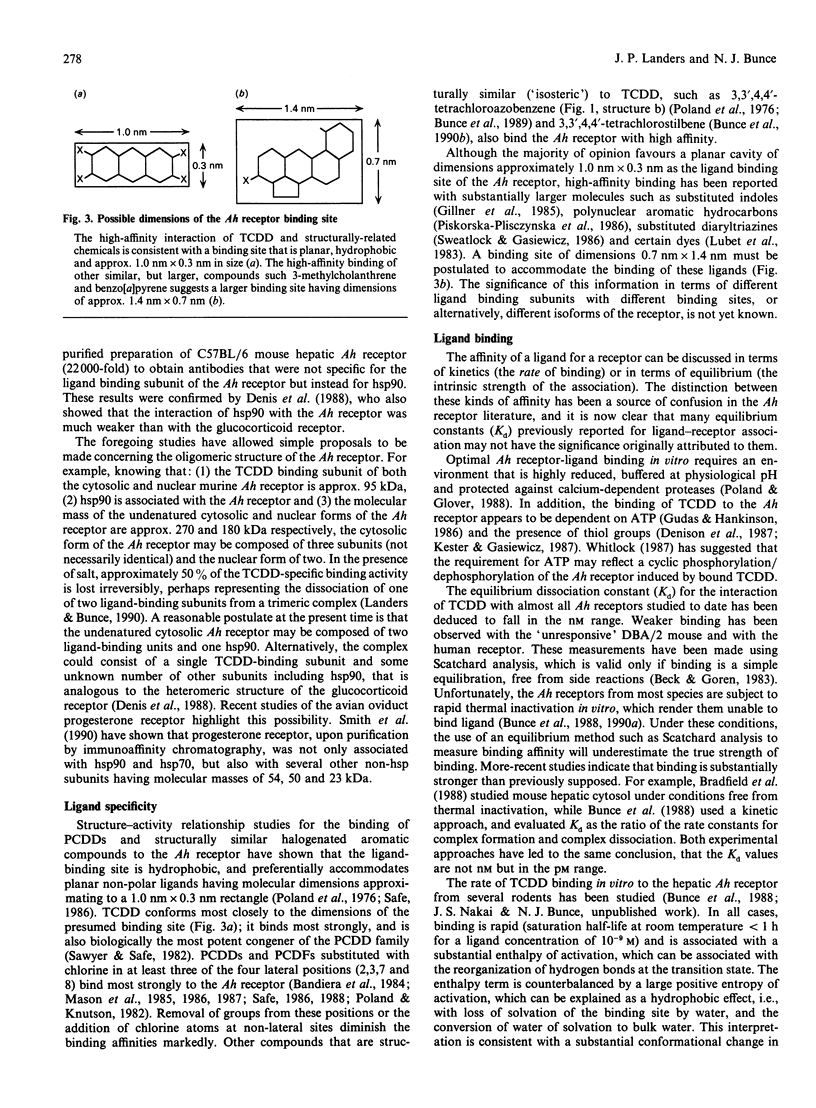
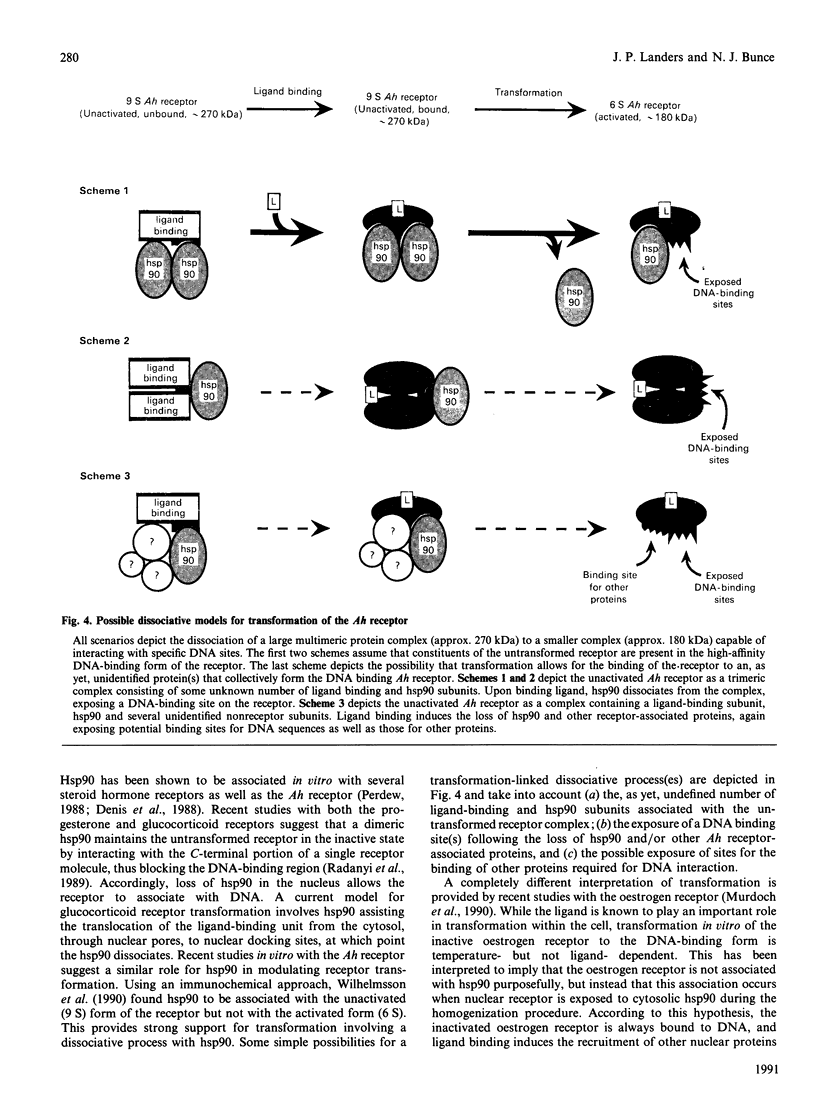
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antakly T., Eisen H. J. Immunocytochemical localization of glucocorticoid receptor in target cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):1984–1989. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-1984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astroff B., Zacharewski T., Safe S., Arlotto M. P., Parkinson A., Thomas P., Levin W. 6-Methyl-1,3,8-trichlorodibenzofuran as a 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin antagonist: inhibition of the induction of rat cytochrome P-450 isozymes and related monooxygenase activities. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;33(2):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baars A. J., Jansen M., Breimer D. D. The influence of phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on glutathione S-transferase activity of rat liver cytosol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(21):2487–2497. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly A., Atger M., Atger P., Cerbon M. A., Alizon M., Vu Haï M. T., Logeat F., Milgrom E. The rabbit uteroglobin gene. Structure and interaction with the progesterone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10384–10389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandiera S., Sawyer T. W., Campbell M. A., Fujita T., Safe S. Competitive binding to the cytosolic 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin receptor. Effects of structure on the affinities of substituted halogenated biphenyls--a QSAR analysis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 15;32(24):3803–3813. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandiera S., Sawyer T., Romkes M., Zmudzka B., Safe L., Mason G., Keys B., Safe S. Polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs): effects of structure on binding to the 2,3,7,8-TCDD cytosolic receptor protein, AHH induction and toxicity. Toxicology. 1984 Aug;32(2):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(84)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister R., Biegel L., Davis D., Astroff B., Safe S. 6-Methyl-1,3,8-trichlorodibenzofuran (MCDF) as a 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin antagonist in C57BL/6 mice. Toxicology. 1989 Feb;54(2):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(89)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty P., Neal R. A. Induction of DT-diaphorase by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (ICDD). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 12;68(1):197–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. S., Goren H. J. Simulation of association curves and 'Scatchard' plots of binding reactions where ligand and receptor are degraded or internalized. J Recept Res. 1983;3(5):561–577. doi: 10.3109/10799898309041948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegel L., Harris M., Davis D., Rosengren R., Safe L., Safe S. 2,2',4,4',5,5'-hexachlorobiphenyl as a 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin antagonist in C57BL/6J mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 1;97(3):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(89)90261-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum L. S., Weber H., Harris M. W., Lamb J. C., 4th, McKinney J. D. Toxic interaction of specific polychlorinated biphenyls and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: increased incidence of cleft palate in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;77(2):292–302. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(85)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombick D. W., Madhukar B. V., Brewster D. W., Matsumura F. TCDD (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin) causes increases in protein kinases particularly protein kinase C in the hepatic plasma membrane of the rat and the guinea pig. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):296–302. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd-Leinen P. A., Fournier D., Spelsberg T. C. Nonfunctioning progesterone receptors in the developed oviducts from estrogen-withdrawn immature chicks and in aged nonlaying hens. Endocrinology. 1982 Jul;111(1):30–36. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-1-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradfield C. A., Kende A. S., Poland A. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of Ah receptor-ligand binding: use of [125I]2-iodo-7,8-dibromodibenzo-p-dioxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;34(2):229–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster D. W., Madhukar B. V., Matsumura F. Influence of 2,3,7,8-TCDD on the protein composition of the plasma membrane of hepatic cells from the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 16;107(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91670-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster D. W., Matsumura F. TCDD (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin) reduces lipoprotein lipase activity in the adipose tissue of the guinea pig. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):810–817. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunce N. J., Landers J. P., Safe S. H. Kinetic models for association of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin with the Ah receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Nov 15;267(1):384–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byard J. L. The toxicological significance of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related compounds in human adipose tissue. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1987;22(4):381–403. doi: 10.1080/15287398709531081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt-Duke J. M. Tissue distribution of the receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the rat. Cancer Res. 1979 Aug;39(8):3172–3176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson-Jurica M. A., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Steroid receptor family: structure and functions. Endocr Rev. 1990 May;11(2):201–220. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Miksicek R., Schütz G., Arnemann J., Beato M. The hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumour virus mediates progesterone induction. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2237–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. L., Cone C. M., Morey-Holton E., Feldman D. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in cultured rat osteoblast-like cells. Glucocorticoid treatment increases receptor content. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4350–4355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T. F., Williams C. H. Teratogenic studies with 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D in the hamster. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1971 Nov-Dec;6(6):559–567. doi: 10.1007/BF01796866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colton T. Herbicide exposure and cancer. JAMA. 1986 Sep 5;256(9):1176–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. G., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Selective binding of chicken progesterone receptor A subunit to a DNA fragment containing ovalbumin gene sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 15;105(1):96–104. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. C., Dold K. M., Greenlee W. F. An in vitro model for studying the toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to human thymus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 30;89(2):256–268. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(87)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. C., Greenlee W. F. Characterization of a specific binding protein for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in human thymic epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 May;35(5):713–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. C., Hodgson E. Cytochrome P-450 induction by 3-methylcholanthrene and its antagonism by 2,2-dimethyl-5-t-butyl-1,3-benzodioxole. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 15;35(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90510-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney K. D., Gaylor D. W., Hogan M. D., Falk H. L., Bates R. R., Mitchell I. Teratogenic evaluation of 2,4,5-T. Science. 1970 May 15;168(3933):864–866. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3933.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney K. D., Moore J. A. Teratology studies with 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1971 Nov;20(3):396–403. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(71)90282-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Knoll B. J., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. A 5'-flanking sequence essential for progesterone regulation of an ovalbumin fusion gene. Nature. 1983 Oct 6;305(5934):551–554. doi: 10.1038/305551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Cuthill S., Wikström A. C., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A. Association of the dioxin receptor with the Mr 90,000 heat shock protein: a structural kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):801–807. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80566-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A. The molybdate-stabilized nonactivated glucocorticoid receptor contains a dimer of Mr 90,000 non-hormone-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11803–11806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Protein-DNA interactions at recognition sites for the dioxin-Ah receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16478–16482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr The DNA recognition site for the dioxin-Ah receptor complex. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17221–17224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Harper P. A., Okey A. B. Ah receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Codistribution of unoccupied receptor with cytosolic marker enzymes during fractionation of mouse liver, rat liver and cultured Hepa-1c1 cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Mar 3;155(2):223–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Vella L. M., Okey A. B. Ah receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rat liver: lack of sensitivity to alkaline phosphatase when compared with that of glucocorticoid receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Sep;273(2):458–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Vella L. M., Okey A. B. Structure and function of the Ah receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Species difference in molecular properties of the receptors from mouse and rat hepatic cytosols. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):3987–3995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Vella L. M., Okey A. B. Structure and function of the Ah receptor: sulfhydryl groups required for binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to cytosolic receptor from rodent livers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 1;252(2):388–395. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. S., Vella L. M. The hepatic Ah receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: species differences in subunit dissociation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Mar;277(2):382–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90594-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denomme M. A., Leece B., Li A., Towner R., Safe S. Elevation of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) polychlorinated biphenyls. Structure-activity relationships. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jan 15;35(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubik D., Dembinski T. C., Shiu R. P. Stimulation of c-myc oncogene expression associated with estrogen-induced proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 15;47(24 Pt 1):6517–6521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink C. J., Gasiewicz T. A., Whitlock J. P., Jr Protein-DNA interactions at a dioxin-responsive enhancer. Evidence that the transformed Ah receptor is heteromeric. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20708–20712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink C. J., Whitlock J. P., Jr 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible, Ah receptor-mediated bending of enhancer DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5718–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingerhut M. A., Halperin W. E., Marlow D. A., Piacitelli L. A., Honchar P. A., Sweeney M. H., Greife A. L., Dill P. A., Steenland K., Suruda A. J. Cancer mortality in workers exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 24;324(4):212–218. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101243240402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K. L., Wieben E. D., Woloschak G. E., Spelsberg T. C. Rapid regulation of c-myc protooncogene expression by progesterone in the avian oviduct. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1796–1800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick D. F., Firestone D., Ress J., Allen J. R. Studies of the chick edema disease. 10. Toxicity of chick edema factors in the chick, chick embryo, and monkey. Poult Sci. 1973 Jul;52(4):1637–1641. doi: 10.3382/ps.0521637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. Interactions among a subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors: the regulatory zipper model. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1293–1301. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa-Sehara A., Sogawa K., Nishi C., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Regulatory DNA elements localized remotely upstream from the drug-metabolizing cytochrome P-450c gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1465–1477. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo M. A., Hesse E. J., Macdonald G. J., Umbreit T. H. Interactive effects of estradiol and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on hepatic cytochrome P-450 and mouse uterus. Toxicol Lett. 1986 Jul-Aug;32(1-2):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(86)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasiewicz T. A., Bauman P. A. Heterogeneity of the rat hepatic Ah receptor and evidence for transformation in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2116–2120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasiewicz T. A., Neal R. A. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin tissue distribution, excretion, and effects on clinical chemical parameters in guinea pigs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90475-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasiewicz T. A., Neal R. A. The examination and quantitation of tissue cytosolic receptors for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin using hydroxylapatite. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 15;124(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasiewicz T. A., Rucci G. Cytosolic receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Evidence for a homologous nature among various mammalian species. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;26(1):90–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaub M. P., Bellard M., Scheuer I., Chambon P., Sassone-Corsi P. Activation of the ovalbumin gene by the estrogen receptor involves the fos-jun complex. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1267–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90422-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring U., Tomkins G. M. A new mechanism for steroid unresponsiveness: loss of nuclear binding activity of a steroid hormone receptor. Cell. 1974 Nov;3(3):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierthy J. F., Crane D. Reversible inhibition of in vitro epithelial cell proliferation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Jun 15;74(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillner M., Bergman J., Cambillau C., Fernström B., Gustafsson J. A. Interactions of indoles with specific binding sites for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rat liver. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;28(4):357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillner M., Haldosén L. A., Gustafsson S. A., Gustafsson J. A. Detection of specific binding of [1,6-3H]2,3,7,8-tetrachlordibenzo-p- dioxin ([3H]TCDD) in human leukocytes using electrofocusing in polyacrylamide gel. Toxicol Lett. 1989 Apr;47(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(89)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golas C. L., Prokipcak R. D., Okey A. B., Manchester D. K., Safe S., Fujita T. Competitive binding of 7-substituted-2,3-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxins with human placental ah receptor--a QSAR analysis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 15;40(4):737–741. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger A., Horton M., Katzmann J., Spelsberg T. C. Characterization of the chromatin acceptor sites for the avian oviduct progesterone receptor using monoclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5811–5816. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger A., Littlefield B. A., Katzmann J., Spelsberg T. C. Monoclonal antibodies recognizing the nuclear binding sites of the avian oviduct progesterone receptor. Endocrinology. 1986 Jun;118(6):2235–2241. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-6-2235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberger A., Spelsberg T. C. Partial purification and preparation of polyclonal antibodies against candidate chromatin acceptor proteins for the avian oviduct progesterone receptor. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2103–2109. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Autoregulation plus upstream positive and negative control regions associated with transcriptional activation of the mouse P1(450) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7269–7288. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Toft D., Shyamala G., Smith D., Notides A. Hormone receptors: studies on the interaction of estrogen with the uterus. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1968;24:45–80. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9827-9.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig J. B., De Matteis F. Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on drug metabolism and hepatic microsomes of rats and mice. Environ Health Perspect. 1973 Sep;5:211–219. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7305211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig J. B. Effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-1,4-dioxin on drug metabolism in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Dec 1;21(23):3196–3198. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruol D. J., Wolfe K. A. Transformed glucocorticoid receptors consist of multiple subspecies with differing capacities to bind DNA-cellulose. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2929–2936. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas J. M., Hankinson O. Reversible inactivation of the Ah receptor associated with changes in intracellular ATP levels. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Sep;128(3):449–456. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas J. M., Karenlampi S. O., Hankinson O. Intracellular location of the Ah receptor. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Sep;128(3):441–448. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J. A., Carlstedt-Duke J., Poellinger L., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Brönnegård M., Gillner M., Dong Y., Fuxe K., Cintra A. Biochemistry, molecular biology, and physiology of the glucocorticoid receptor. Endocr Rev. 1987 May;8(2):185–234. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-2-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haake J. M., Safe S., Mayura K., Phillips T. D. Aroclor 1254 as an antagonist of the teratogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Lett. 1987 Oct;38(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(87)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankinson O., Andersen R. D., Birren B. W., Sander F., Negishi M., Nebert D. W. Mutations affecting the regulation of transcription of the cytochrome P1-450 gene in the mouse Hepa-1 cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1790–1795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannah R. R., Lund J., Poellinger L., Gillner M., Gustafsson J. A. Characterization of the DNA-binding properties of the receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 15;156(2):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. C., Gorski J. Conformational and electrostatic properties of unoccupied and liganded estrogen receptors determined by aqueous two-phase partitioning. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6078–6085. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. C., Gorski J. Conformational transitions of the estrogen receptor monomer. Effects of estrogens, antiestrogen, and temperature. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13990–13996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapgood J., Cuthill S., Denis M., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A. Specific protein-DNA interactions at a xenobiotic-responsive element: copurification of dioxin receptor and DNA-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. A., Golas C. L., Okey A. B. Characterization of the Ah receptor and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and benz(a)anthracene in the human A431 squamous cell carcinoma line. Cancer Res. 1988 May 1;48(9):2388–2395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry E. C., Rucci G., Gasiewicz T. A. Characterization of multiple forms of the Ah receptor: comparison of species and tissues. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6430–6440. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst M., Feldman D. Glucocorticoid regulation of 1,25(OH)2vitamin D3 receptors: divergent effects on mouse and rat intestine. Endocrinology. 1982 Oct;111(4):1400–1402. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-4-1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoar S. K., Blair A., Holmes F. F., Boysen C. D., Robel R. J., Hoover R., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Agricultural herbicide use and risk of lymphoma and soft-tissue sarcoma. JAMA. 1986 Sep 5;256(9):1141–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R. E., Stehr-Green P. A., Webb K. B., Evans R. G., Knutsen A. P., Schramm W. F., Staake J. L., Gibson B. B., Steinberg K. K. Health effects of long-term exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. JAMA. 1986 Apr 18;255(15):2031–2038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong F. D., Huang H. J., To H., Young L. J., Oro A., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Structure of the human retinoblastoma gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5502–5506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff J. E., Moore J. A., Saracci R., Tomatis L. Long-term hazards of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Environ Health Perspect. 1980 Jun;36:221–240. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8036221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Estolano M. G., Galeazzi D. R., Whitlock J. P., Jr Superinduction of cytochrome P1-450 gene transcription by inhibition of protein synthesis in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5648–5653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Whitlock J. P., Jr Regulation of cytochrome P1-450 gene transcription by 2,3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5400–5402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issemann I., Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):645–650. doi: 10.1038/347645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakoby W. B., Ziegler D. M. The enzymes of detoxication. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20715–20718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Suzuki T., Kawashima T., Stumpf W. E., Jungblut P. W., DeSombre E. R. A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):632–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. B., Galeazzi D. R., Fisher J. M., Whitlock J. P., Jr Control of cytochrome P1-450 gene expression by dioxin. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1499–1502. doi: 10.1126/science.3856321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan V. C., Tate A. C., Lyman S. D., Gosden B., Wolf M. F., Bain R. R., Welshons W. V. Rat uterine growth and induction of progesterone receptor without estrogen receptor translocation. Endocrinology. 1985 May;116(5):1845–1857. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-5-1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawajiri K., Watanabe J., Gotoh O., Tagashira Y., Sogawa K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Structure and drug inducibility of the human cytochrome P-450c gene. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelling C. K., Menahan L. A., Peterson R. E. Hepatic indices of thyroid status in rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 15;36(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90702-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kester J. E., Gasiewicz T. A. Characterization of the in vitro stability of the rat hepatic receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 1;252(2):606–625. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi M. Autopsy of patients with yusho. Am J Ind Med. 1984;5(1-2):19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. J., Greene G. L. Monoclonal antibodies localize oestrogen receptor in the nuclei of target cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):745–747. doi: 10.1038/307745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klyzsejko-Stefanowicz L., Chiu J. F., Tsai Y. H., Hnilica L. S. Acceptor proteins in rat androgenic tissue chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1954–1958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C., Poland A. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: examination of biochemical effects involved in the proliferation and differentiation of XB cells. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Oct;121(1):143–151. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C., Poland A. Response of murine epidermis to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: interaction of the ah and hr loci. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost S. L., Smith D. F., Sullivan W. P., Welch W. J., Toft D. O. Binding of heat shock proteins to the avian progesterone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3829–3838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurl R. N., Lund J., Poellinger L., Gustafsson J. A. Differential effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on nuclear RNA polymerase activity in the rat liver and thymus. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 1;31(15):2459–2462. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. P., Birse L. M., Nakai J. S., Winhall M. J., Bunce N. J. Chemically induced hepatic cytosol from the Sprague-Dawley rat: evidence for specific binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to components kinetically distinct from the Ah receptor. Toxicol Lett. 1990 May;51(3):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(90)90072-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. P., Bunce N. J. Hepatic Ah receptor from the Wistar rat: role of solvation in receptor structure and inactivation. J Biochem Toxicol. 1990 Spring;5(1):33–39. doi: 10.1002/jbt.2570050106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. P., Piskorska-Pliszczynska J., Zacharewski T., Bunce N. J., Safe S. Photoaffinity labeling of the nuclear Ah receptor from mouse Hepa 1c1c7 cells using 2,3,7,8-[3H]tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18463–18471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Shew J. Y., Hong F. D., Sery T. W., Donoso L. A., Young L. J., Bookstein R., Lee E. Y. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein associated with DNA binding activity. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):642–645. doi: 10.1038/329642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legraverend C., Hannah R. R., Eisen H. J., Owens I. S., Nebert D. W., Hankinson O. Regulatory gene product of the Ah locus. Characterization of receptor mutants among mouse hepatoma clones. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6402–6407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung H. W., Poland A., Paustenbach D. J., Murray F. J., Andersen M. E. Pharmacokinetics of [125I]-2-iodo-3,7,8-trichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in mice: analysis with a physiological modeling approach. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990 May;103(3):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(90)90314-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubet R. A., Connolly G., Kouri R. E., Nebert D. W., Bigelow S. W. Biological effects of the Sudan dyes. Role of the Ah cytosolic receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Oct 15;32(20):3053–3058. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhukar B. V., Brewster D. W., Matsumura F. Effects of in vivo-administered 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on receptor binding of epidermal growth factor in the hepatic plasma membrane of rat, guinea pig, mouse, and hamster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7407–7411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manchester D. K., Gordon S. K., Golas C. L., Roberts E. A., Okey A. B. Ah receptor in human placenta: stabilization by molybdate and characterization of binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, 3-methylcholanthrene, and benzo(a)pyrene. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4861–4868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks T. A., Kimmel G. L., Staples R. E. Influence of symmetrical polychlorinated biphenyl isomers on embryo and fetal development in mice. I. Teratogenicity of 3, 3', 4, 4', 5, 5',-hexachlorobiphenyl. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;61(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason G., Farrell K., Keys B., Piskorska-Pliszczynska J., Safe L., Safe S. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins: quantitative in vitro and in vivo structure-activity relationships. Toxicology. 1986 Oct;41(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(86)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason G., Sawyer T., Keys B., Bandiera S., Romkes M., Piskorska-Pliszczynska J., Zmudzka B., Safe S. Polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs): correlation between in vivo and in vitro structure-activity relationships. Toxicology. 1985 Oct;37(1-2):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(85)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason G., Zacharewski T., Denomme M. A., Safe L., Safe S. Polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and related compounds: quantitative in vivo and in vitro structure-activity relationships. Toxicology. 1987 Jun;44(3):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(87)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. E., Okey A. B. Cytosolic and nuclear binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to the Ah receptor in extra-hepatic tissues of rats and mice. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar;123(1):209–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastroiacovo P., Spagnolo A., Marni E., Meazza L., Bertollini R., Segni G., Borgna-Pignatti C. Birth defects in the Seveso area after TCDD contamination. JAMA. 1988 Mar 18;259(11):1668–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G. Chloracne from the accidental production of tetrachlorodibenzodioxin. Br J Ind Med. 1973 Jul;30(3):276–283. doi: 10.1136/oem.30.3.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Duddy S. K., Håkansson H., Orrenius S. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin kills immature thymocytes by Ca2+-mediated endonuclease activation. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):256–259. doi: 10.1126/science.3262923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A., Reddy V. R., Piper W. N. Depression of rat testicular 17-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase after administration of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 1;36(5):727–731. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90726-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Bodwell J. E., Munck A. Glucocorticoid receptors lacking hormone-binding activity are bound in nuclei of ATP-depleted cells. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):478–480. doi: 10.1038/324478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Israel D., Whitlock J. P., Jr Biochemical and genetic analysis of variant mouse hepatoma cells defective in the induction of benzo(a)pyrene-metabolizing enzyme activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3523–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. A., Ostrowski M. C., Hager G. L., Simons S. S., Jr Covalent and noncovalent receptor-glucocorticoid complexes preferentially bind to the same regions of the long terminal repeat of murine mammary tumor virus proviral DNA. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6883–6889. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milnes M. H. Formation of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin by thermal decomposition of sodium 2,4,5,-trichlorophenate. Nature. 1971 Aug 6;232(5310):395–396. doi: 10.1038/232395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarelli P., Marocchi A., Brambilla P., Gerthoux P., Young D. S., Mantel N. Clinical laboratory manifestations of exposure to dioxin in children. A six-year study of the effects of an environmental disaster near Seveso, Italy. JAMA. 1986 Nov 21;256(19):2687–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch F. E., Meier D. A., Furlow J. D., Grunwald K. A., Gorski J. Estrogen receptor binding to a DNA response element in vitro is not dependent upon estradiol. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8377–8385. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito K., Isohashi F., Tsukanaka K., Horiuchi M., Okamoto K., Matsunaga T., Sakamoto Y. Effects of D- and L-thyroxine on the glucocorticoid binding capacity of adult rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 14;129(2):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal R. A., Beatty P. W., Gasiewicz T. A. Studies of the mechanisms of toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:204–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Goujon F. M., Gielen J. E. Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction by polycyclic hydrocarbons: simple autosomal dominant trait in the mouse. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 29;236(65):107–110. doi: 10.1038/newbio236107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Jensen N. M., Perry J. W., Oka T. Association between ornithine decarboxylase induction and the Ah locus in mice treated with polycyclic aromatic compounds. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6836–6842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B., Bondy G. P., Mason M. E., Kahl G. F., Eisen H. J., Guenthner T. M., Nebert D. W. Regulatory gene product of the Ah locus. Characterization of the cytosolic inducer-receptor complex and evidence for its nuclear translocation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11636–11648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B., Bondy G. P., Mason M. E., Nebert D. W., Forster-Gibson C. J., Muncan J., Dufresne M. J. Temperature-dependent cytosol-to-nucleus translocation of the Ah receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in continuous cell culture lines. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11415–11422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B., Dubé A. W., Vella L. M. Binding of benzo(a)pyrene and dibenz(a,h)anthracene to the Ah receptor in mouse and rat hepatic cytosols. Cancer Res. 1984 Apr;44(4):1426–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B. Enzyme induction in the cytochrome P-450 system. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(2):241–298. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B., Vella L. M. Elevated binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and 3-methylcholanthrene to the Ah receptor in hepatic cytosols from phenobarbital-treated rats and mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Feb 15;33(4):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okey A. B., Vella L. M., Harper P. A. Detection and characterization of a low affinity form of cytosolic Ah receptor in livers of mice nonresponsive to induction of cytochrome P1-450 by 3-methylcholanthrene. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;35(6):823–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okret S., Poellinger L., Dong Y., Gustafsson J. A. Down-regulation of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA by glucocorticoid hormones and recognition by the receptor of a specific binding sequence within a receptor cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5899–5903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. R., Gasiewicz T. A., Neal R. A. Tissue distribution, excretion, and metabolism of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in the Golden Syrian hamster. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;56(1):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortí E., Mendel D. B., Smith L. I., Munck A. Agonist-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear dephosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptors in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9728–9731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens I. S. Genetic regulation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase induction by polycyclic aromatic compounds in mice. Co-segregation with aryl hydrocarbon (benzo(alpha)pyrene) hydroxylase induction. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2827–2833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdew G. H. Association of the Ah receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13802–13805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdew G. H., Hollenback C. E. Analysis of photoaffinity-labeled aryl hydrocarbon receptor heterogeneity by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 3;29(26):6210–6214. doi: 10.1021/bi00478a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdew G. H., Poland A. Purification of the Ah receptor from C57BL/6J mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9848–9852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. E., Madhukar B. V., Yang K. H., Matsumura F. Depression of adenosine triphosphatase activities in isolated liver surface membranes of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-treated rats: correlation with effects on ouabain biliary excretion and bile flow. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Aug;210(2):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piskorska-Pliszczynska J., Keys B., Safe S., Newman M. S. The cytosolic receptor binding affinities and AHH induction potencies of 29 polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol Lett. 1986 Nov;34(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(86)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poellinger L., Lund J., Gillner M., Hansson L. A., Gustafsson J. A. Physicochemical characterization of specific and nonspecific polyaromatic hydrocarbon binders in rat and mouse liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13535–13542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A. P., Glover E., Robinson J. R., Nebert D. W. Genetic expression of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity. Induction of monooxygenase activities and cytochrome P1-450 formation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in mice genetically "nonresponsive" to other aromatic hydrocarbons. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5599–5606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: a potent inducer of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase. Science. 1973 Feb 2;179(4072):476–477. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4072.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. An estimate of the maximum in vivo covalent binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to rat liver protein, ribosomal RNA, and DNA. Cancer Res. 1979 Sep;39(9):3341–3344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. Ca2+-dependent proteolysis of the Ah receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Feb 15;261(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. Characterization and strain distribution pattern of the murine Ah receptor specified by the Ahd and Ahb-3 alleles. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;38(3):306–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. Chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins: potent inducers of delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. II. A study of the structure-activity relationship. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Nov;9(6):736–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E., Ebetino F. H., Kende A. S. Photoaffinity labeling of the Ah receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6352–6365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E., Kende A. S. Stereospecific, high affinity binding of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by hepatic cytosol. Evidence that the binding species is receptor for induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4936–4946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E. Variation in the molecular mass of the Ah receptor among vertebrate species and strains of rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1439–1449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90811-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Greenlee W. F., Kende A. S. Studies on the mechanism of action of the chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and related compounds. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979 May 31;320:214–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb56603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Knutson J. C. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons: examination of the mechanism of toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:517–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. L., Moore R. W., Inhorn S. L., Hagen T. C., Peterson R. E. Thyroid status and thermogenesis in rats treated with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 15;84(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt R. M., Dencker L., Diewert V. M. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced cleft palate in the mouse: evidence for alterations in palatal shelf fusion. Teratog Carcinog Mutagen. 1984;4(5):427–436. doi: 10.1002/tcm.1770040505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. Interaction of hsp90 with steroid receptors: organizing some diverse observations and presenting the newest concepts. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Nov 12;74(1):C69–C76. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90198-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokipcak R. D., Denison M. S., Okey A. B. Nuclear Ah receptor from mouse hepatoma cells: effect of partial proteolysis on relative molecular mass and DNA-binding properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Dec;283(2):476–483. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90670-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokipcak R. D., Faber L. E., Okey A. B. Characterization of the Ah receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: use of chemical crosslinking and a monoclonal antibody directed against a 59-kDa protein associated with steroid receptors. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 1;274(2):648–658. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokipcak R. D., Okey A. B. Physicochemical characterization of the nuclear form of Ah receptor from mouse hepatoma cells exposed in culture to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Dec;267(2):811–828. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puhvel S. M., Ertl D. C., Lynberg C. A. Increased epidermal transglutaminase activity following 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: in vivo and in vitro studies with mouse skin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 30;73(1):42–47. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radanyi C., Renoir J. M., Sabbah M., Baulieu E. E. Chick heat-shock protein of Mr = 90,000, free or released from progesterone receptor, is in a dimeric form. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2568–2573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind A. B., Gannon M., Gross S. S. Arachidonic acid metabolism by dioxin-induced cytochrome P-450: a new hypothesis on the role of P-450 in dioxin toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1180–1188. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91573-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts L. Dioxin risks revisited. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):624–626. doi: 10.1126/science.1846976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romkes M., Safe S. Comparative activities of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and progesterone as antiestrogens in the female rat uterus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 15;92(3):368–380. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(88)90177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rories C., Lau C. K., Fink K., Spelsberg T. C. Rapid inhibition of c-myc gene expression by a glucocorticoid in the avian oviduct. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jun;3(6):991–1001. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-6-991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rories C., Spelsberg T. C. Ovarian steroid action on gene expression: mechanisms and models. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:653–681. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. Q., Ramsey J. C., Wentzler T. H., Hummel R. A., Gehring P. J. The fate of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin following single and repeated oral doses to the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 May;36(2):209–226. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P., Jr, Ruh T. S. Binding of the estradiol-receptor complex to reconstituted nucleoacidic protein from calf uterus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 May 15;782(1):18–25. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safe S. H. Comparative toxicology and mechanism of action of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1986;26:371–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.26.040186.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer T., Safe S. PCB isomers and congeners: induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase and ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase enzyme activities in rat hepatoma cells. Toxicol Lett. 1982 Sep;13(1-2):87–93. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(82)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Beato M. Contacts between hormone receptor and DNA double helix within a glucocorticoid regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3029–3033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. J., Diehl E. E., Davidson C. J., Puk M. J., Webb M. L., Litwack G. Effects of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A, S protein, and S peptide on activation of purified rat hepatic glucocorticoid-receptor complexes. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):5955–5961. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. J., Miller-Diener A., Webb M. L., Litwack G. Thermal activation of the purified rat hepatic glucocorticoid receptor. Evidence for a two-step mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16255–16262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh S., Yonemoto W., Brugge J., Bauer V. J., Riehl R. M., Sullivan W. P., Toft D. O. A 90,000-dalton binding protein common to both steroid receptors and the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60v-src. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14292–14296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Gorski J. An interaction between the 5' flanking distal and proximal regulatory domains of the rat prolactin gene is required for transcriptional activation by estrogens. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1226–1234. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. P., Paustenbach D. J., Murray F. J. A critical evaluation of the use of mutagenesis, carcinogenesis, and tumor promotion data in a cancer risk assessment of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;7(1):57–88. doi: 10.1016/0273-2300(87)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala G. Estradiol receptors in mouse mammary tumors: absence of the transfer of bound estradiol from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1623–1630. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90795-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbergeld E. K., Gasiewicz T. A. Dioxins and the Ah receptor. Am J Ind Med. 1989;16(4):455–474. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700160411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Sistare F. D., Chakraborti P. K. Steroid binding activity is retained in a 16-kDa fragment of the steroid binding domain of rat glucocorticoid receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14493–14497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloop T. C., Lucier G. W. Dose-dependent elevation of Ah receptor binding by TCDD in rat liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987 May;88(3):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(87)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. C., Elsasser M. S., Harmon J. M. Analysis of glucocorticoid receptor activation by high resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of affinity-labeled receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13285–13292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Faber L. E., Toft D. O. Purification of unactivated progesterone receptor and identification of novel receptor-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3996–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Fujisawa-Sehara A., Yamane M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Location of regulatory elements responsible for drug induction in the rat cytochrome P-450c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8044–8048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparschu G. L., Dunn F. L., Rowe V. K. Study of the teratogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the rat. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1971 Jun;9(3):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0015-6264(71)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C., Littlefield B. A., Seelke R., Dani G. M., Toyoda H., Boyd-Leinen P., Thrall C., Kon O. L. Role of specific chromosomal proteins and DNA sequences in the nuclear binding sites for steroid receptors. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1983;39:463–517. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571139-5.50016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C. Nuclear binding of progesterone in chick oviduct. Multiple binding sites in vivo and transcriptional response. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj1560391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl B. U., Rozman K. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-induced appetite suppression in the Sprague-Dawley rat is not a direct effect on feed intake regulation in the brain. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;106(1):158–162. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(90)90116-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Klock G., Schütz G. A DNA sequence of 15 base pairs is sufficient to mediate both glucocorticoid and progesterone induction of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7871–7875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suskind R. R., Hertzberg V. S. Human health effects of 2,4,5-T and its toxic contaminants. JAMA. 1984 May 11;251(18):2372–2380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. K., Maeda Y., Nakao K., Wakim N. G., Duhring J. L., Faber L. E. A 59-kilodalton protein associated with progestin, estrogen, androgen, and glucocorticoid receptors. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5269–5275. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Kouri R. E., Hutton J. J. The genetics of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction in mice: a single gene difference between C57BL-6J and DBA-2J. Biochem Genet. 1972 Apr;6(2):157–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00486400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunberg T., Ahlborg U. G., Wahlström B. Comparison between the effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and six other compounds on the vitamin A storage, the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase and the aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in the rat liver. Arch Toxicol. 1984 Mar;55(1):16–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00316580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbreit T. H., Gallo M. A. Physiological implications of estrogen receptor modulation by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Lett. 1988 Jul;42(1):5–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(88)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waithe W. I., Michaud M., Harper P. A., Okey A. B., Anderson A. The Ah receptor, cytochrome P450IA1 mRNA induction, and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in a human lymphoblastoid cell line. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 1;41(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90014-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Adler S., Nelson C., Greene G. L., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. A single domain of the estrogen receptor confers deoxyribonucleic acid binding and transcriptional activation of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jan;2(1):14–21. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-1-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Denison M. S., Fisher J. M., Shen E. S. Induction of hepatic cytochrome P450 gene expression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Apr;6(2):169–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Galeazzi D. R. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin receptors in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. Nuclear location and strength of nuclear binding. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):980–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr Genetic and molecular aspects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:251–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr The regulation of gene expression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Jun;39(2):147–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsson A., Cuthill S., Denis M., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Poellinger L. The specific DNA binding activity of the dioxin receptor is modulated by the 90 kd heat shock protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):69–76. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08081.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]