Abstract
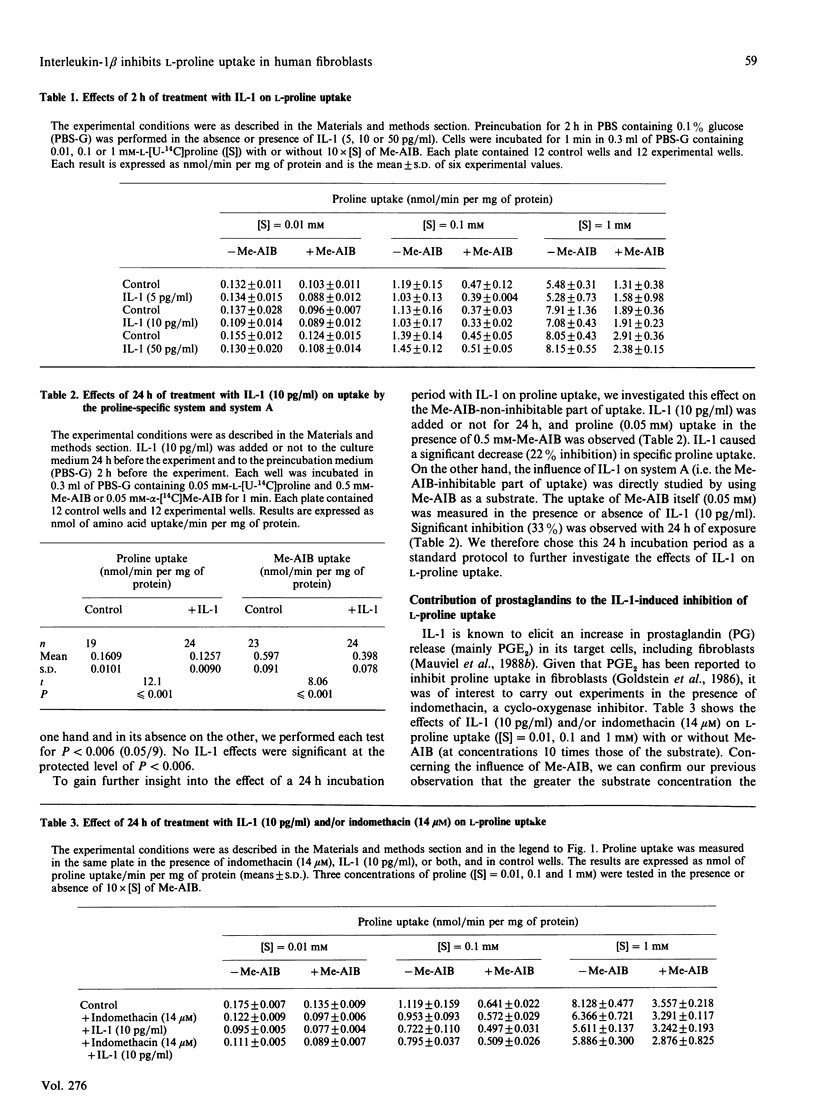
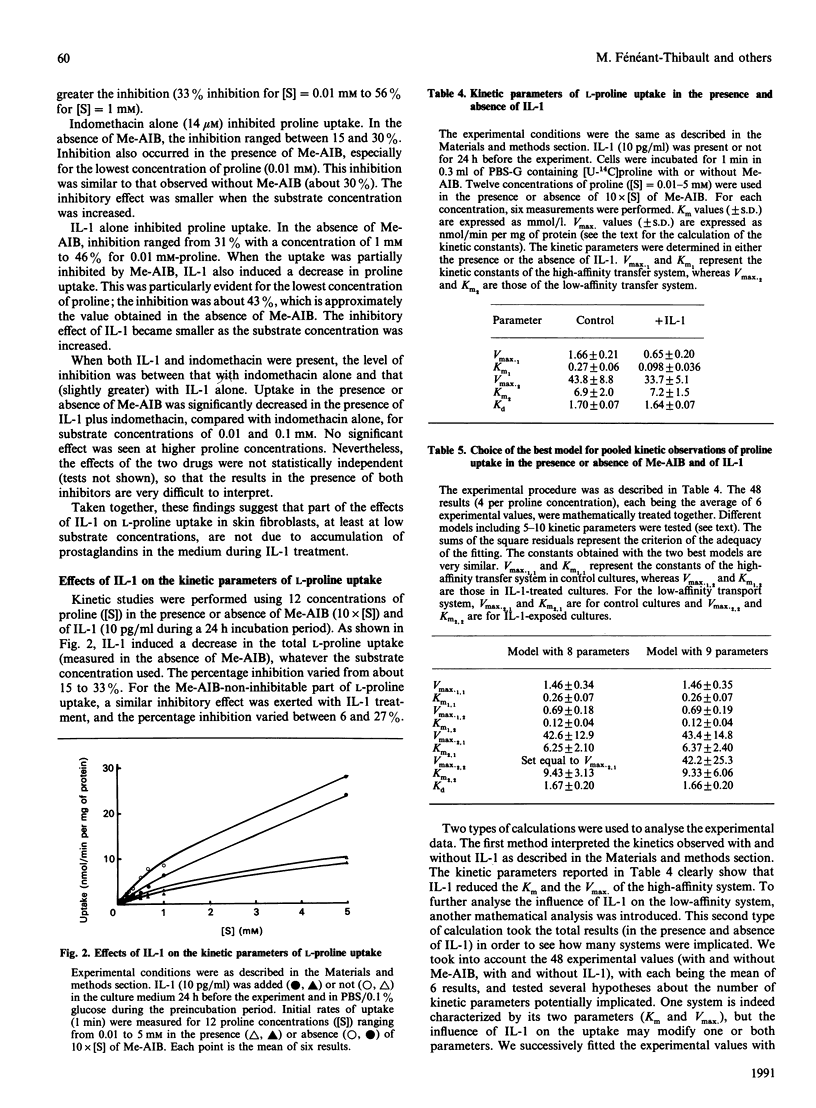
The effects of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1) on L-proline uptake in human skin fibroblasts were investigated. Exposure of the fibroblasts to IL-1 (5, 10 or 50 pg/ml) for 2 h did not change L-proline uptake. In contrast, inhibition was observed after 6 h of IL-1 treatment, and only 60% of the control uptake remained after incubation for 24 h with 10 pg of IL-1/ml. IL-1 depressed the activity of both transfer systems; the low-affinity system inhibited by alpha-(methylamino)isobutyric acid (Me-AIB), corresponding to system A, and a high-affinity transfer system which is unaffected by Me-AIB. The inhibitory effect increased as the L-proline concentration decreased. To determine whether IL-1-induced prostaglandin release influences proline uptake, indomethacin (14 microM) was added as a cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor. Indomethacin itself decreased L-proline uptake but to a lesser extent than did IL-1. When IL-1 was tested in the presence of indomethacin, the inhibition of L-proline uptake was still observed, with values between those obtained with each substance in isolation. This suggests that the inhibitory effect of IL-1 on proline uptake by skin fibroblast does not only involve the prostaglandins that accumulate in the medium, but no firm conclusion can be drawn, due to the fact that the inhibition by the two agents was not statistically independent. Kinetic analyses for 1 min combined with inhibition experiments showed that IL-1 induced a decrease in the Km and Vmax, values of the high-affinity transport system, whereas it increased the Km of system A. Therefore the two systems of proline uptake in skin fibroblasts are probably inhibited by IL-1 via different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argilés J. M., López-Soriano F. J., Wiggins D., Williamson D. H. Comparative effects of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (cachectin), interleukin-1-beta and tumour growth on amino acid metabolism in the rat in vivo. Absorption and tissue uptake of alpha-amino[1-14C]isobutyrate. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):357–362. doi: 10.1042/bj2610357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannai S., Kasuga H. Anti-inflammatory drug inhibition of transport of cystine and glutamate in cultured human fibroblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 May 15;34(10):1852–1854. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer B. M., Almeida A. P., Beaven M. A. Inhibition of the expression of the "A" system of amino acid transport by anti-inflammatory drugs during cell culture growth and mitogenic stimulation of thymus lymphocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Dec;219(3):752–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer B. M., Lo T. N., Beaven M. A. Anti-inflammatory drugs alter amino acid transport in HTC cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8784–8790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocquet J., Langris M., Daireaux M., Jouis V., Pujol J. P., Beliard R., Loyau G. Mononuclear cell-mediated modulation of synovial cell metabolism. II. Increased hyaluronic acid synthesis by a monocyte cell factor (MCF). Exp Cell Res. 1985 Sep;160(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., White M. F., Connor J. R. Interleukin 1 stimulates prostaglandin synthesis and cyclic AMP accumulation in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: interactions between two second messenger systems. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):29–33. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar S., Harvey A. K. Induction of interleukin-1 receptors on chondrocytes by fibroblast growth factor: a possible mechanism for modulation of interleukin-1 activity. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Feb;138(2):236–246. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W. D., Cook J. S. Parallel changes in amino acid transport and protein kinase C localization in LLC-PK1 cells treated with TPA or diradylglycerols. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Jul;132(1):104–110. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feneant-Thibault M., Moatti N., Maccario J., Corriat A., Lemonnier A. L-proline uptake in human fibroblasts: evidence for a high-affinity system in addition to system A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feneant M., Moatti N., Maccario J., Gautier M., Guerroui S., Lemonnier A. Evidence that cycloleucine affects the high-affinity systems of amino acid uptake in cultured human fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):309–315. doi: 10.1042/bj2240309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzola G. C., Dall'Asta V., Franchi-Gazzola R., White M. F. The cluster-tray method for rapid measurement of solute fluxes in adherent cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):368–374. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring M. B., Krane S. M. Modulation by recombinant interleukin 1 of synthesis of types I and III collagens and associated procollagen mRNA levels in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16724–16729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. H., Sakowski S., Meeker D., Franzblau C., Polgar P. The effect of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) on amino acid uptake and protein formation by lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8734–8737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. G., Borghetti A. F., Gazzola G. C. The regulation of amino acid transport in animal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 15;515(4):329–366. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamerman D., Wood D. D. Interleukin 1 enhances synovial cell hyaluronate synthesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Oct;177(1):205–210. doi: 10.3181/00379727-177-1-rc1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kester M., Simonson M. S., Mené P., Sedor J. R. Interleukin-1 generates transmembrane signals from phospholipids through novel pathways in cultured rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):718–723. doi: 10.1172/JCI113937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohan D. E., Schreiner G. F. Interleukin 1 modulation of renal epithelial glucose and amino acid transport. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 2):F879–F886. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.6.F879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Heino J., Vuorio E. Interleukin-1 increases collagen production and mRNA levels in cultured skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 6;929(2):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langris M., Daireaux M., Jouis V., Bocquet J., Loyau G. Interleukin-1-like factor (mononuclear cell factor) modulates proteoglycan synthesis in cultured human synovial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 19;927(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner J. Effectors of amino acid transport processes in animal cell membranes. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1985;81(4):713–739. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(85)90903-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauviel A., Heino J., Kähäri V. M., Hartmann D. J., Loyau G., Pujol J. P., Vuorio E. Comparative effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on collagen production and corresponding procollagen mRNA levels in human dermal fibroblasts. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Feb;96(2):243–249. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauviel A., Temime N., Charron D., Loyau G., Pujol J. P. Interleukin-1 alpha and beta induce interleukin-1 beta gene expression in human dermal fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1209–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80761-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauviel A., Teyton L., Bhatnagar R., Penfornis H., Laurent M., Hartmann D., Bonaventure J., Loyau G., Saklatvala J., Pujol J. P. Interleukin-1 alpha modulates collagen gene expression in cultured synovial cells. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):247–255. doi: 10.1042/bj2520247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Dayer J. M., Krane S. M., Mergenhagen S. E. Stimulation of rheumatoid synovial cell collagenase and prostaglandin production by partially purified lymphocyte-activating factor (interleukin 1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2474–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Kilian P. L., Lewis J. C., Paganelli K. A., Chizzonite R. A. The interleukin 1 receptor. Dynamics of interleukin 1 binding and internalization in T cells and fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2906–2912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Hembry R. M., Reynolds J. J. Characterization of a specific antiserum to rabbit stromelysin and demonstration of the synthesis of collagenase and stromelysin by stimulated rabbit articular chondrocytes. Coll Relat Res. 1986 Oct;6(4):351–363. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(86)80005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E., Villereal M. L. Na+ influx and cell growth in cultured human fibroblasts. Effect of indomethacin. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jan;143(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Raghow R., Stricklin G. P., Poppleton H., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Modulation of fibroblast functions by interleukin 1: increased steady-state accumulation of type I procollagen messenger RNAs and stimulation of other functions but not chemotaxis by human recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and beta. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):311–318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Smith G. N., Jr, Lachman L. B., Endres R. O., Poppleton H. M., Hasty K. A., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Stimulation of glycosaminoglycan synthesis in cultured human dermal fibroblasts by interleukin 1. Induction of hyaluronic acid synthesis by natural and recombinant interleukin 1s and synthetic interleukin 1 beta peptide 163-171. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):629–636. doi: 10.1172/JCI113927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Savage N., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 stimulates diacylglycerol production in T lymphocytes by a novel mechanism. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Daniels G. A., Boerner P., Lin J. Neutral amino acid transport systems in animal cells: potential targets of oncogene action and regulators of cellular growth. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;104(1):1–20. doi: 10.1007/BF01871898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. H., Maynard M., Bomsztyk K. Effect of interleukin-1 on intracellular concentration of sodium, calcium, and potassium in 70Z/3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5699–5701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. A. Articular cartilage cultured with catabolin (pig interleukin 1) synthesizes a decreased number of normal proteoglycan molecules. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):869–878. doi: 10.1042/bj2270869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokohama H., Negishi M., Sugama K., Hayashi H., Ito S., Hayaishi O. Inhibition of prostaglandin E2-induced phosphoinositide metabolism by phorbol ester in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):957–962. doi: 10.1042/bj2550957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


