Abstract
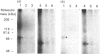
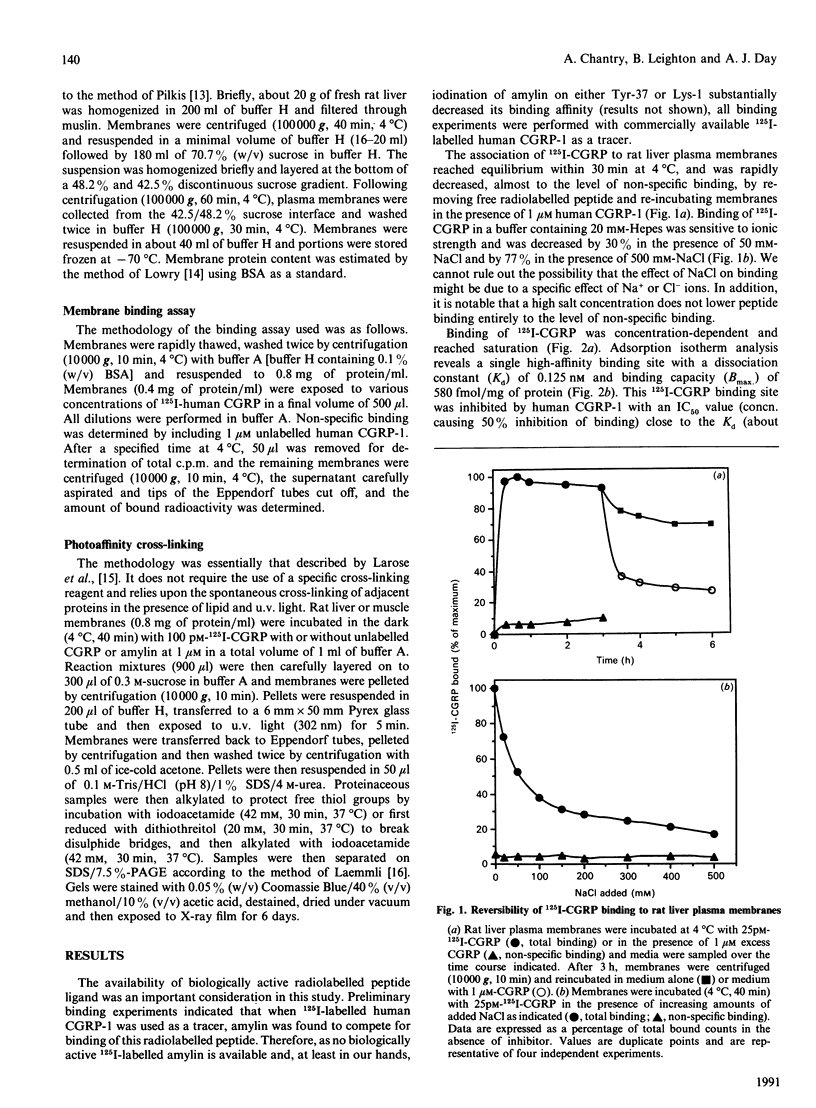
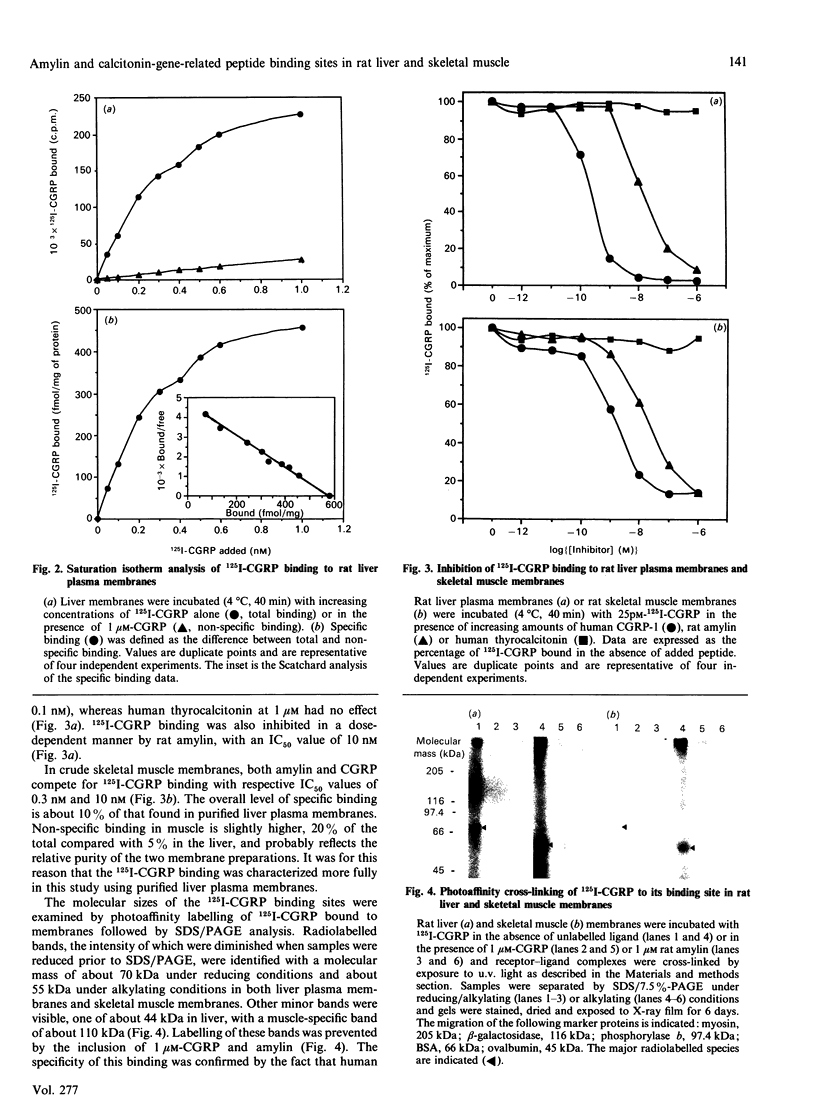
This study examines whether the high degree of sequence identity between amylin and calcitonin-gene-related peptide (CGRP) is reflected in their cross-reactivity at the level of membrane receptor binding. Rat liver plasma membranes contain a specific saturable binding site for 125I-labelled human CGRP-1. Binding reached equilibrium within 30 min and was rapidly reversed by re-incubating membranes in the presence of 1 microM human CGRP. In addition, the presence of 50 mM- or 500 mM-NaCl lowered specific binding by 30% and 77% respectively. Scatchard analysis was consistent with a single high-affinity site with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 0.125 nM and binding capacity (Bmax.) of 580 fmol/mg of membrane protein. Specific binding of 125I-labelled human CGRP-1 to both liver and skeletal muscle membranes was inhibited by human CGRP-1 [IC50 (concn. causing half-maximal inhibition of binding) 0.1-0.3 nM], and rat amylin (IC50 10 nM), but not by human calcitonin. Covalent cross-linking of 125I-CGRP to its binding site in rat skeletal muscle and liver membranes resulted in labelling of a major species of about 70 kDa under reducing conditions and about 55 kDa under alkylating conditions, as visualized on SDS/PAGE. These radiolabelled species were absent in the presence of CGRP or amylin at 1 microM. These results are indicative of a common binding site for both CGRP and amylin in liver and skeletal muscle, and it is suggested that both peptides mediate their actions through the same effector system. The normal physiological importance and the relevance to the pathology of type 2 diabetes of these data are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amara S. G., Jonas V., Rosenfeld M. G., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):240–244. doi: 10.1038/298240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer L. H., MacIntyre I., Zaidi M. Peptides from the calcitonin genes: molecular genetics, structure and function. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):377–390. doi: 10.1042/bj2550377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. J., Leighton B., Dimitriadis G. D., Parry-Billings M., Kowalchuk J. M., Howland K., Rothbard J. B., Willis A. C., Reid K. B. Amylin found in amyloid deposits in human type 2 diabetes mellitus may be a hormone that regulates glycogen metabolism in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7763–7766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. J., Willis A. C., Clark A., Turner R. C., Sim R. B., Reid K. B. Purification and characterization of a peptide from amyloid-rich pancreases of type 2 diabetic patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8628–8632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foord S. M., Craig R. K. Isolation and characterisation of a human calcitonin-gene-related-peptide receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):373–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings C. G., Mudge A. W. Chick myotubes in culture express high-affinity receptors for calcitonin gene-related peptide. Brain Res. 1989 Dec 18;504(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91357-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutter D., Orena S. J., Andrews K. M. Suppression of insulin-stimulated glucose transport in L6 myocytes by calcitonin gene-related peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):461–467. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91742-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larose L., McNicoll N., Rondeau J. J., Escher E., De Lean A. Photoaffinity labelling of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF)-R1 receptor by underivatized 125I-ANF. Involvement of lipid peroxidation. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):379–384. doi: 10.1042/bj2670379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton B., Cooper G. J. Pancreatic amylin and calcitonin gene-related peptide cause resistance to insulin in skeletal muscle in vitro. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):632–635. doi: 10.1038/335632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton B., Cooper G. J. The role of amylin in the insulin resistance of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsukawa T., Takemura J., Asai J., Nakazato M., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Matsukura S. Islet amyloid polypeptide response to glucose, insulin, and somatostatin analogue administration. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):639–642. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina J. M., Cooper G. J., Leighton B., Olefsky J. M. Induction of insulin resistance in vivo by amylin and calcitonin gene-related peptide. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):260–265. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita T., Yamaguchi A., Fujita T., Chiba T. Activation of adenylate cyclase by islet amyloid polypeptide with COOH-terminal amide via calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors on rat liver plasma membranes. Diabetes. 1990 Jul;39(7):875–877. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.39.7.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa A., Harris V., McCorkle S. K., Unger R. H., Luskey K. L. Amylin secretion from the rat pancreas and its selective loss after streptozotocin treatment. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):973–976. doi: 10.1172/JCI114528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okimura Y., Chihara K., Abe H., Kita T., Kashio Y., Sato M., Fujita T. Calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system and peripheral organs of rats. Regul Pept. 1987 Jun;17(6):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(87)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Exton J. H., Johnson R. A., Park C. R. Effects of glucagon on cyclic AMP and carbohydrate metabolism in livers from diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):250–267. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo J., Polak J. M., Fernandez L., Ghatei M. A., Mulderry P., Bloom S. R. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactive sensory and motor nerves of the rat, cat, and monkey esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1985 Feb;88(2):444–451. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90505-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Hiroshima O., Yuzuriha T., Yamato C., Saito A., Kimura S., Hirabayashi T., Goto K. Calcitonin gene-related peptide-binding sites of porcine cardiac muscles and coronary arteries: solubilization and characterization. J Neurochem. 1989 Jun;52(6):1919–1924. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Hayashi N., Kasahara A., Matsuda H., Fusamoto H., Sato N., Hillyard C. J., Girgis S., MacIntyre I., Emson P. C. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the hepatic and splanchnic vascular systems of the rat. Hepatology. 1986 Jul-Aug;6(4):676–681. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takami K., Hashimoto K., Uchida S., Tohyama M., Yoshida H. Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide on the cyclic AMP level of isolated mouse diaphragm. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;42(3):345–350. doi: 10.1254/jjp.42.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamori M., Yoshikawa H. Effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide on skeletal muscle via specific binding site and G protein. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Mar;90(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi A., Chiba T., Okimura Y., Yamatani T., Morishita T., Nakamura A., Inui T., Noda T., Fujita T. Receptors for calcitonin gene-related peptide on the rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):383–391. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80725-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]