Abstract
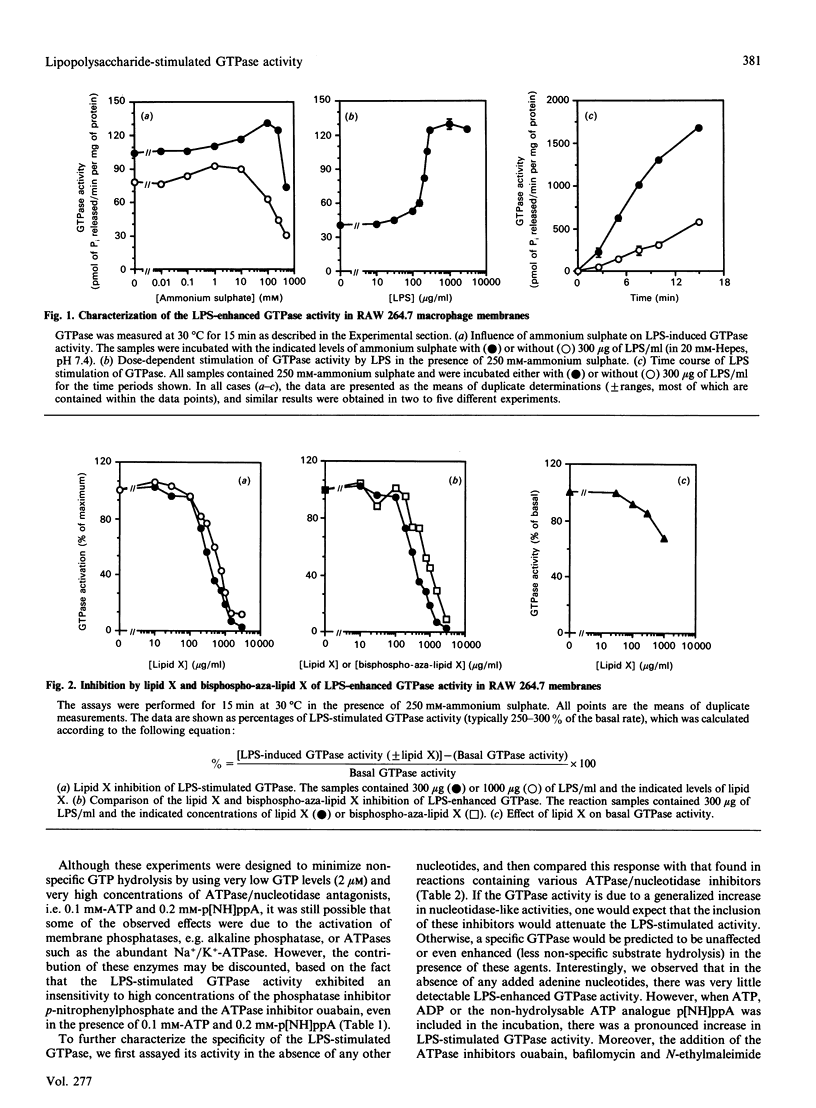
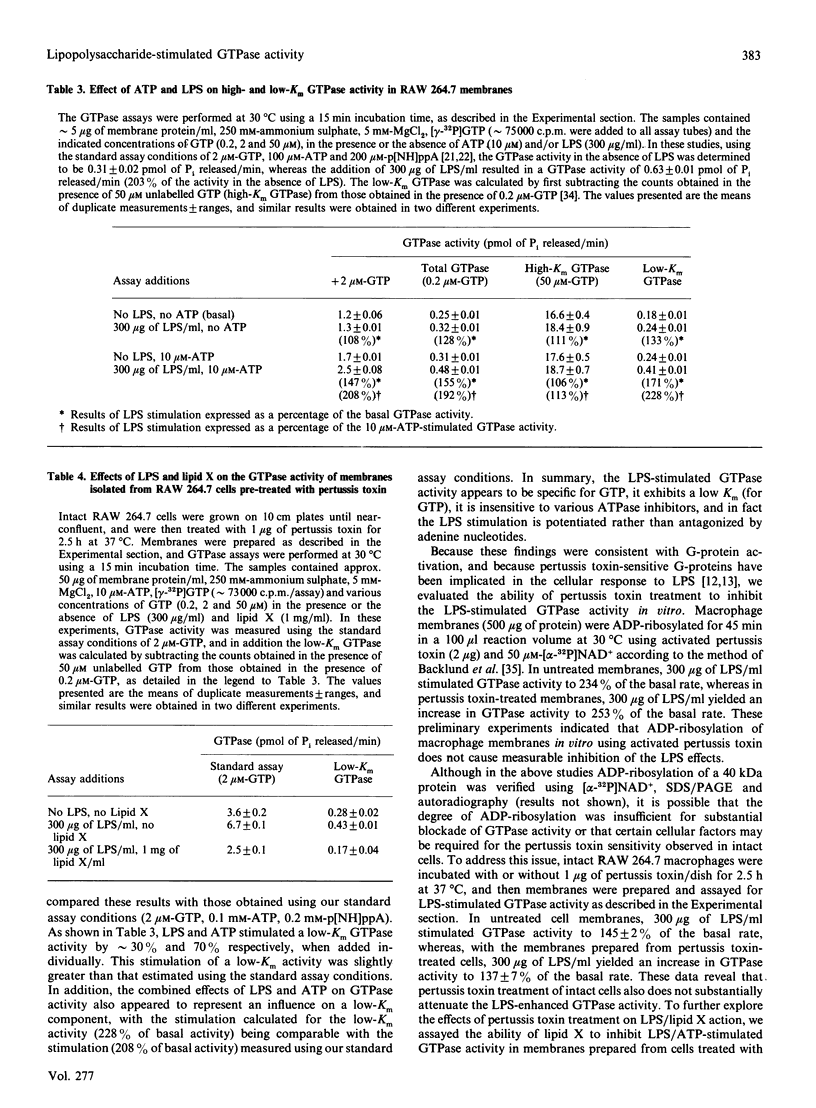
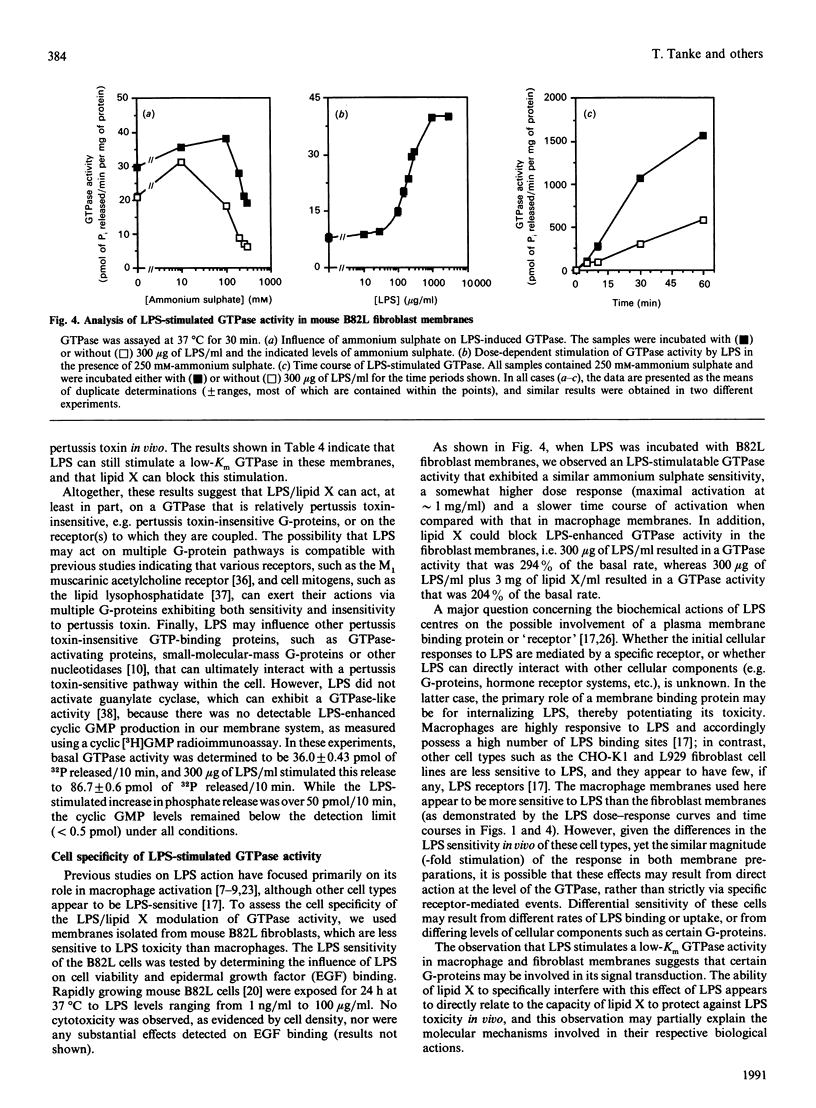
The molecular mechanisms surrounding the toxicity and high mortality rate that accompany the release of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) are unclear, although its potent activity suggests that an amplification system is involved. Because previous studies suggest that a guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (G-protein) may participate in LPS action, we have evaluated the effects of LPS on GTPase activity in membranes isolated from macrophage (RAW 264.7) and fibroblast (B82L) cell lines. LPS induced substantial GTPase activation (200-300% above basal), and kinetic analyses indicated that the maximal LPS-stimulated increase in velocity is observed within 15 min, that it is a low-Km (for GTP) activity, that it can be enhanced by ammonium sulphate, and that it appears to be pertussis toxin-insensitive. Moreover, the LPS-enhanced GTPase activity was not antagonized by phosphatase/ATPase inhibitors such as p-nitrophenyl phosphate, ouabain, bafilomycin or N-ethylmaleimide, and in fact was potentiated by the addition of ATP or ADP. Conversely, the LPS precursor, lipid X, which can decrease the lethal effects of LPS, was found to dose-dependently inhibit the LPS-mediated stimulation of GTPase activity. Half-maximal inhibition was seen at the same lipid X/LPS ratio known to be effective in vivo, i.e. 1:1(w/w). These effects appear to be specific because other phospholipids, detergents and glycosides neither stimulated basal, nor inhibited LPS-induced, GTPase activity. These data suggest the involvement of a GTPase in LPS action, and indicate that lipid X may act to directly antagonize LPS at this level.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aschauer H., Grob A., Hildebrandt J., Schuetze E., Stuetz P. Highly purified lipid X is devoid of immunostimulatory activity. Isolation and characterization of immunostimulating contaminants in a batch of synthetic lipid X. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9159–9164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backlund P. S., Jr, Aksamit R. R., Unson C. G., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. M., Milligan G. Immunochemical and electrophoretic characterization of the major pertussis toxin substrate of the RAW264 macrophage cell line. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2040–2046. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry L. J. Bacterial toxins. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1977 Nov;5(3):239–318. doi: 10.3109/10408447709082601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertics P. J., Chen W. S., Hubler L., Lazar C. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N. Alteration of epidermal growth factor receptor activity by mutation of its primary carboxyl-terminal site of tyrosine self-phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3610–3617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Mahoney J., Le Trang N., Pekala P., Cerami A. Purification of cachectin, a lipoprotein lipase-suppressing hormone secreted by endotoxin-induced RAW 264.7 cells. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):984–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkland T. P., Cornwell R. D., Golenbock D. T., Proctor R. A. Comparative study of lipopolysaccharide-, lipid IVa-, and lipid X-induced tumor necrosis factor production in murine macrophage-like cell lines. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;256:399–402. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-5140-6_35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan C. S., Reynolds K. L., Brenner E. R. Analysis of 1,186 episodes of gram-negative bacteremia in non-university hospitals: the effects of antimicrobial therapy. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):629–638. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):538–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen D. S., Baker B., Dubyak G. R. Pertussis toxin produces differential inhibitory effects on basal, P2-purinergic, and chemotactic peptide-stimulated inositol phospholipid breakdown in HL-60 cells and HL-60 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16181–16189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel-Issakani S., Spiegel A. M., Strulovici B. Lipopolysaccharide response is linked to the GTP binding protein, Gi2, in the promonocytic cell line U937. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20240–20247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenbock D. T., Hampton R. Y., Raetz C. R., Wright S. D. Human phagocytes have multiple lipid A-binding sites. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):4069–4075. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.4069-4075.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenbock D. T., Leggett J. E., Rasmussen P., Craig W. A., Raetz C. R., Proctor R. A. Lipid X protects mice against fatal Escherichia coli infection. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):779–784. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.779-784.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenbock D. T., Will J. A., Raetz C. R., Proctor R. A. Lipid X ameliorates pulmonary hypertension and protects sheep from death due to endotoxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2471–2476. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2471-2476.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Golenbock D. T., Raetz C. R. Lipid A binding sites in membranes of macrophage tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14802–14807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of hormone-sensitive GTP-dependent regulatory proteins by chloride. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3597–3602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakway J. P., DeFranco A. L. Pertussis toxin inhibition of B cell and macrophage responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):743–746. doi: 10.1126/science.3095921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasper J. R., Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Molecular mechanism of beta-adrenergic receptor blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. FASEB J. 1988 Oct;2(13):2891–2894. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.13.2901994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Freeman M., Rohrer L., Zabrecky J., Matsudaira P., Krieger M. Type I macrophage scavenger receptor contains alpha-helical and collagen-like coiled coils. Nature. 1990 Feb 8;343(6258):531–535. doi: 10.1038/343531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Moore R. N., McGhee J. R., Rosenstreich D. L., Mergenhagen S. E. The primary role of lymphoreticular cells in the mediation of host responses to bacterial endotoxim. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):55–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Arai H., Inoue K. Scavenger receptor-mediated uptake and metabolism of lipid vesicles containing acidic phospholipids by mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5226–5231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno N., Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide interaction with lysozyme. Binding of lipopolysaccharide to lysozyme and inhibition of lysozyme enzymatic activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4434–4441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Tokumitsu Y., Kondo Y., Ui M. P2-purinergic receptors are coupled to two signal transduction systems leading to inhibition of cAMP generation and to production of inositol trisphosphate in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13483–13490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons W. J., Stiles G. L. Heterologous desensitization of the inhibitory A1 adenosine receptor-adenylate cyclase system in rat adipocytes. Regulation of both Ns and Ni. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):841–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prpic V., Weiel J. E., Somers S. D., DiGuiseppi J., Gonias S. L., Pizzo S. V., Hamilton T. A., Herman B., Adams D. O. Effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide on the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):526–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz S., Chinkers M., Garbers D. L. The guanylate cyclase/receptor family of proteins. FASEB J. 1989 Jul;3(9):2026–2035. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.9.2568301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W. The role of G proteins in transmembrane signalling. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 15;272(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2720001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Yoshihara Y., Misawa H., Fukushima N., Katada T., Ui M., Takagi H., Satoh M. The kyotorphin (tyrosine-arginine) receptor and a selective reconstitution with purified Gi, measured with GTPase and phospholipase C assays. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3732–3741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoeller R. A., Wightman P. D., Anderson M. S., Raetz C. R. Accumulation of lysophosphatidylinositol in RAW 264.7 macrophage tumor cells stimulated by lipid A precursors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17212–17220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Corven E. J., Groenink A., Jalink K., Eichholtz T., Moolenaar W. H. Lysophosphatidate-induced cell proliferation: identification and dissection of signaling pathways mediated by G proteins. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


