Abstract
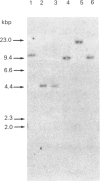
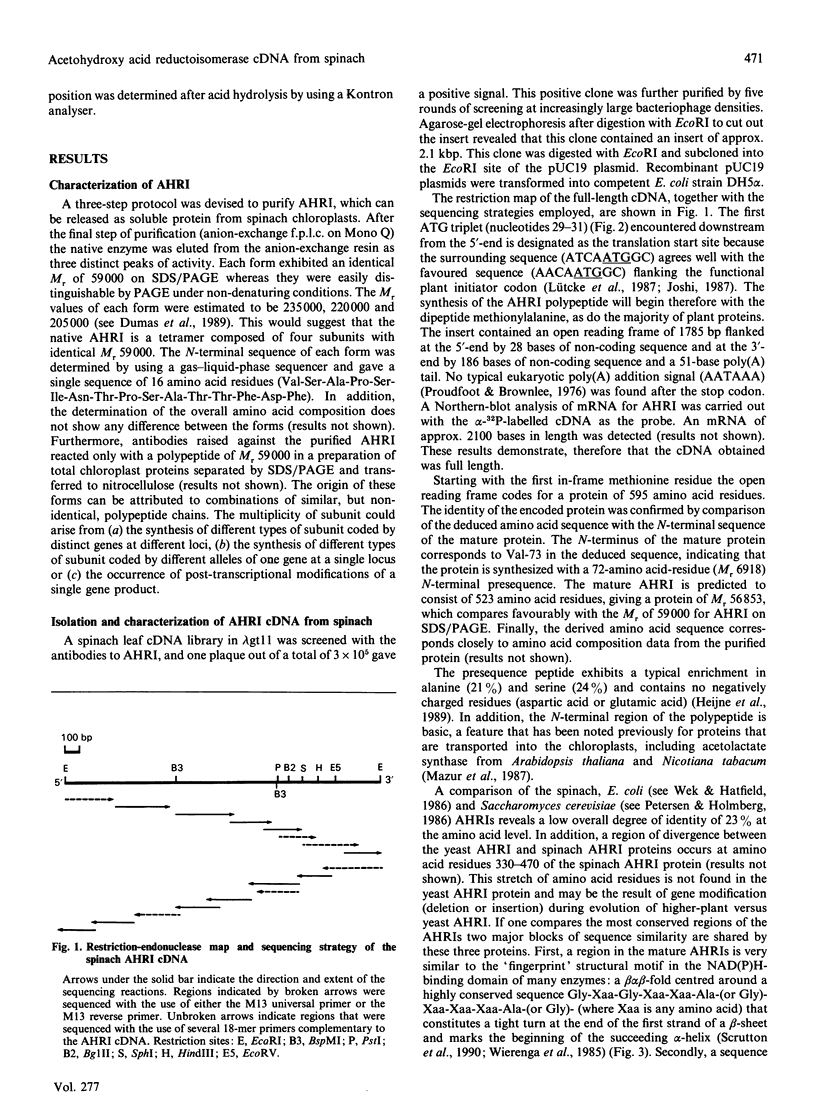
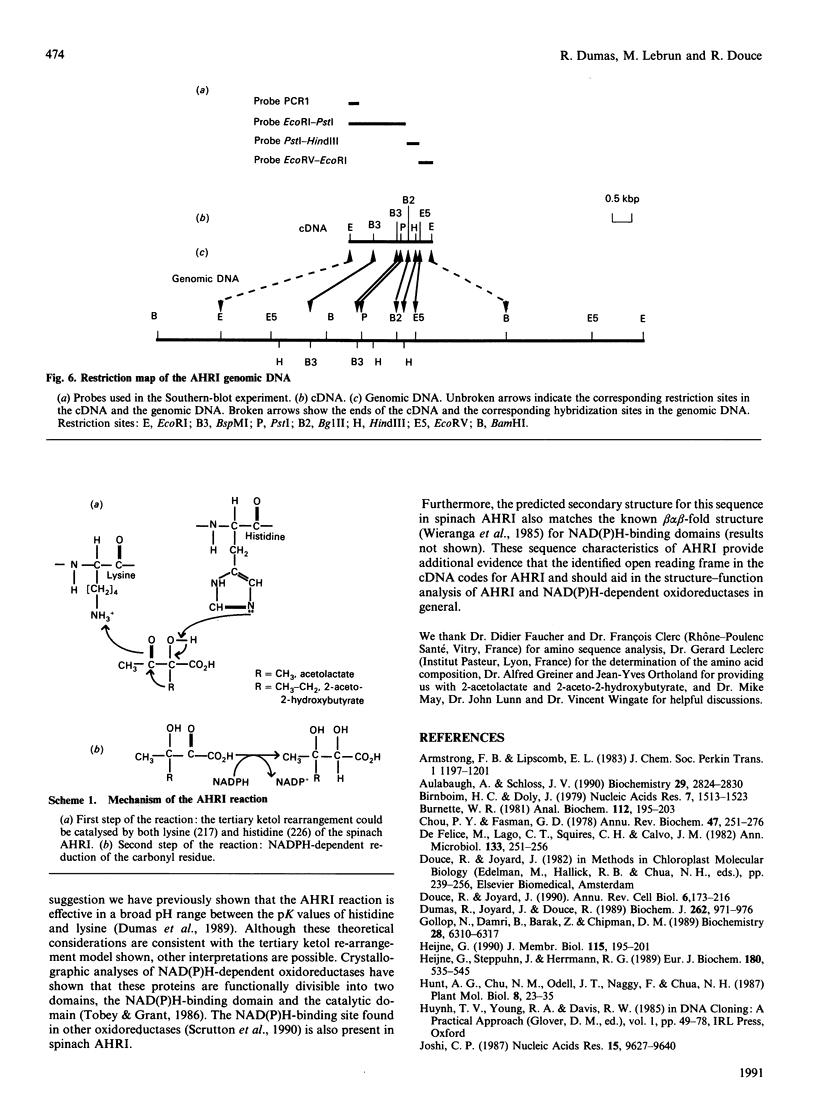
Acetohydroxy acid reductoisomerase (AHRI), the second enzyme in the parallel isoleucine/valine-biosynthetic pathway, catalyses an unusual two-step reaction in which the substrate, either 2-acetolactate or 2-aceto-2-hydroxybutyrate, is converted via an alkyl migration and an NADPH-dependent reduction to give 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutyrate or 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylvalerate respectively. We have isolated and characterized a full-length cDNA from a lambda gt11 spinach library encoding the complete acetohydroxy acid reductoisomerase protein precursor. The 2050-nucleotide sequence contains a 1785-nucleotide open reading frame. The derived amino acid sequence indicates that the protein precursor consists of 595 amino acid residues including a presequence peptide of 72 amino acid residues. The N-terminal sequence of the first 16 amino acid residues of the purified AHRI confirms the identity of the cDNA. The derived amino acid sequence from this open reading frame shows 23% identity with the deduced amino acid sequences of the Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae AHRI proteins. There are two blocks of conserved amino acid residues in these three proteins. One of these is a sequence similar to the 'fingerprint' region of the NAD(P)H-binding site found in a large number of NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductases. The other, a short sequence (Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-Ser-His-Gly-Phe) containing the amino acids lysine and histidine, could well be the catalytic site of the first step of the AHRI reaction. Southern-blot analysis indicated that AHRI is encoded by a single gene per haploid genome of about 7.5 kbp containing at least four introns.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aulabaugh A., Schloss J. V. Oxalyl hydroxamates as reaction-intermediate analogues for ketol-acid reductoisomerase. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2824–2830. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douce R., Joyard J. Biochemistry and function of the plastid envelope. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:173–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumas R., Joyard J., Douce R. Purification and characterization of acetohydroxyacid reductoisomerase from spinach chloroplasts. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 15;262(3):971–976. doi: 10.1042/bj2620971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollop N., Damri B., Barak Z., Chipman D. M. Kinetics and mechanism of acetohydroxy acid synthase isozyme III from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6310–6317. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. Putative polyadenylation signals in nuclear genes of higher plants: a compilation and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9627–9640. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H. A., Chow K. C., Mickel F. S., Moss K. A., Kern H. F., Scheele G. A. Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur B. J., Chui C. F., Smith J. K. Isolation and characterization of plant genes coding for acetolactate synthase, the target enzyme for two classes of herbicides. Plant Physiol. 1987 Dec;85(4):1110–1117. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.4.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen J. G., Holmberg S. The ILV5 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is highly expressed. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9631–9651. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan E. D., Kohlhaw G. B. Subcellular localization of isoleucine-valine biosynthetic enzymes in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):631–637. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.631-637.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Blancard J., Fourcart J., Limonne F., Girot P., Boschetti E. Nouveaux échangeurs d'ions Trisacryl: intérêt et application au fractionnement des protéines du plasma humain. Ann Pharm Fr. 1981;39(5):403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Van Dyk D. E., Vasta J. F., Kutny R. M. Purification and properties of Salmonella typhimurium acetolactate synthase isozyme II from Escherichia coli HB101/pDU9. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4952–4959. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Spönemann P., Köcher H., Wengenmayer F. The herbicidally active experimental compound Hoe 704 is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme acetolactate reductoisomerase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 10;238(2):375–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrutton N. S., Berry A., Perham R. N. Redesign of the coenzyme specificity of a dehydrogenase by protein engineering. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):38–43. doi: 10.1038/343038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirley B. W., Ham D. P., Senecoff J. F., Berry-Lowe S. L., Zurfluh L. L., Shah D. M., Meagher R. B. Comparison of the expression of two highly homologous members of the soybean ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit gene family. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jun;14(6):909–925. doi: 10.1007/BF00019389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobey K. L., Grant G. A. The nucleotide sequence of the serA gene of Escherichia coli and the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein, D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12179–12183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Hatfield G. W. Nucleotide sequence and in vivo expression of the ilvY and ilvC genes in Escherichia coli K12. Transcription from divergent overlapping promoters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2441–2450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wek R. C., Hauser C. A., Hatfield G. W. The nucleotide sequence of the ilvBN operon of Escherichia coli: sequence homologies of the acetohydroxy acid synthase isozymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):3995–4010. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.3995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Felice M., Lago C. T., Squires C. H., Calvo J. M. Acetohydroxy acid synthase isoenzymes of Escherichia coli K12 and Salmonella typhimurium. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Steppuhn J., Herrmann R. G. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):535–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. The signal peptide. J Membr Biol. 1990 May;115(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF01868635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]