Abstract
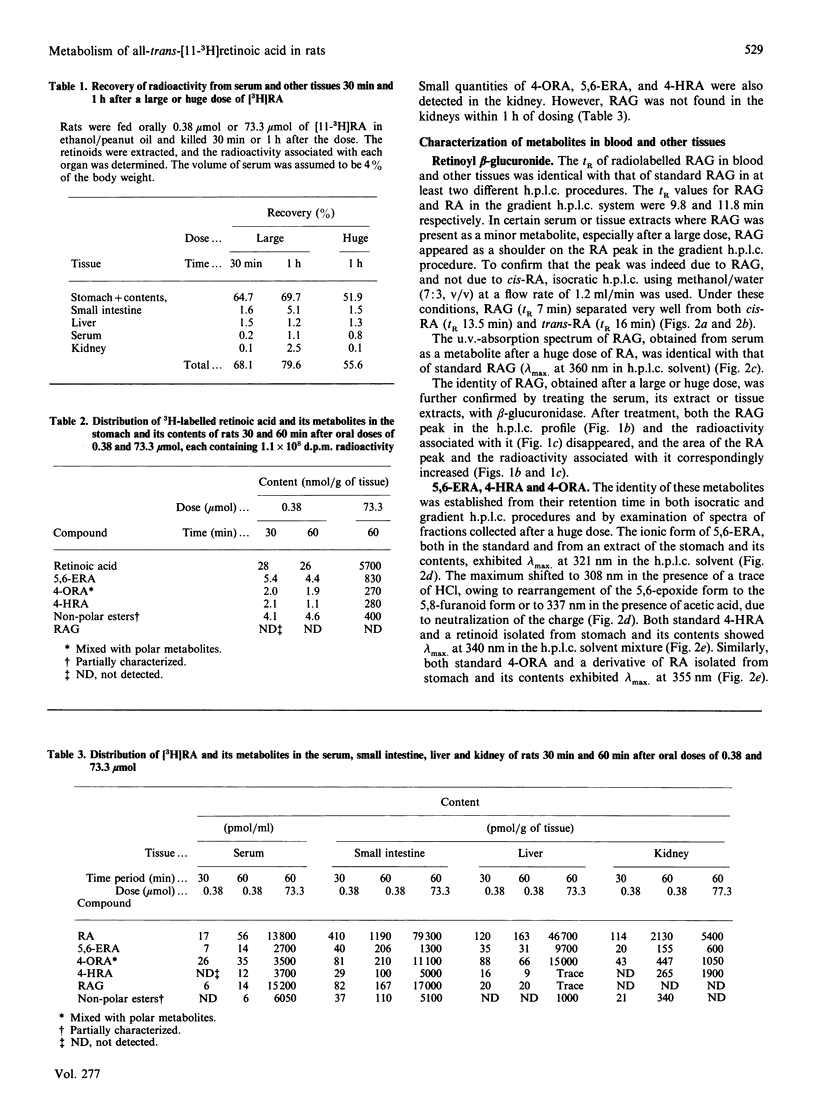
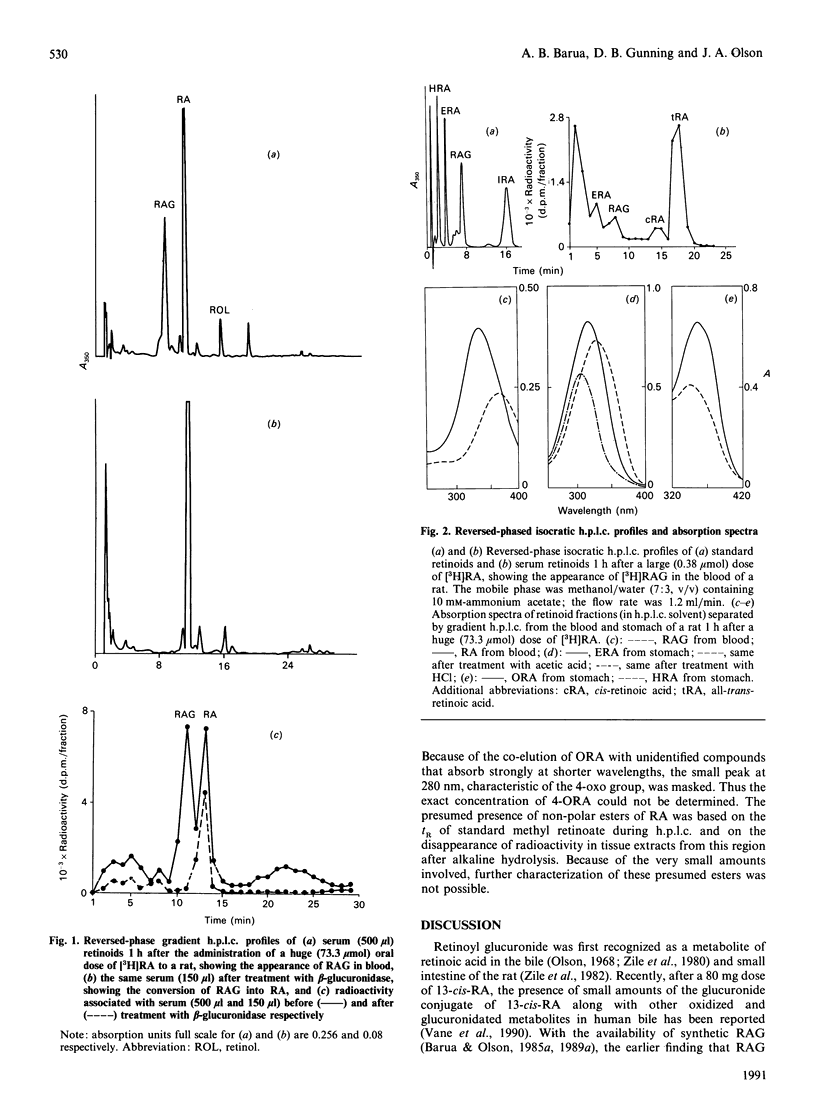
Soon after [11-3H]retinoic acid (RA) (1.1 x 10(8) d.p.m.) was administered orally to rats either as a large dose (115 micrograms = 0.38 mumol/rat) or mixed with unlabelled RA as a huge dose (22 mg = 73.33 mumol/rat), retinoyl beta-glucuronide (RAG) was identified and characterized as a significant metabolite in the serum and small intestine. Of the administered dose, 70% remained unchanged as retinoic acid in the stomach up to 1 h. Significant amounts of 5,6-epoxyretinoic acid, 4-hydroxyretinoic acid, esters of retinoic acid and several polar retinoids, including 4-oxoretinoic acid, were also detected in the stomach. No significant difference was observed in the nature of the retinoids found after a large or a huge dose; however, the ratio of RAG/RA was higher after a huge dose than after a large dose. Thus RAG, which is biologically active in vivo and in vitro, is formed quickly in significant amounts in tissues after a dose of RA.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barua A. B., Olson J. A. Chemical synthesis of all-trans retinoyl beta-glucuronide. J Lipid Res. 1985 Oct;26(10):1277–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barua A. B., Olson J. A. Chemical synthesis of all-trans-[11-3H]retinoyl beta-glucuronide and its metabolism in rats in vivo. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):403–409. doi: 10.1042/bj2630403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barua A. B., Olson J. A. Retinoyl beta-glucuronide: an endogenous compound of human blood. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986 Apr;43(4):481–485. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/43.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barua A. B., Olson J. A. Synthesis of 4, 4-difluoro analogs of retinol and retinoic acid. J Lipid Res. 1984 Mar;25(3):304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F., Zile M., Sietsema W. K. The metabolism of retinoic acid to 5,6-epoxyretinoic acid, retinoyl-beta-glucuronide, and other polar metabolites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981 Feb 27;359:25–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb12734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunagin P. E., Jr, Zachman R. D., Olson J. A. The identification of metabolites of retinal and retinoic acid in rat bile. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 27;124(1):71–85. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallup J. M., Barua A. B., Furr H. C., Olson J. A. Effects of retinoid beta-glucuronides and N-retinoyl amines on the differentiation of HL-60 cells in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1987 Dec;186(3):269–274. doi: 10.3181/00379727-186-42612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janick-Buckner D., Barua A. B., Olson J. A. Induction of HL-60 cell differentiation by water-soluble and nitrogen-containing conjugates of retinoic acid and retinol. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):320–325. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.2001792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochhar D. M. Teratogenic activity of retinoic acid. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;70(3):398–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb01308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo M. A., Iida S., Lieber C. S. Retinoic acid metabolism by a system reconstituted with cytochrome P-450. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Oct;234(1):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Summerbell D. Retinoic acid-binding protein in the chick limb bud: identification at developmental stages and binding affinities of various retinoids. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1986 Sep;97:239–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A. M., Napoli J. L. Identification of 5,6-epoxyretinoic acid as an endogenous retinol metabolite. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1730–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A. M., Napoli J. L., Yoshizawa S., DeLuca H. F. 5,6-epoxyretinoic acid is a physiological metabolite of retinoic acid in the rat. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):475–481. doi: 10.1042/bj1860475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli J. L., McCormick A. M. Tissue dependence of retinoic acid metabolism in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 23;666(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K., Olson J. A. Natural occurrence and biological activity of vitamin A derivatives in rat bile. J Nutr. 1967 Dec;93(4):461–469. doi: 10.1093/jn/93.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A. Some aspects of vitamin A metabolism. Vitam Horm. 1968;26:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60751-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva D. P., Jr, DeLuca H. F. Metabolism of retinoic acid in vivo in the vitamin A-deficient rat. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):33–41. doi: 10.1042/bj2060033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson B. N., Frolik C. A., Zaharevitz D. W., Roller P. P., Sporn M. B. Dose-dependent kinetics of all-trans-retinoic acid in rats. Plasma levels and excretion into bile, urine, and faeces. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 15;30(2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane F. M., Bugge C. J., Rodriguez L. C., Rosenberger M., Doran T. I. Human biliary metabolites of isotretinoin: identification, quantification, synthesis, and biological activity. Xenobiotica. 1990 Feb;20(2):193–207. doi: 10.3109/00498259009047155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane F. M., Buggé C. J. Identification of 4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid as the major metabolite of 13-cis-retinoic acid in human blood. Drug Metab Dispos. 1981 Nov-Dec;9(6):515–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zile M. H., Cullum M. E., Simpson R. U., Barua A. B., Swartz D. A. Induction of differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60 by retinoyl glucuronide, a biologically active metabolite of vitamin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2208–2212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zile M. H., Inhorn R. C., DeLuca H. F. Metabolism in vivo of all-trans-retinoic acid. Biosynthesis of 13-cis-retinoic acid and all-trans- and 13-cis-retinoyl glucuronides in the intestinal mucosa of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3544–3550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zile M. H., Schnoes H. K., DeLuca H. F. Characterization of retinoyl beta-glucuronide as a minor metabolite of retinoic acid in bile. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3230–3233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


