Abstract
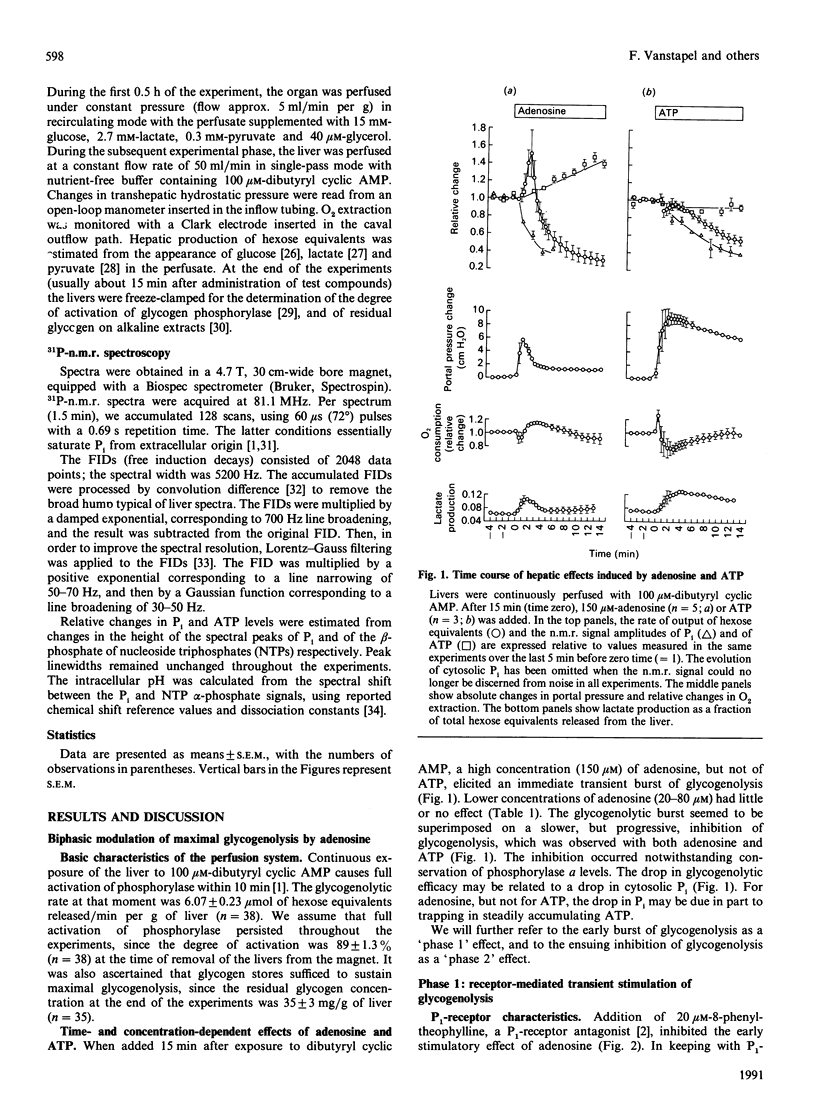
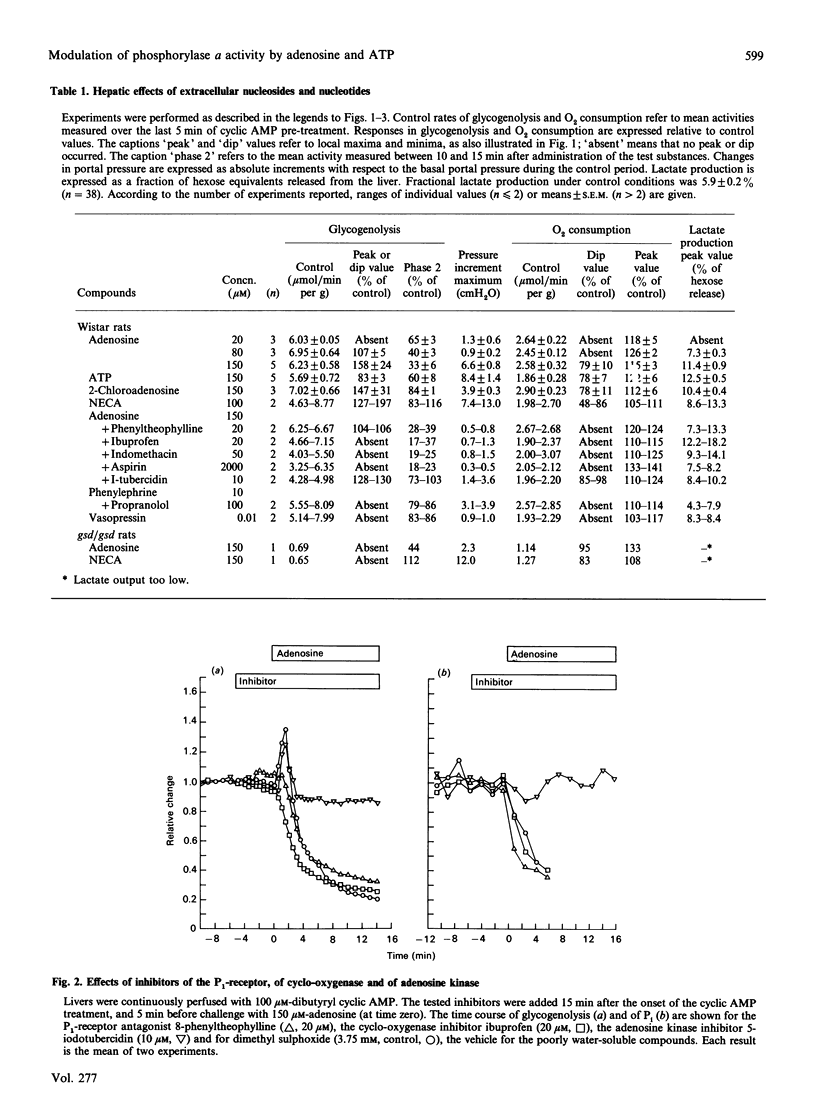
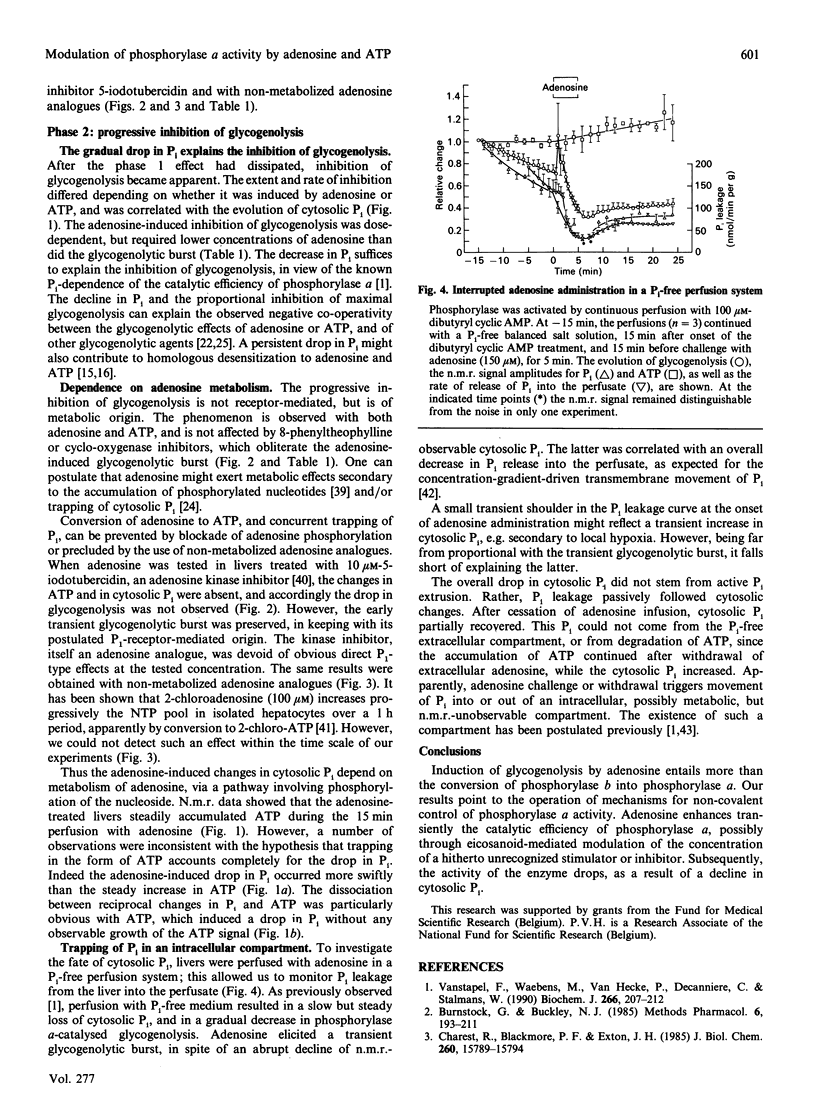
Rat livers perfused at constant flow via the portal vein with dibutyryl cyclic AMP produced glucose equivalents at a steady maximal rate (6 mumol/min per g of liver). Addition of adenosine (150 microM) caused a biphasic effect. (i) First, the glycogenolytic rate rose transiently, to a mean peak of 150% of control levels after 2 min. This glycogenolytic burst was reproduced by two P1-receptor agonists, but not by ATP, and was blocked by a P1-antagonist (8-phenyltheophylline), as well as by inhibitors of eicosanoid synthesis (indomethacin, ibuprofen or aspirin). It did not occur in phosphorylase-kinase-deficient livers. The adenosine-induced glycogenolytic burst coincided with moderate and transient changes in portal pressure (+6 cmH2O) and O2 consumption (-20%), but it could not be explained by an increase in cytosolic Pi, since the n.m.r. signal fell precipitously. (ii) Subsequently, the rate of glycogenolysis decreased to one-third of the preadenosine value, in spite of persistent maximal activation of phosphorylase. The decrease could be linked to the decline in cytosolic Pi: both changes were prevented by the adenosine kinase inhibitor 5-iodotubercidin, whereas they were not affected by ibuprofen or 8-phenyltheophylline, and were not reproduced by non-metabolized adenosine analogues. In comparison with adenosine, ATP caused a slower decrease of Pi and of glycogenolysis. The fate of the cytosolic Pi was unclear, especially with administered ATP, which did not increase the n.m.r.-detectable intracellular ATP.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altin J. G., Bygrave F. L. Prostaglandin F2 alpha and the thromboxane A2 analogue ONO-11113 stimulate Ca2+ fluxes and other physiological responses in rat liver. Further evidence that prostanoids may be involved in the action of arachidonic acid and platelet-activating factor. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):677–685. doi: 10.1042/bj2490677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartrons R., Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. The ability of adenosine to decrease the concentration of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in isolated hepatocytes. A cyclic AMP-mediated effect. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):157–163. doi: 10.1042/bj2180157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckh K., Otto R., Ji S., Jungermann K. Control of oxygen uptake, microcirculation and glucose release by circulating noradrenaline in perfused rat liver. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Jul;366(7):671–678. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busshardt E., Gerok W., Häussinger D. Regulation of hepatic parenchymal and non-parenchymal cell function by the diadenine nucleotides Ap3A and Ap4A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 9;1010(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Fisher R. A., Robertson S. M., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and vasoconstriction by adenosine and adenosine analogues in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):35–41. doi: 10.1042/bj2480035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton D. B., Robertson S. M., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis by adenine nucleotides in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):773–780. doi: 10.1042/bj2370773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carabaza A., Ricart M. D., Mor A., Guinovart J. J., Ciudad C. J. Role of AMP on the activation of glycogen synthase and phosphorylase by adenosine, fructose, and glutamine in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2724–2732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteleijn E., Kuiper J., van Rooij H. C., Kamps J. A., Koster J. F., van Berkel T. J. Hormonal control of glycogenolysis in parenchymal liver cells by Kupffer and endothelial liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2699–2703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. M., Exton J. H. A rapid method for the determination of glycogen content and radioactivity in small quantities of tissue or isolated hepatocytes. Anal Biochem. 1976 Mar;71(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claeyssens S., Hamet M., Chedeville A., Basuyau J. P., Lavoinne A. Influence of 2-chloroadenosine on the nucleotide content of isolated rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. Determination of maltase and isomaltase activities with a glucose-oxidase reagent. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:547–551. doi: 10.1042/bj0800547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL P. M., PRICHARD M. M. L. Effects of stimulation of the hepatic nerves and of adrenaline upon the circulation of the portal venous blood within the liver. J Physiol. 1951 Aug;114(4):538–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Shepherd R. E. Adenosine, cyclic AMP metabolism, and glycogenolysis in rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8066–8070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Robertson S. M., Olson M. S. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and vasoconstriction in the perfused rat liver by the thromboxane A2 analogue U-46619. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4631–4638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Foix A. M., Rodriguez-Gil J. E., Guinovart J. J., Bosch F. Prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha affect glycogen synthase and phosphorylase in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):93–97. doi: 10.1042/bj2610093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. F., Paterson A. R., Caldwell I. C., Paul B., Chan M. C., Lau K. F. Inhibitors of nucleoside and nucleotide metabolism. Cancer Chemother Rep 2. 1972 Nov;3(1):71–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer L. J., Lowenstein J. M. Effects of adenosine and adenosine analogues on glycogen metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 15;35(24):4529–4536. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90775-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Busshardt E., Stehle T., Stoll B., Wettstein M., Gerok W. Stimulation of thromboxane release by extracellular UTP and ATP from perfused rat liver. Role of icosanoids in mediating the nucleotide responses. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 1;178(1):249–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Stehle T., Gerok W., Tran-Thi T. A., Decker K. Hepatocyte heterogeneity in response to extracellular ATP. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 15;169(3):645–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Stehle T. Hepatocyte heterogeneity in response to icosanoids. The perivenous scavenger cell hypothesis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;175(2):395–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Stehle T., Tran-Thi T. A., Decker K., Gerok W. Prostaglandin responses in isolated perfused rat liver: Ca2+ and K+ fluxes, hemodynamic and metabolic effects. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Nov;368(11):1509–1513. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.2.1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles R. A., Griffiths J. R., Stevens A. N., Gadian D. G., Porteous R. Effects of fructose on the energy metabolism and acid-base status of the perfused starved-rat liver. A 31phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):191–202. doi: 10.1042/bj1920191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles R. A., Stevens A. N., Griffiths J. R., Morris P. G. Phosphorylation status of liver by 31P-n.m.r. spectroscopy, and its implications for metabolic control. A comparison of 31P-n.m.r. spectroscopy (in vivo and in vitro) with chemical and enzymic determinations of ATP, ADP and Pi. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):141–151. doi: 10.1042/bj2290141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail N. A., Hems D. A. Effects of adenosine on glucose and lipid metabolism and hepatic blood flow. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 May 1;27(9):1341–1345. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellner K., Fieber R. S., Marek H. Enzymatische Bestimmung der Brenztraubensäure (Pyruvat) im Blut ohne Enteiweissung. Z Med Lab Diagn. 1981;22(5):301–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoinne A., Buc H. A., Claeyssens S., Pinosa M., Matray F. The mechanism by which adenosine decreases gluconeogenesis from lactate in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):449–454. doi: 10.1042/bj2460449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P., Cornell N. W., Krebs H. A. Effect of adenosine on the adenine nucleotide content and metabolism of hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):593–599. doi: 10.1042/bj1520593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy C. R., Cunningham C. C., Radda G. K. The metabolic state of the rat liver in vivo measured by 31P-NMR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchand J. C., Lavoinne A., Giroz M., Matray F. The influence of adenosine on intermediary metabolism of isolated hepatocytes. Biochimie. 1979;61(11-12):1273–1282. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(80)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oetjen E., Schweickhardt C., Unthan-Fechner K., Probst I. Stimulation of glucose production from glycogen by glucagon, noradrenaline and non-degradable adenosine analogues is counteracted by adenosine and ATP in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):337–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2710337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Tokumitsu Y., Kondo Y., Ui M. P2-purinergic receptors are coupled to two signal transduction systems leading to inhibition of cAMP generation and to production of inositol trisphosphate in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13483–13490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sestoft L., Kristensen L. O. Determination of unidirectional fluxes of phosphate across plasma membrane in isolated perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1979 May;236(5):C202–C210. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1979.236.5.C202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Gevers G. The catalytic activity of phosphorylase b in the liver. With a note on the assay in the glycogenolytic direction. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 15;200(2):327–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2000327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Chance B., Quistorff B. A possible role of inorganic phosphate as a regulator of oxidative phosphorylation in combined urea synthesis and gluconeogenesis in perfused rat liver. A phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10034–10040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran-Thi T. A., Häussinger D., Gyufko K., Decker K. Stimulation of prostaglandin release by Ca2+-mobilizing agents from the perfused rat liver. A comparative study on the action of ATP, UTP, phenylephrine, vasopressin and nerve stimulation. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Jan;369(1):65–68. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandebroeck A., Bollen M., De Wulf H., Stalmans W. An assessment of the importance of intralysosomal and of alpha-amylolytic glycogenolysis in the liver of normal rats and of rats with a glycogen-storage disease. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 16;153(3):621–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanstapel F., Waebens M., Van Hecke P., Decanniere C., Stalmans W. The cytosolic concentration of phosphate determines the maximal rate of glycogenolysis in perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):207–212. doi: 10.1042/bj2660207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


