Abstract
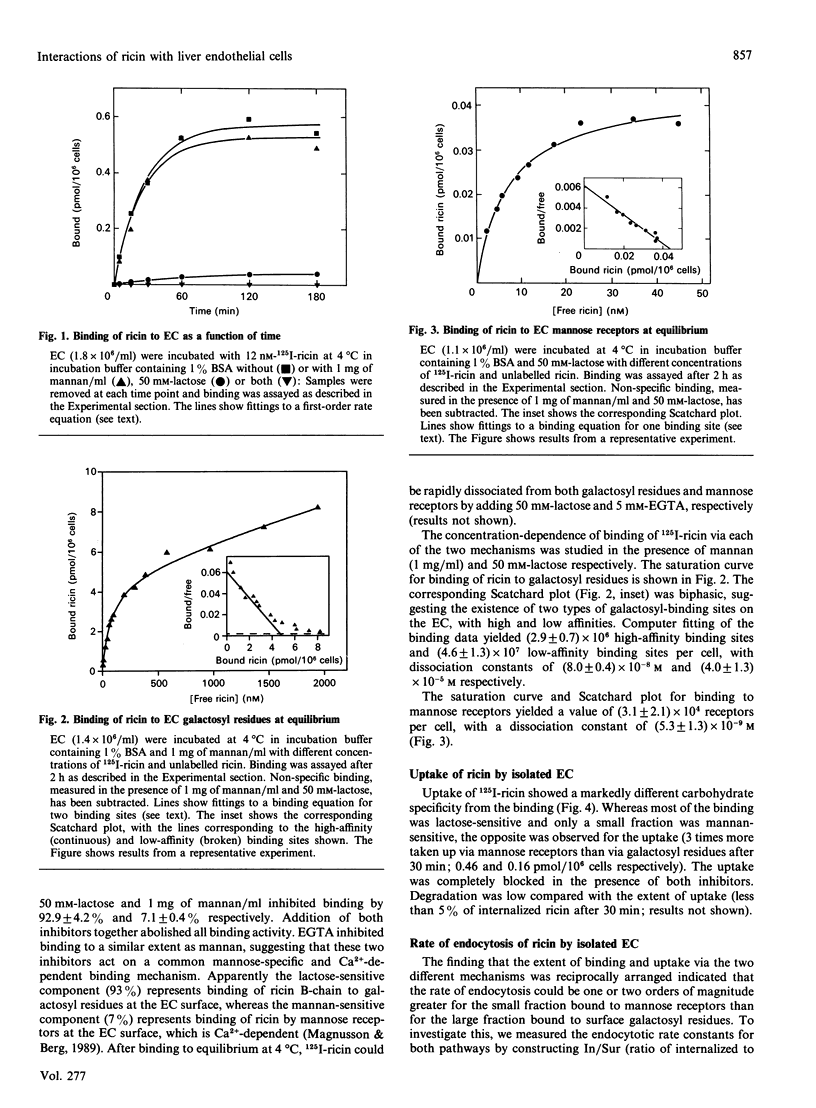
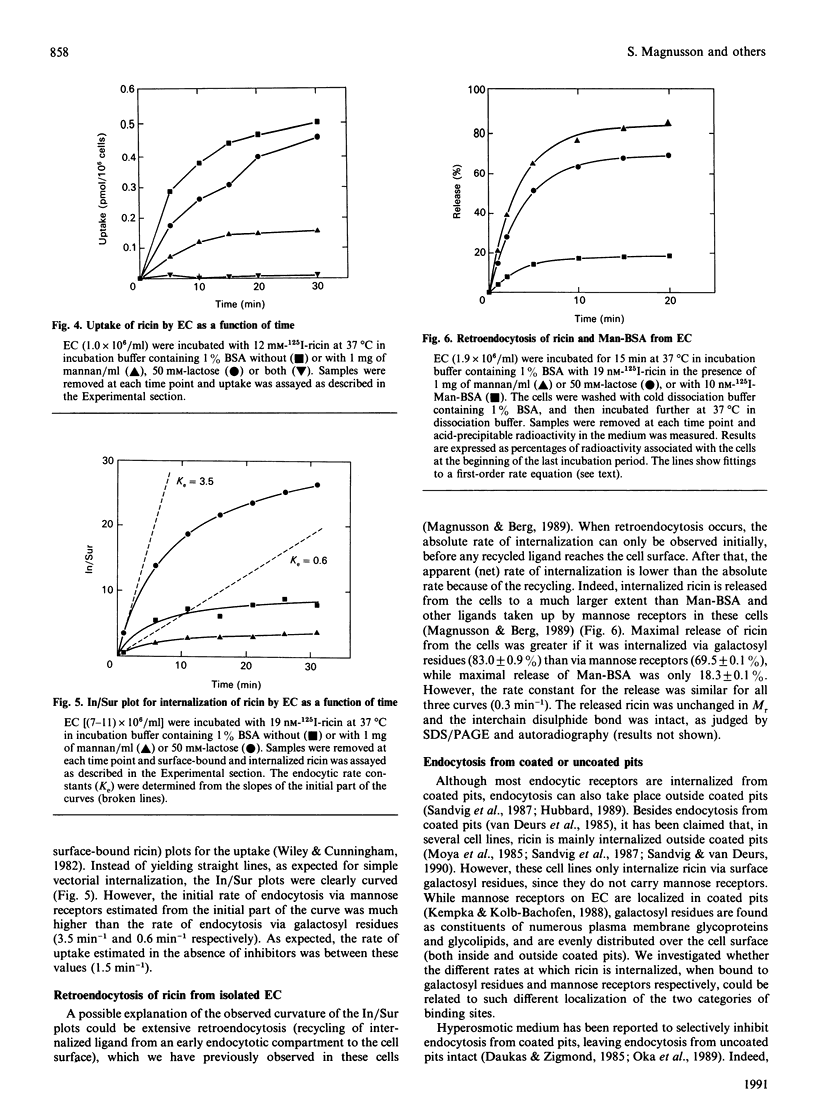
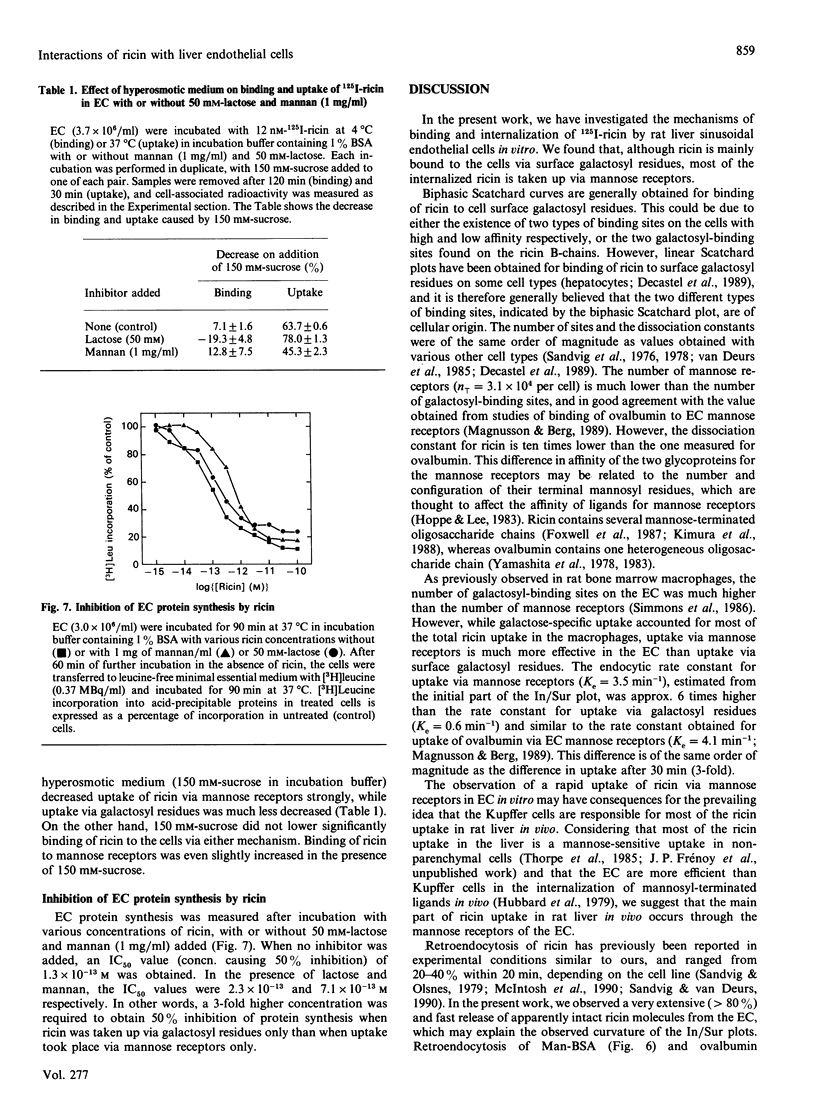
We have investigated the interactions of the plant toxin ricin with sinusoidal endothelial rat liver cells (EC). In these cells, ricin can be bound and internalized via either cell surface galactosyl residues or mannose receptors. Binding and uptake via galactosyl residues and mannose receptors was studied in the presence of mannan (1 mg/ml) and lactose (50 mM) respectively. Whereas most of the ricin binding was accounted for by cell surface galactosyl residues, uptake of ricin via mannose receptors was much more efficient than uptake via galactosyl residues. Internalized ricin is subject to extensive retroendocytosis (recycling to the cell surface from an early endocytic compartment). Retroendocytosis occurs after internalization of ricin via either pathway and to a much greater extent than for other glycoproteins taken up via mannose receptors of the EC. Hyperosmolarity (150 mM-sucrose), which is known to inhibit endocytosis from coated pits, strongly inhibited ricin uptake via mannose receptors, but had less effect on uptake via galactosyl residues. This suggests that only part of the galactose-specific uptake takes place from coated pits. Protein synthesis in EC was very sensitive to ricin [concn. causing half-maximal inhibition (IC50) = 1.3 x 10(-13) M]. Mannan was slightly more effective than lactose in protecting the EC protein synthesis from ricin toxicity.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structural determinants of Ricinus communis agglutinin and toxin specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9795–9799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Boman D., Seglen P. O. Induction of tryptophan oxygenase in primary rat liver cell suspensions by glucocorticoid hormone. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jun;72(2):571–574. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingen A., Creppy E. E., Gut J. P., Dirheimer G., Kirn A. The Kupffer cell is the first target in ricin-induced hepatitis. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1987 Apr;19(2):247–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braham K., Junqua S., Tursz T., Le Pecq J. B., Lipinski M. Kinetic analysis of choriocarcinoma cell intoxication induced by ricin and ricin A chain immunotoxin. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):806–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daukas G., Zigmond S. H. Inhibition of receptor-mediated but not fluid-phase endocytosis in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1673–1679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decastel M., Haentjens G., Aubery M., Goussault Y. Differential entry of ricin into malignant and normal rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Feb;180(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmanuel F., Turpin E., Alfsen A., Frénoy J. P. Separation of ricin A- and B-chains after dithiothreitol reduction. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):134–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foxwell B. M., Blakey D. C., Brown A. N., Donovan T. A., Thorpe P. E. The preparation of deglycosylated ricin by recombination of glycosidase-treated A- and B-chains: effects of deglycosylation on toxicity and in vivo distribution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 20;923(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertler A. A., Frankel A. E. Immunotoxins: a clinical review of their use in the treatment of malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Dec;7(12):1932–1942. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.12.1932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe C. A., Lee Y. C. Stimulation of mannose-binding activity in the rabbit alveolar macrophage by simple sugars. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12831–12834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe C. A., Lee Y. C. The binding and processing of mannose-bovine serum albumin derivatives by rabbit alveolar macrophages. Effect of the sugar density. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14193–14199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L. Endocytosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;1(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Wilson G., Ashwell G., Stukenbrok H. An electron microscope autoradiographic study of the carbohydrate recognition systems in rat liver. I. Distribution of 125I-ligands among the liver cell types. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):47–64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempka G., Kolb-Bachofen V. Binding, uptake, and transcytosis of ligands for mannose-specific receptors in rat liver: an electron microscopic study. Exp Cell Res. 1988 May;176(1):38–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Hase S., Kobayashi Y., Kyogoku Y., Ikenaka T., Funatsu G. Structures of sugar chains of ricin D. J Biochem. 1988 Jun;103(6):944–949. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindberg G. M., Magnusson S., Berg T., Smedsrød B. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of ovalbumin by two carbohydrate-specific receptors in rat liver cells. The intracellular transport of ovalbumin to lysosomes is faster in liver endothelial cells than in parenchymal cells. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):197–203. doi: 10.1042/bj2700197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson S., Berg T. Extremely rapid endocytosis mediated by the mannose receptor of sinusoidal endothelial rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):651–656. doi: 10.1042/bj2570651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh D., Timar J., Davies A. J. The intracellular movement and cycling of ricin. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;52(1):77–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsigny M., Roche A. C., Midoux P. Uptake of neoglycoproteins via membrane lectin(s) of L1210 cells evidenced by quantitative flow cytofluorometry and drug targeting. Biol Cell. 1984;51(2):187–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya M., Dautry-Varsat A., Goud B., Louvard D., Boquet P. Inhibition of coated pit formation in Hep2 cells blocks the cytotoxicity of diphtheria toxin but not that of ricin toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):548–559. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J. The interaction of Ricinus communis agglutinin with normal and tumor cell surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka J. A., Christensen M. D., Weigel P. H. Hyperosmolarity inhibits galactosyl receptor-mediated but not fluid phase endocytosis in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):12016–12024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Sandvig K., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Immunotoxins--entry into cells and mechanisms of action. Immunol Today. 1989 Sep;10(9):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Carew T. E., Glass C. K., Green S. R., Taylor C. A., Jr, Attie A. D. A radioiodinated, intracellularly trapped ligand for determining the sites of plasma protein degradation in vivo. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):791–800. doi: 10.1042/bj2120791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsden C. S., Drayson M. T., Bell E. B. The toxicity, distribution and excretion of ricin holotoxin in rats. Toxicology. 1989 Apr;55(1-2):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(89)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Effect of temperature on the uptake, excretion and degradation of abrin and ricin by HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Entry of the toxic proteins abrin, modeccin, ricin, and diphtheria toxin into cells. II. Effect of pH, metabolic inhibitors, and ionophores and evidence for toxin penetration from endocytotic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7504–7513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Acidification of the cytosol inhibits endocytosis from coated pits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):679–689. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Binding, uptake and degradation of the toxic proteins abrin and ricin by toxin-resistant cell variants. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):13–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb11992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Selective modulation of the endocytic uptake of ricin and fluid phase markers without alteration in transferrin endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6382–6388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger P. H., Doebber T. W., Mandell B. F., White R., DeSchryver C., Rodman J. S., Miller M. J., Stahl P. Plasma clearance of glycoproteins with terminal mannose and N-acetylglucosamine by liver non-parenchymal cells. Studies with beta-glucuronidase, N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase, ribonuclease B and agalacto-orosomucoid. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):103–109. doi: 10.1042/bj1760103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons B. M., Stahl P. D., Russell J. H. Mannose receptor-mediated uptake of ricin toxin and ricin A chain by macrophages. Multiple intracellular pathways for a chain translocation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7912–7920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilleter D. N., Paine A. J., Stirpe F. A comparison of the accumulation of ricin by hepatic parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells and its inhibition of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):495–500. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilleter D. N., Price R. J., Thorpe P. E. Modification of the carbohydrate in ricin with metaperiodate and cyanoborohydride mixtures: effect on binding, uptake and toxicity to parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 27;842(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrød B., Pertoft H., Gustafson S., Laurent T. C. Scavenger functions of the liver endothelial cell. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):313–327. doi: 10.1042/bj2660313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe P. E., Detre S. I., Foxwell B. M., Brown A. N., Skilleter D. N., Wilson G., Forrester J. A., Stirpe F. Modification of the carbohydrate in ricin with metaperiodate-cyanoborohydride mixtures. Effects on toxicity and in vivo distribution. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turpin E., Goussault Y., Lis H., Sharon N. Nature of the receptor sites for galactosyl-specific lectins on human lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jun;152(2):486–492. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90650-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. The endocytotic rate constant. A cellular parameter for quantitating receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4222–4229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Tachibana Y., Kobata A. The structures of the galactose-containing sugar chains of ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3862–3869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Ueda I., Kobata A. Sulfated asparagine-linked sugar chains of hen egg albumin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14144–14147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenilman M. E., Fiani M., Stahl P. D., Brunt E. M., Flye M. W. Selective depletion of Kupffer cells in mice by intact ricin. Transplantation. 1989 Jan;47(1):200–203. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198901000-00043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zentz C., Frénoy J. P., Bourrillon R. Binding of galactose and lactose to ricin. Equilibrium studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 26;536(1):18–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Tønnessen T. I., Petersen O. W., Sandvig K., Olsnes S. Routing of internalized ricin and ricin conjugates to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):37–47. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


