Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a hemoglobinopathy characterized by the occurrence of vaso‐occlusive events, severe chronic hemolytic anemia, and ultimately chronic complications and end‐organ damages. 1 , 2 , 3 SCD pathophysiology has been shown to be extremely complex, resulting from microcirculatory dysfunctions associated with altered vaso‐regulation and activation of inflammation cascades responsible of sterile inflammatory state, endothelial and neutrophil activation, and release of neutrophil extracellular trap (NET). 1 , 4 , 5 , 6 More recently, a dysfunctional erythropoiesis has been described in SS patients characterized by high level of reticulocytes, increased apoptosis at the later stage of erythropoiesis, and abnormal retention of mitochondria in red blood cells (RBCs). 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 It is noteworthy that the functionality of these mitochondria in mature sickle RBCs remains controversial 11 , 12 and mechanisms responsible for the mitochondrial retention during erythropoiesis have not been identified. Besides these unanswered points, several groups reported in vitro evidence that plasma mitochondrial DNA released by hemolysis of these abnormal RBCs could trigger type I interferon production 12 and NET release in SCD patients. 13 Altogether, these studies suggested that mitochondrial DNA from sickle mature RBCs could play a key role in the proinflammatory state associated with the disease.
In the present study, we characterized mature RBCs retaining mitochondria in a large cohort of the two main SCD genotypes, that is, SS and SC adult patients (71 and 40 patients, respectively) compared to 21 AA control individuals. We analyzed associations between mitochondria retention and hemolysis as well as inflammation markers (see patients and methods in Supporting Information and Supporting Information S1: Table 1 for the biological and demographic parameters).
Mitochondria presence in mature RBCs, total, and stress reticulocytes was assessed using flow cytometry (CD71/TO and/or MitoTracker Deep Red (MTKDR) staining) (Figure 1A). SS patients exhibited significant higher percentage of total circulating reticulocytes (5.0% ± 2.2%) compared to AA healthy donors (1.1% ± 0.4%), with a significant intermediate phenotype for SC patients (3.6% ± 1.7%) (Figure 1Bi). SS patients presented significant high levels of stress reticulocytes (2.6% ± 1.2%) compared to very low level observed in AA healthy donors (0.14 ± 0.09) while SC patients exhibited significant intermediate level (1.8% ± 1.0%) (Figure 1Bii). We did not observe significant difference of total and stress reticulocyte percentages between hydroxyurea (HU)‐treated and nontreated SS patients (Figure 1Biii,iv). Percentage of mitochondria+‐total reticulocytes was significantly higher in SS patients (25.0% ± 13.2%) compared to AA healthy donors (11.9% ± 8.1%), with an intermediate percentage for SC patients (19.1±13.1%) not statistically different with either AA nor SS individuals (Figure 1Ci). The same pattern was observed for stress reticulocytes with significant high level of mitochondria+‐stress reticulocytes in SS patients (40% ± 16.4%) compared to SC patients (26.0% ± 15.5%) and AA donors (26.0% ± 8.4%) (Figure 1Cii). HU treatment did not impact mitochondria retention in total and stress reticulocytes (Figure 1Ciii,iv). We showed that mature RBCs from SS patients exhibited an abnormal mitochondria retention rate (0.46% ± 0.5%) 13 times higher than that of AA controls (0.03% ± 0.06%). SC patients exhibited intermediate percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs (0.21 ± 0.06) significantly different than that of both SS and AA individuals (Figure 1Di). Hydroxyurea treatment did not impact the percentage of mitochondrial retention in mature RBCs of SS patients (Figure 1Dii).
Figure 1.
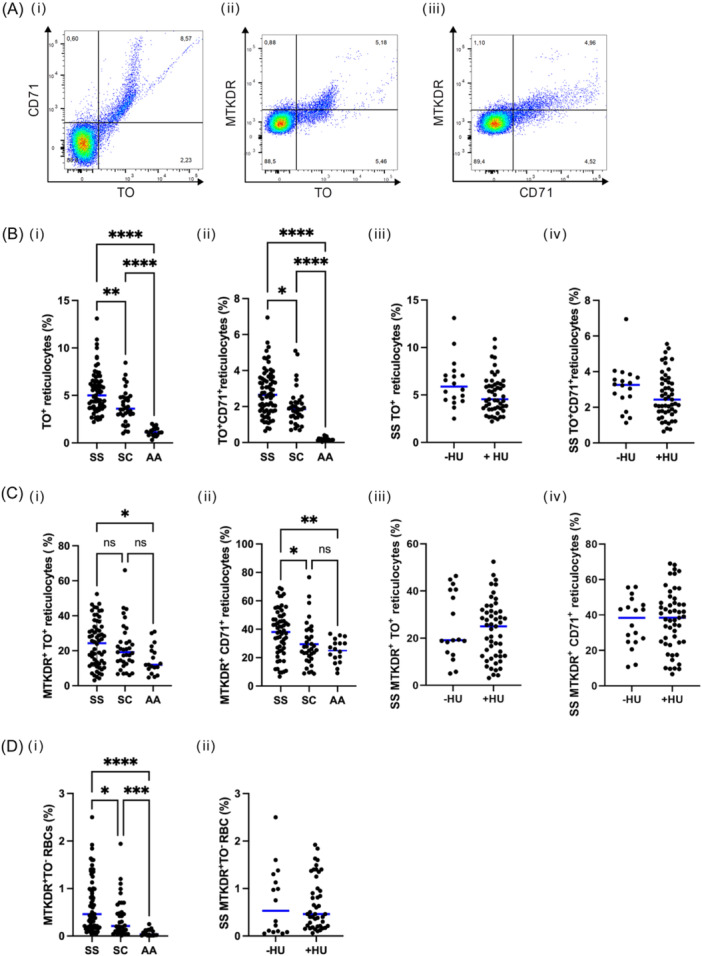
Detection and quantification of circulating erythroid cells retaining mitochondria by flow cytometry in SS, SC patients, and AA healthy individuals. (A) Flow cytometry gating strategy of CD71/TO and/or MitoTracker Deep Red (MTKDR) staining. (B) Percentage of total (i) and stress (ii) reticulocytes in SS, SC patients, and AA healthy individuals and total (iii) and stress (iv) reticulocytes in SS patients treated or not with HU. (C) Percentage of mitochondria retention in total (i) and stress (ii) reticulocytes in SS, SC patients, and AA healthy individuals and in total (iii) and stress (iv) reticulocytes in SS patients treated or not by HU. (D) Mitochondria retention in mature RBCs in SS and SC patients and in AA controls (i) and in SS patients treated or not with HU (ii).
We then investigated the correlations between the percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs and markers of hemolysis as well as hemorheological parameters of SS and SC patients (Supporting Information S1: Table 2A). The percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs was negatively correlated with hemoglobin level in SS patients and with RBC deformability in SC patients while a trend was observed in SS patients. The percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs was positively correlated with the one of total (TO+) and stress reticulocytes (CD71+) in both SS and SC patients (Supporting Information S1: Table 2B).
To assess a link between SCD proinflammatory state and mitochondria retention, we analyzed plasma levels of 11 cytokines (IL6, IFNγ, TNFα, IFNα2, IL1β, IL4, IL5, IL8, IL10, IL22, and IL12p70) in the three groups. Four of investigated cytokines exhibited differential expression levels between SCD and AA individuals, that is, IL6, IFNγ, TNFα, and IFNα2 (Figure 2Ai–iv and Supporting Information S1: Figure 1). Interestingly, HU treatment did not impact cytokines levels in SS patients (Figure 2Av–viii). No correlation was detected between the percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs and plasma levels of the four cytokines displaying differential inter‐group levels (Supporting Information S1: Table 3).
Figure 2.
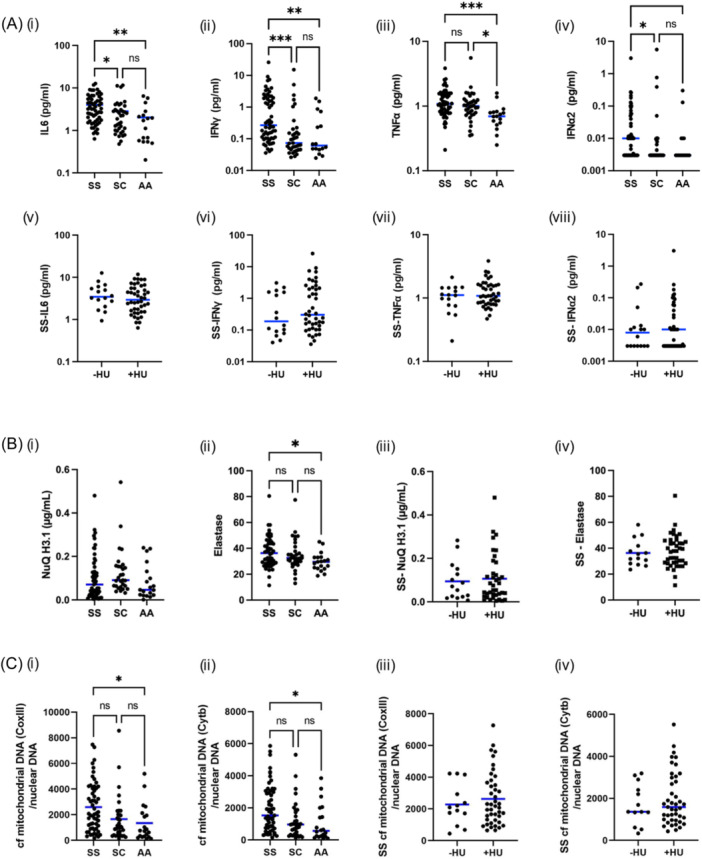
Quantification of plasmatic cytokines, NET markers, and cf mitochondrial DNA in SS, SC, and AA individuals. (A) Plasma levels of IL6 (i), IFNγ (ii), TNFα (iii) and IFN α2 (iv) in SS, SC and AA individuals and of IL6 (v), IFNγ (vi), TNFα (vii), and IFN α2 (viii) in SS patients treated or not with HU (B) NuQ H3.1 (i) and elastase (ii) level in SS, SC, and AA individuals and NuQ H3.1 (iii) and elastase (iv) level in SS patients treated or not with HU (C) CoxIII (i) and Cytb (ii) mRNA quantification in SS, SC, and AA individuals and CoxIII (iii) and Cytb (iv) in SS patients treated or not with HU.
In addition, we investigated in vivo NET formation by analyzing plasma concentration of histone H3‐containing cell free (cf) nucleosomes and elastase (Figure 2Bi,ii). Levels of histone H3‐containing cf nucleosomes was similar between SS, SC or AA groups (Figure 2Bi), while increased plasmatic elastase level was detected in SS patients compared to SC patients or AA healthy donors (Figure 2Bii). HU treatment did not modify NET formation markers (Figure 2Biii,iv). No correlation between plasmatic level of elastase and the percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs has been observed (Supporting Information S1: Table 3).
Finally, we determined the ratio of cf mitochondrial DNA/nuclear DNA in the cohort. We performed the analysis on two mitochondrial genes: Cytochrome b and subunit III of cytochrome c oxidase (Figure 2Ci,ii). cf mitochondrial DNA was significantly higher in SS patients compared to healthy controls, with an intermediate phenotype for SC patients. HU treatment did not impact the ratio of cf mitochondrial DNA/nuclear DNA in the cohort (Figure 2Ciii,iv). Unexpectedly, no correlation was observed between the percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs and plasmatic cf mitochondria DNA in any of the patient groups (Supporting Information S1: Table 4).
In conclusion, our data highlight that: (i) a RBC subpopulation containing mitochondria is observed in a consequent cohort of SS and SC patients, although with a lower extent in the latter patient group, (ii) the percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs is correlated with Hb level, hemolysis marker, in SS (iii) the percentage of mitochondria+‐mature RBCs is not associated to the inflammation phenotype of SS and SC patients.
Several studies showed the presence of this abnormal circulating erythroid population containing mitochondria both in SS patients and in SCD mouse model, and more recently in SC patients. 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 However, it is noteworthy to highlight that the phenotyping of mature circulating RBCs is not consistent in‐between studies. Indeed, most of these studies define the mature circulating RBC based on the absence of CD71 marker (CD71− cells), that is, the transferrin receptor, at the cell surface. 9 , 12 However, chronic anemia occurring in SCD results in the premature release into the bloodstream of immature stress reticulocytes expressing cell‐surface CD71. Meaning that stress reticulocytes can be identified as CD71+TO+ cells while classical reticulocytes are CD71−TO+ and mature RBCs are CD71−TO−. In the current study, we clearly showed that in AA individuals, circulating reticulocytes have all lost CD71 expression while remaining TO+. In consequence, mature RBCs should be identified as TO− cells and not only as CD71− cells. This characterization is very relevant for studies that attempt to evaluate mitochondrial function in circulating erythroid cells, as mitochondria could remain functional in reticulocytes but not in mature RBCs.
Based on this reliable erythroid population characterization, we establish that classical and stress reticulocytes as well as mature RBCs in SCD patients contain mitochondria and that this abnormal retention is correlated to Hb level, one marker of hemolysis and thus is probably resulting from stress erythropoiesis. 14 As SCD represents also a chronic inflammatory disorder, we investigated a large panel of proinflammatory markers and show that plasmatic levels of IL6, TNFα, IFNα et IFNγ are higher in SS patients compared to those of AA donors with intermediate levels for SC patients. 6 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 Unexpectedly, no correlation was found between these higher levels of inflammation mediators and the percentage of mature RBCs containing mitochondria, highly suggesting that, at basal state, mitochondria retention in mature RBCs is not directly link to the SCD inflammatory context. Several studies described a link between the persistence of mitochondria in circulating erythroid cells and inflammation in disorders besides SCD such as RETT syndrome and lupus, notably through in vitro neutrophil and/or macrophages activation. 12 , 19 , 20 , 21 However, our data collected in vivo in SS and SC patients did not show any correlation between higher neutrophil activation and erythroid mitochondrial retention, suggesting that mitochondrial retention and neutrophil activation are probably not directly related. Finally, our data support the evidence that mitochondrial DNA is circulating freely in plasma of SS patients and with a lower rate in SC patients, but still higher than those observed in healthy donors. However, cf mitochondrial DNA level did not correlate with mitochondria retention in erythroid cells, thus suggesting that the detected cf mitochondrial DNA did not arise exclusively from erythroid cells, but most likely from other circulating cells such as neutrophils. This hypothesis is supported by the study of Caielli et al., showing the capacity of neutrophils to release cf mitochondrial DNA in vitro independently of NETs formation or necrosis. 19
Overall, our current study strongly reinforces the concept of an abnormal mitochondria retention in SS and more surprisingly in SC patients, and finely characterizes the erythroid population that retained mitochondria. We assumed that this abnormal retention of mitochondria is related to the patient's hemolytic status and is not associated with inflammation markers.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Marc Romana, Sandrine Laurance, Caroline Le Van Kim, Mariano A. Ostuni, Maryse Etienne‐Julan: Conceptualization. Laetitia Claer, Karim Dorgham, Mariano A. Ostuni, Sandrine Laurance, Marc Romana, Maryse Etienne‐Julan: Methodology. Sandrine Laurance, Marc Romana, Mariano A. Ostuni, Caroline Le Van Kim, Maryse Etienne‐Julan: Validation. Sandrine Laurance, Marc Romana, Mariano A. Ostuni, Lea Kuznicki, Laetitia Claer: Formal analysis. Lea Kuznicki, Laetitia Claer, Karim Dorgham, Marie‐Dominique Hardy‐Dessources, Sylvie Ravion, Yohann Garnier, Vanessa Tarer, Benoit Tressières, Sophie D. Lefevre: Investigation. Karim Dorgham, Maryse Etienne‐Julan, Veronique Baccini: Resources. Sandrine Laurance, Marc Romana, Laetitia Claer, Lea Kuznicki, Mariano A. Ostuni, Caroline Le Van Kim, Maryse Etienne‐Julan: Data curation. Sandrine Laurance, Marc Romana: Writing original draft preparation. Sandrine Laurance, Marc Romana, Mariano A. Ostuni, Caroline Le Van Kim, Maryse Etienne‐Julan, Lea Kuznicki, Laetitia Claer: Writing review and editing. Sandrine Laurance, Marc Romana, Maryse Etienne‐Julan: Project administration. Sandrine Laurance, Marc Romana, Caroline Le Van Kim: Funding acquisition.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
FUNDING
This work was supported by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (Inserm), and the Laboratory of Excellence GR‐Ex.
Supporting information
Supporting information.
Supporting information.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
REFERENCES
- 1. Kato GJ, Steinberg MH, Gladwin MT. Intravascular hemolysis and the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(3):750‐760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Rees DC, Williams TN, Gladwin MT. Sickle‐cell disease. Lancet. 2010;376(9757):2018‐2031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kato GJ, Piel FB, Reid CD, et al. Sickle cell disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Nader E, Romana M, Connes P. The red blood cell‐inflammation vicious circle in sickle cell disease. Front Immunol. 2020;11:454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Zhang D, Xu C, Manwani D, Frenette PS. Neutrophils, platelets, and inflammatory pathways at the nexus of sickle cell disease pathophysiology. Blood. 2016;127(7):801‐809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Sundd P, Gladwin MT, Novelli EM. Pathophysiology of sickle cell disease. Annu Rev Pathol: Mech Dis. 2019;14:263‐292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Sara El Hoss H, Sylvie Cochet C, Auria Godard G, et al. Fetal hemoglobin rescues ineffective erythropoiesis in sickle cell disease. Haematologica. 2021;106(10):2707‐2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Esperti S, Nader E, Boisson C, et al. Mitochondria retention in mature RBCs from haemoglobin SC patients. Br J Haematol. 2023;202(5):e36‐e38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Esperti S, Nader E, Stier A, et al. Increased retention of functional mitochondria in mature sickle red blood cells is associated with increased sickling tendency, hemolysis and oxidative stress. Haematologica. 2023;108:3086‐3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Jagadeeswaran R, Vazquez BA, Thiruppathi M, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of LSD1 and mTOR reduces mitochondrial retention and associated ROS levels in the red blood cells of sickle cell disease. Exp Hematol. 2017;50:46‐52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Martino S, Arlet JB, Odièvre MH, et al. Deficient mitophagy pathways in sickle cell disease. Br J Haematol. 2021;193(5):988‐993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Moriconi C, Dzieciatkowska M, Roy M, et al. Retention of functional mitochondria in mature red blood cells from patients with sickle cell disease. Br J Haematol. 2022;198(3):574‐586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Tumburu L, Ghosh‐Choudhary S, Seifuddin FT, et al. Circulating mitochondrial DNA is a proinflammatory DAMP in sickle cell disease. Blood. 2021;137(22):3116‐3126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Gallivan A, Alejandro M, Kanu A, et al. Reticulocyte mitochondrial retention increases reactive oxygen species and oxygen consumption in mouse models of sickle cell disease and phlebotomy‐induced anemia. Exp Hematol. 2023;122:55‐62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hermand P, Slim A, Emilie‐Fleur G, et al. The proteome of neutrophils in sickle cell disease reveals an unexpected activation of interferon alpha signaling pathway. Haematologica. 2020;105(12):2851‐2854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Platt OS. Sickle cell anemia as an inflammatory disease. J Clin Invest. 2000;106(3):337‐338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Barbu EA, Mendelsohn L, Samsel L, Thein SL. Pro‐inflammatory cytokines associate with NETosis during sickle cell vaso‐occlusive crises. Cytokine. 2020;127:154933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Conran N, Belcher JD. Inflammation in sickle cell disease. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2018;68(2‐3):263‐299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Caielli S, Athale S, Domic B, et al. Oxidized mitochondrial nucleoids released by neutrophils drive type I interferon production in human lupus. J Exp Med. 2016;213(5):697‐713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Caielli S, Cardenas J, de Jesus AA, et al. Erythroid mitochondrial retention triggers myeloid‐dependent type I interferon in human SLE. Cell. 2021;184(17):4464‐4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Sbardella D, Tundo GR, Campagnolo L, et al. Retention of mitochondria in mature human red blood cells as the result of autophagy impairment in Rett Syndrome. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting information.
Supporting information.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.


