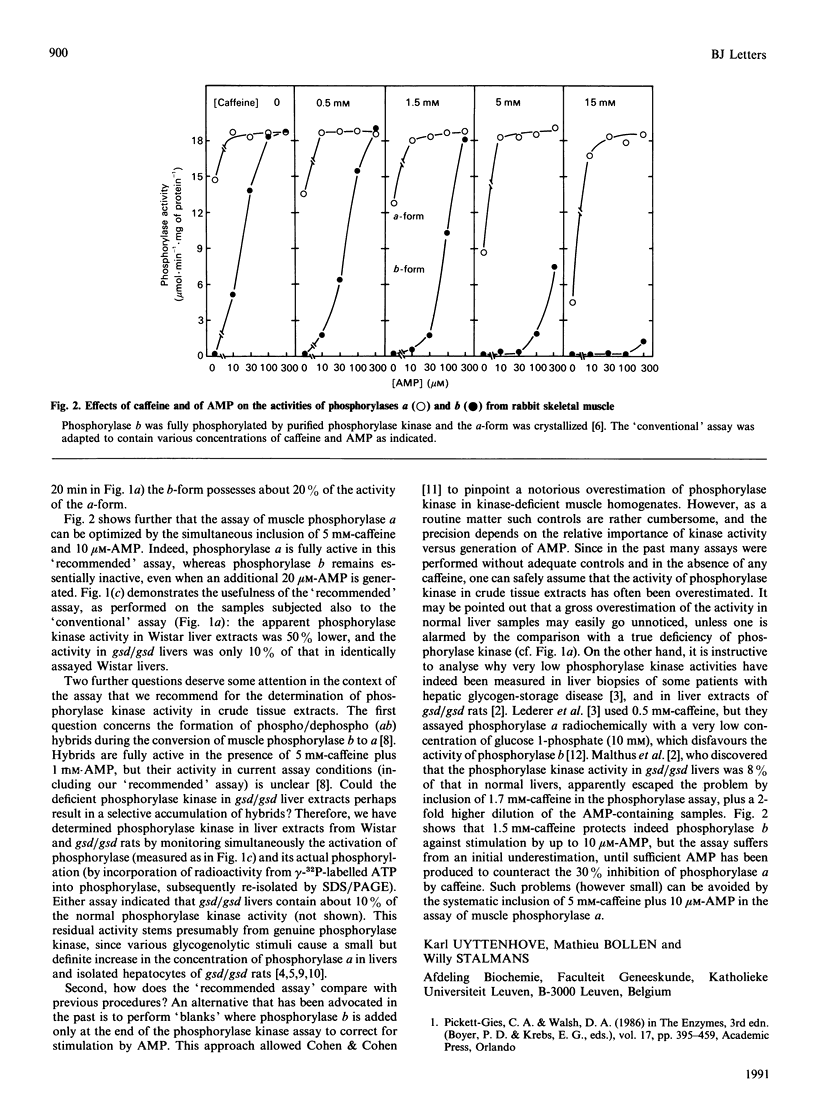
Full text
PDF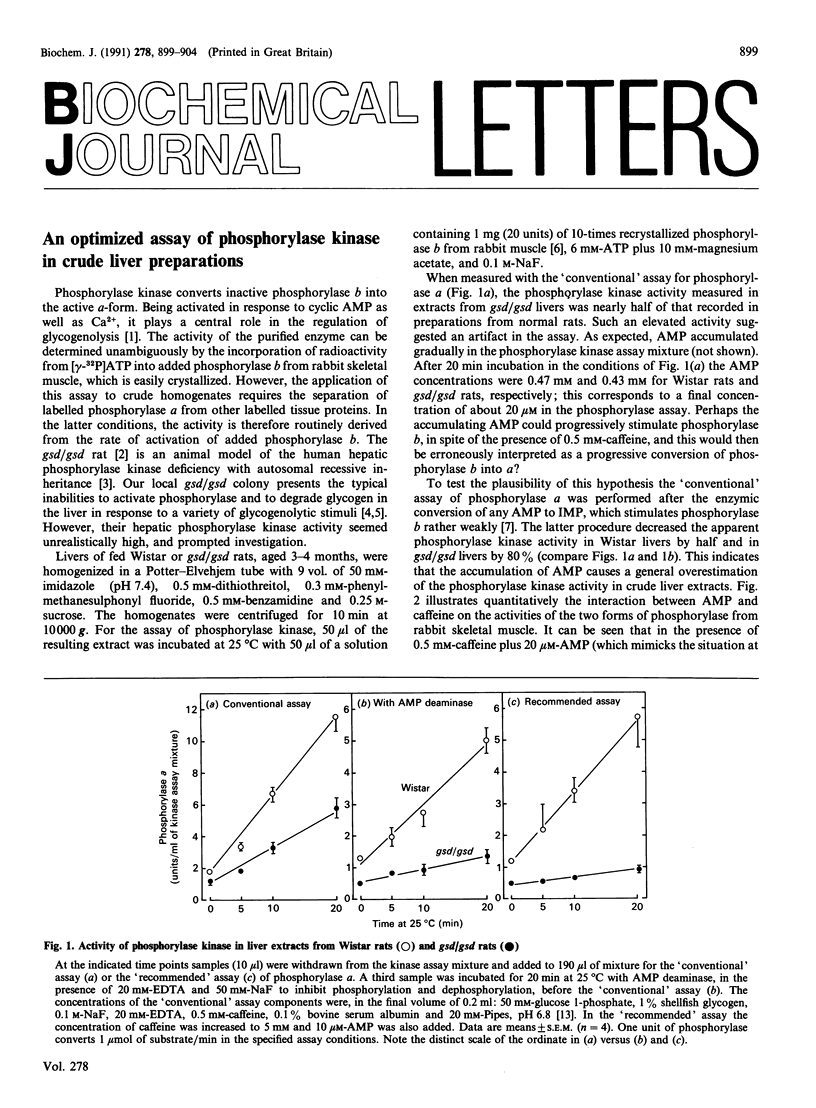

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniw J. F., Nimmo H. G., Yeaman S. J., Cohen P. Comparison of the substrate specificities of protein phosphatases involved in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):423–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1620423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. J., Wang J. H. Studies on the allosteric activation of glycogen phosphorylase b by Nucleotides. I. Activation of phosphorylase b by inosine monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 25;243(22):5892–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T., Cohen P. Skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase deficiency: detection of a protein lacking any activity in ICR-IAn mice. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaglen J. V., Malthus R. S., Redshaw-Loten J. C., Sneyd J. G. The action of anoxia and cyanide on glycogen breakdown in the liver of the gsd/gsd rat. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):323–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer B., Van Hoof F., Van den Berghe G., Hers H. Glycogen phosphorylase and its converter enzymes in haemolysates of normal human subjects and of patients with type VI glycogen-storage disease. A study of phosphorylase kinase deficiency. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;147(1):23–35. doi: 10.1042/bj1470023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutaya G., Sharma R. J., Griffiths J. R. Glycogenolysis in liver of phosphorylase kinase-deficient rats during liver perfusion and ischaemia. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):645–648. doi: 10.1042/bj2140645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthus R., Clark D. G., Watts C., Sneyd J. G. Glycogen-storage disease in rats, a genetically determined deficiency of liver phosphorylase kinase. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):99–106. doi: 10.1042/bj1880099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Hers H. G. The stimulation of liver phosphorylase b by AMP, fluoride and sulfate. A technical note on the specific determination of the a and b forms of liver glycogen phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandebroeck A., Bollen M., De Wulf H., Stalmans W. An assessment of the importance of intralysosomal and of alpha-amylolytic glycogenolysis in the liver of normal rats and of rats with a glycogen-storage disease. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 16;153(3):621–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandebroeck A., Uyttenhove K., Bollen M., Stalmans W. The hepatic glycogenolysis induced by reversible ischaemia or KCN is exclusively catalysed by phosphorylase a. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):685–688. doi: 10.1042/bj2560685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Newsholme P., Cawley K. C., van Patten S. M., Angelos K. L. Motifs of protein phosphorylation and mechanisms of reversible covalent regulation. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jan;71(1):285–304. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.1.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


