Abstract
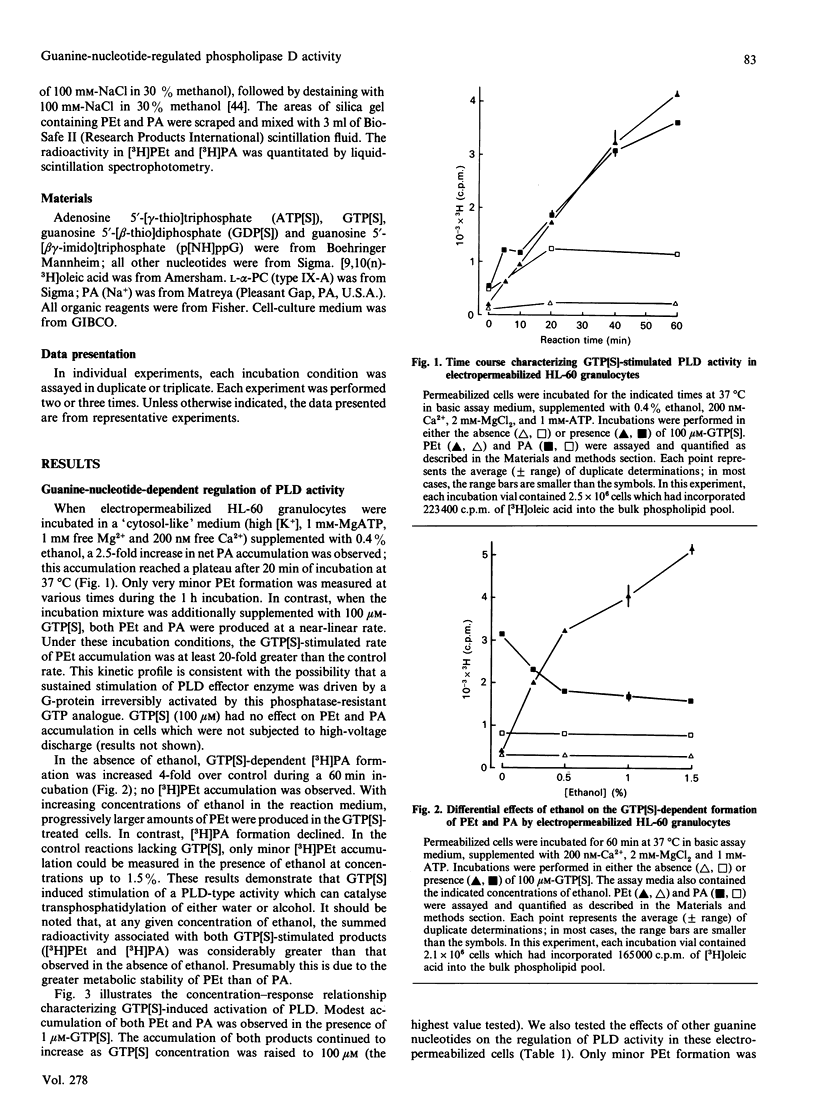
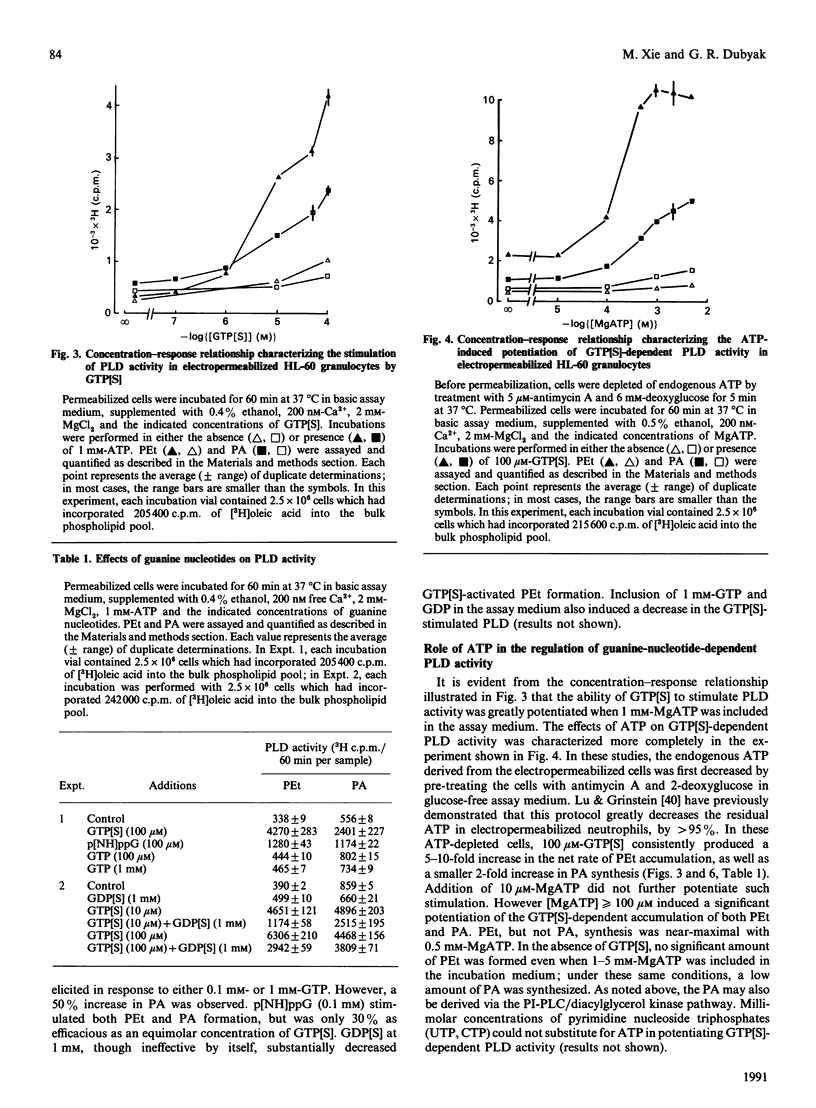
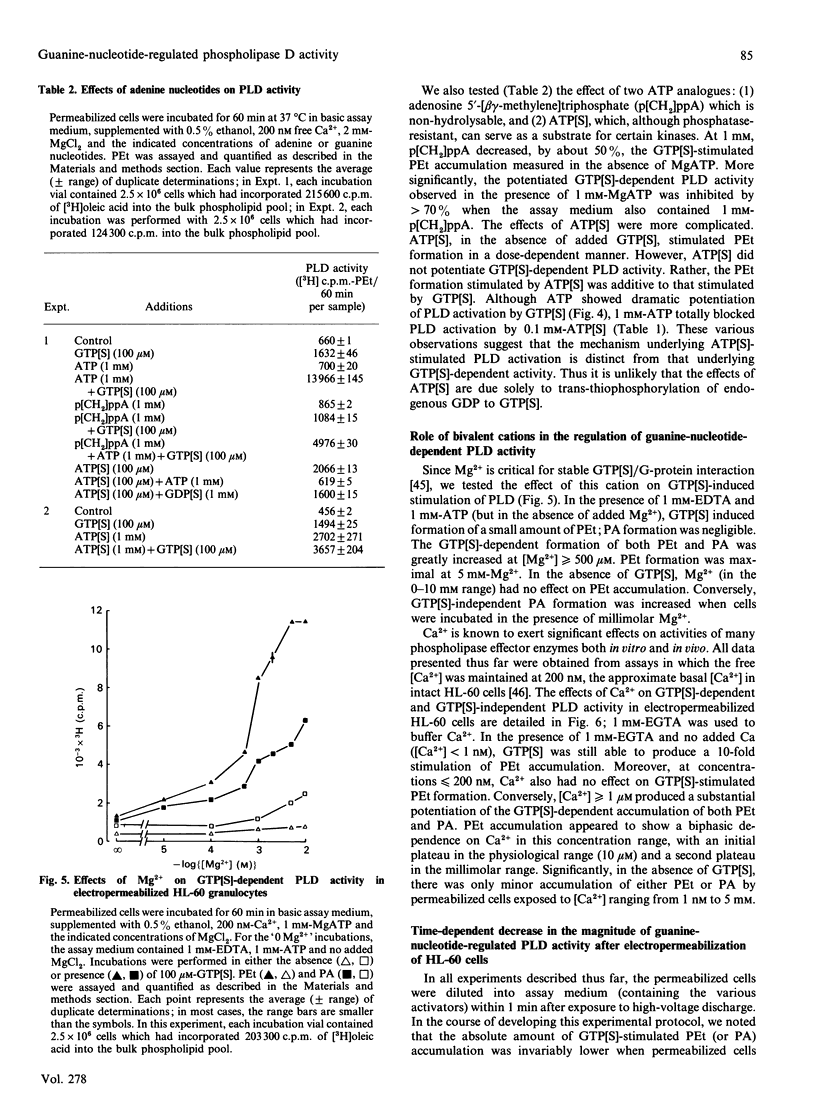
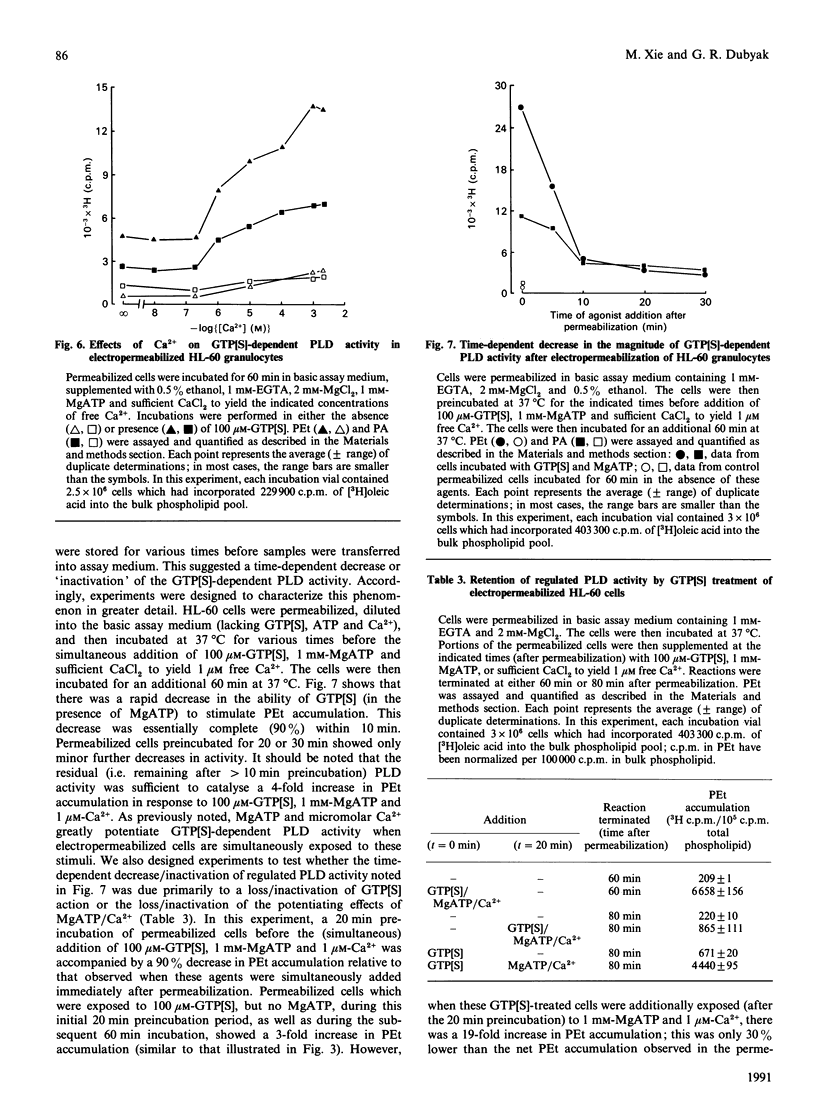
We have characterized the regulation of phospholipase D (PLD) in electropermeabilized HL-60 granulocytes in which endogenous phospholipids were pre-labelled with [3H]oleic acid. Treatment of these permeabilized cells with the non-hydrolysable GTP analogues guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) and guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate induced a sustained (near-linear for up to 60 min) accumulation of phosphatidic acid (PA). In the presence of ethanol a sustained production of phosphatidylethanol (PEt) was also observed. With increasing concentrations of ethanol, PEt formation increased, whereas PA formation declined; this indicated involvement of a PLD-type effector enzyme. The ability of GTP[S] to stimulate this PLD activity was Mg(2+)-dependent and was inhibited by GDP and its non-hydrolysable beta-thio analogue. Ca2+, at concentrations less than or equal to nM, had no effect on the GTP[S]-dependent PLD activity. However, higher concentrations of Ca2+ produced a significant potentiation of this activity. Inclusion of MgATP (greater than or equal to 0.1 mM), but not other nucleoside triphosphates, also induced a large potentiation of GTP[S]-dependent PLD activation. In the absence of guanine nucleotides, MgATP elicited no significant activation of PLD. Significantly, this effect of ATP was not mimicked by adenosine 5'-[beta gamma-methylene]triphosphate, a non-hydrolysable ATP analogue. Rather, this analogue inhibited both basal and ATP-potentiated GTP[S]-dependent PLD activity. This suggests that the ability of ATP to potentiate GTP[S]-dependent PLD activity involves phosphotransferase action rather than simple allosteric effects induced by adenine nucleotide binding. The absolute magnitude of the GTP[S]-dependent PLD activity which could be potentiated by MgATP was decreased by 90% when the permeabilized cells were preincubated for various times before addition of these stimulatory agents. This time-dependent loss of MgATP-induced potentiation was prevented when the permeabilized cells were preincubated in the presence of GTP[S]. These results demonstrate that electropermeabilized HL-60 granulocytes can be used to discriminate synergistic roles for a GTP-binding protein(s) and an ATP-dependent process (kinase?) in the regulation of phospholipase D activity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agwu D. E., McPhail L. C., Chabot M. C., Daniel L. W., Wykle R. L., McCall C. E. Choline-linked phosphoglycerides. A source of phosphatidic acid and diglycerides in stimulated neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1405–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthes J. C., Billah M. M., Cali A., Egan R. W., Siegel M. I. Chemotactic peptide, calcium and guanine nucleotide regulation of phospholipase C activity in membranes from DMSO-differentiated HL60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):825–833. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthes J. C., Eckel S., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D in homogenates from HL-60 granulocytes: implications of calcium and G protein control. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):657–664. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsinde J., Diez E., Fernandez B., Mollinedo F. Biochemical characterization of phospholipase D activity from human neutrophils. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):717–724. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Anthes J. C. The regulation and cellular functions of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):281–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2690281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Eckel S., Mullmann T. J., Egan R. W., Siegel M. I. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by phospholipase D determines phosphatidate and diglyceride levels in chemotactic peptide-stimulated human neutrophils. Involvement of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17069–17077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Pai J. K., Mullmann T. J., Egan R. W., Siegel M. I. Regulation of phospholipase D in HL-60 granulocytes. Activation by phorbol esters, diglyceride, and calcium ionophore via protein kinase- independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9069–9076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Phosphatidate accumulation in hormone-treated hepatocytes via a phospholipase D mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15309–15315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Wilson P. B., Exton J. H. Ca2+-mobilizing hormones elicit phosphatidylethanol accumulation via phospholipase D activation. FEBS Lett. 1987 Dec 10;225(1-2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonser R. W., Thompson N. T., Randall R. W., Garland L. G. Phospholipase D activation is functionally linked to superoxide generation in the human neutrophil. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2640617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Welsh C. J., Zhang Z. C., Cao H. T. Evidence for a protein kinase C-directed mechanism in the phorbol diester-induced phospholipase D pathway of diacylglycerol generation from phosphatidylcholine. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalifa V., Möhn H., Liscovitch M. A neutral phospholipase D activity from rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. Identification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17512–17519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplinski T. J., Niedel J. E. Cyclic nucleotide-induced maturation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):953–964. doi: 10.1172/JCI110707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Allan D. The fatty acid composition of phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidate and 1,2-diacylglycerol in stimulated human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):557–559. doi: 10.1042/bj2220557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S. Ca2+-dependent conversion of phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidate in neutrophils stimulated with fMet-Leu-Phe or ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 15;795(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. ATP stimulates secretion in human neutrophils and HL60 cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein coupled to phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. The receptors for ATP and fMetLeuPhe are independently coupled to phospholipases C and A2 via G-protein(s). Relationship between phospholipase C and A2 activation and exocytosis in HL60 cells and human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):715–723. doi: 10.1042/bj2630715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J. The HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line: proliferation, differentiation, and cellular oncogene expression. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1233–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen D. S., Baker B., Dubyak G. R. Pertussis toxin produces differential inhibitory effects on basal, P2-purinergic, and chemotactic peptide-stimulated inositol phospholipid breakdown in HL-60 cells and HL-60 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16181–16189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen D. S., Lazarus H. M., Shurin S. B., Stoll S. E., Dubyak G. R. Extracellular adenosine triphosphate activates calcium mobilization in human phagocytic leukocytes and neutrophil/monocyte progenitor cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1651–1660. doi: 10.1172/JCI114064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen D. S., Sanders M., Dubyak G. P2-purinergic receptors activate a guanine nucleotide-dependent phospholipase C in membranes from HL-60 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 12;1053(2-3):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domino S. E., Bocckino S. B., Garbers D. L. Activation of phospholipase D by the fucose-sulfate glycoconjugate that induces an acrosome reaction in spermatozoa. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9412–9419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Hill M., Furuya W. Activation of electropermeabilized neutrophils by adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (ATP[S]). Role of phosphatases in stimulus-response coupling. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):755–759. doi: 10.1042/bj2610755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Boyer J. L., Downes C. P. Phosphoinositide hydrolysis by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-activated phospholipase C of turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):583–593. doi: 10.1042/bj2520583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M. Phospholipase D. Adv Lipid Res. 1978;16:267–326. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024916-9.50011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving H. R., Exton J. H. Phosphatidylcholine breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and P2-purinergic agonists. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3440–3443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss Z., Anderson W. B. ATP stimulates the hydrolysis of phosphatidylethanolamine in NIH 3T3 cells. Potentiating effects of guanosine triphosphates and sphingosine. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7345–7350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss Z., Anderson W. B. Phorbol ester stimulates the hydrolysis of phosphatidylethanolamine in leukemic HL-60, NIH 3T3, and baby hamster kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1483–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Scrutton M. C. Gaining access to the cytosol: the technique and some applications of electropermeabilization. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):497–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2340497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Kanfer J. N. Phosphatidylethanol formation via transphosphatidylation by rat brain synaptosomal phospholipase D. J Neurochem. 1987 May;48(5):1597–1603. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie Y., Liscovitch M. Activation of phospholipase D by sphingoid bases in NG108-15 neural-derived cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3868–3872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmar R., Löffelholz K., Sandmann J. On the mechanism of muscarinic hydrolysis of choline phospholipids in the heart. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 15;37(24):4689–4695. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M. Phosphatidylethanol biosynthesis in ethanol-exposed NG108-15 neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells. Evidence for activation of a phospholipase D phosphatidyl transferase activity by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1450–1456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D. J., Grinstein S. ATP and guanine nucleotide dependence of neutrophil activation. Evidence for the involvement of two distinct GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13721–13729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffelholz K. Receptor regulation of choline phospholipid hydrolysis. A novel source of diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1543–1549. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F. Hormone-regulated phosphoinositide turnover in permeabilized cells and membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:111–126. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. W., Feldman D. R., Goldstein K. E., Wagner J. R. Long-term phorbol ester treatment dissociates phospholipase D activation from phosphoinositide hydrolysis and prostacyclin synthesis in endothelial cells stimulated with bradykinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. W., Michaelis K. P2-purinergic agonists stimulate phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylcholine in endothelial cells. Evidence for activation of phospholipase D. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8847–8856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullmann T. J., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Complement C5a activation of phospholipase D in human neutrophils. A major route to the production of phosphatidates and diglycerides. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1901–1908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Handa S. Coomassie brilliant blue staining of lipids on thin-layer plates. Anal Biochem. 1984 Nov 1;142(2):406–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90484-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmith P. E., Mills G. B., Grinstein S. Guanine nucleotides induce tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the respiratory burst in neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):893–897. doi: 10.1042/bj2570893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D catalyzes phospholipid metabolism in chemotactic peptide-stimulated HL-60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12472–12477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Z., Drewes L. R. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor regulates phosphatidylcholine phospholipase D in canine brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21720–21724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold S. L., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Activation of human neutrophil phospholipase D by three separable mechanisms. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):208–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y. Studies of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):546–550. doi: 10.1126/science.2541501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. Phosphatidylethanol formation in human platelets: evidence for thrombin-induced activation of phospholipase D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1090–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80744-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Sandborg R. R. Ca2(+)-induced secretion by electropermeabilized human neutrophils. The roles of Ca2+, nucleotides and protein kinase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 9;1052(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90068-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Guanine nucleotides stimulate polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytotic secretion from HL60 cells permeabilized with streptolysin O. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2500375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tettenborn C. S., Mueller G. C. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate activates phosphatidylethanol and phosphatidylglycerol synthesis by phospholipase D in cell lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):249–255. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel S., Downey G. P., Grinstein S., Pâquet M. R. Activation of permeabilized HL60 cells by vanadate. Evidence for divergent signalling pathways. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):127–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2690127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meulen J., Haslam R. J. Phorbol ester treatment of intact rabbit platelets greatly enhances both the basal and guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-stimulated phospholipase D activities of isolated platelet membranes. Physiological activation of phospholipase D may be secondary to activation of phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):693–700. doi: 10.1042/bj2710693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


