Abstract
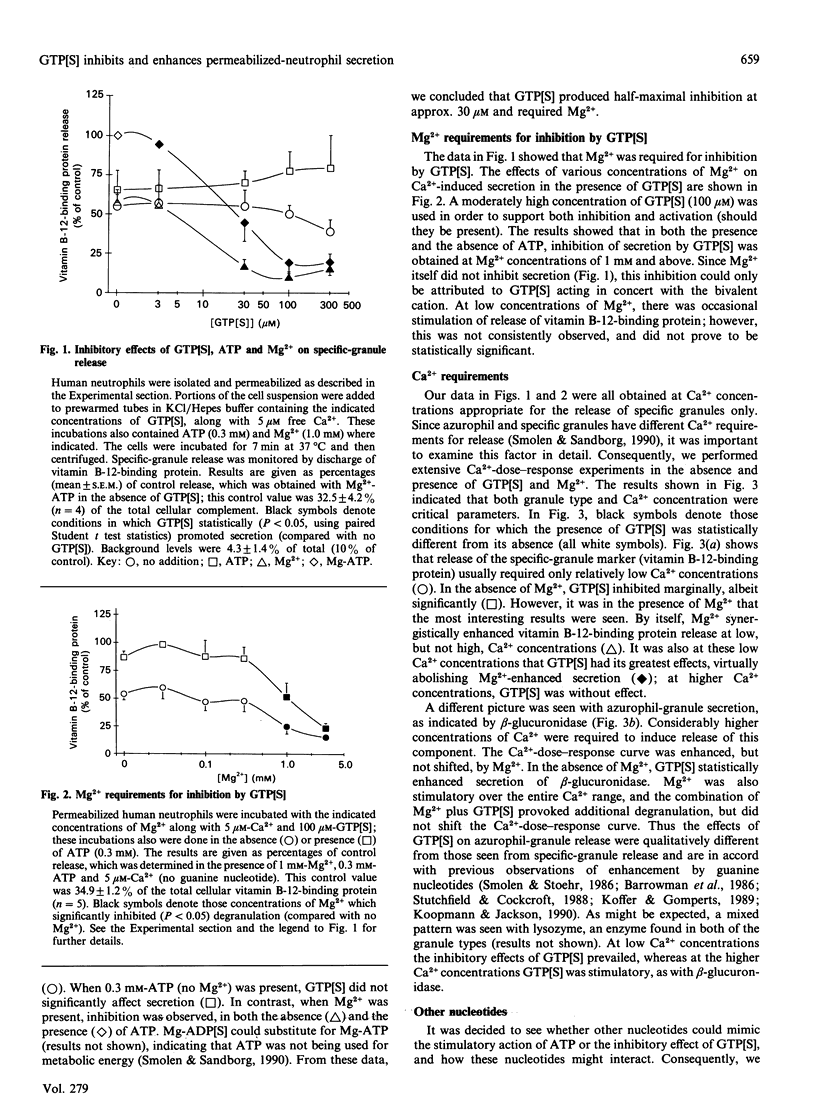
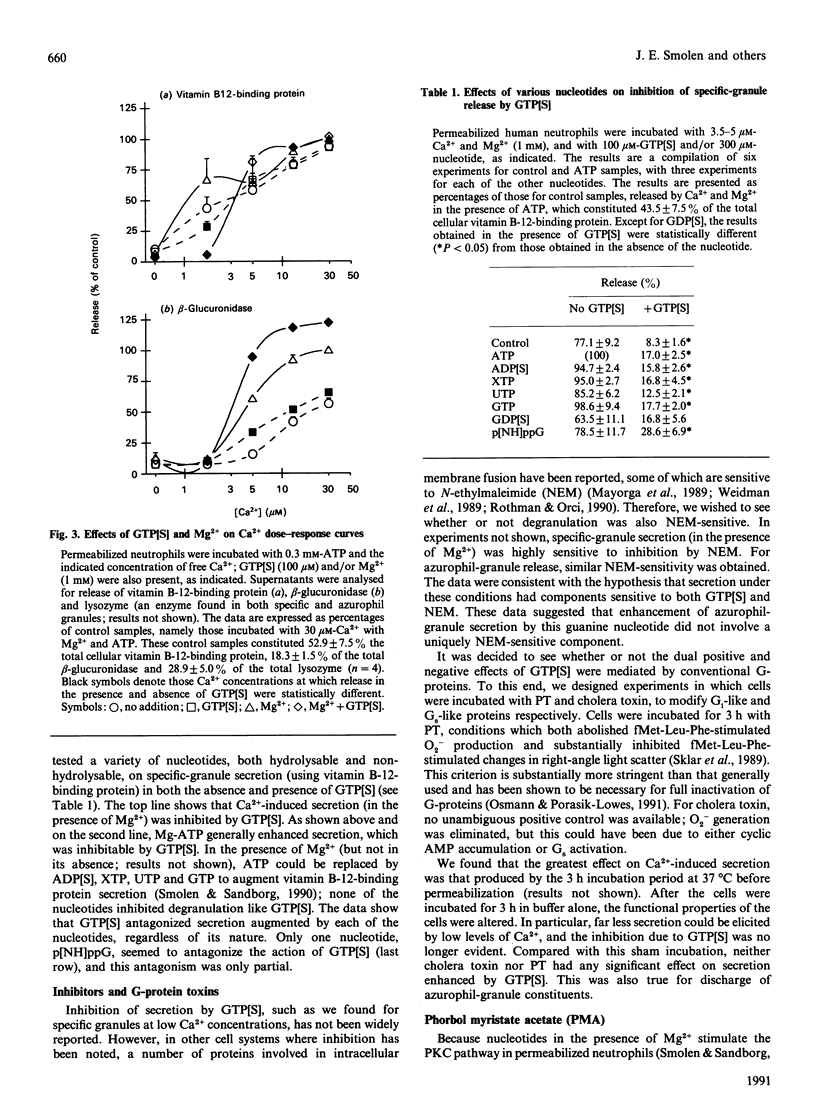
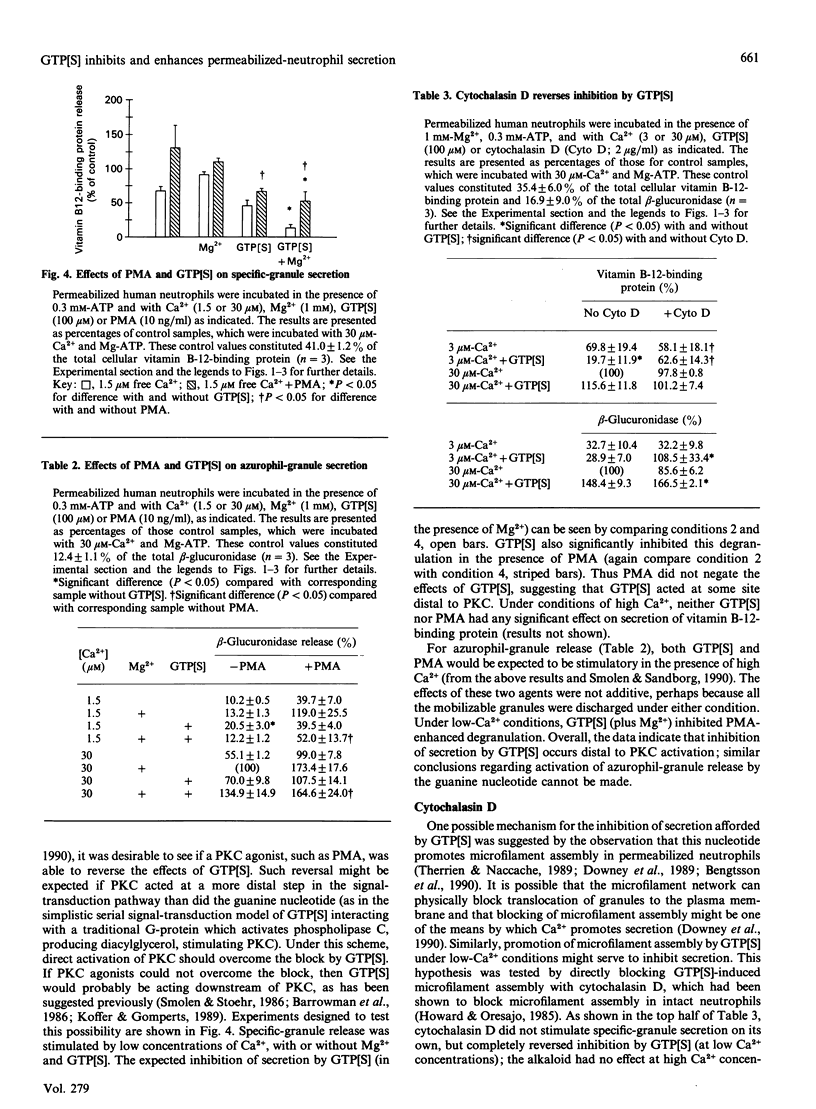
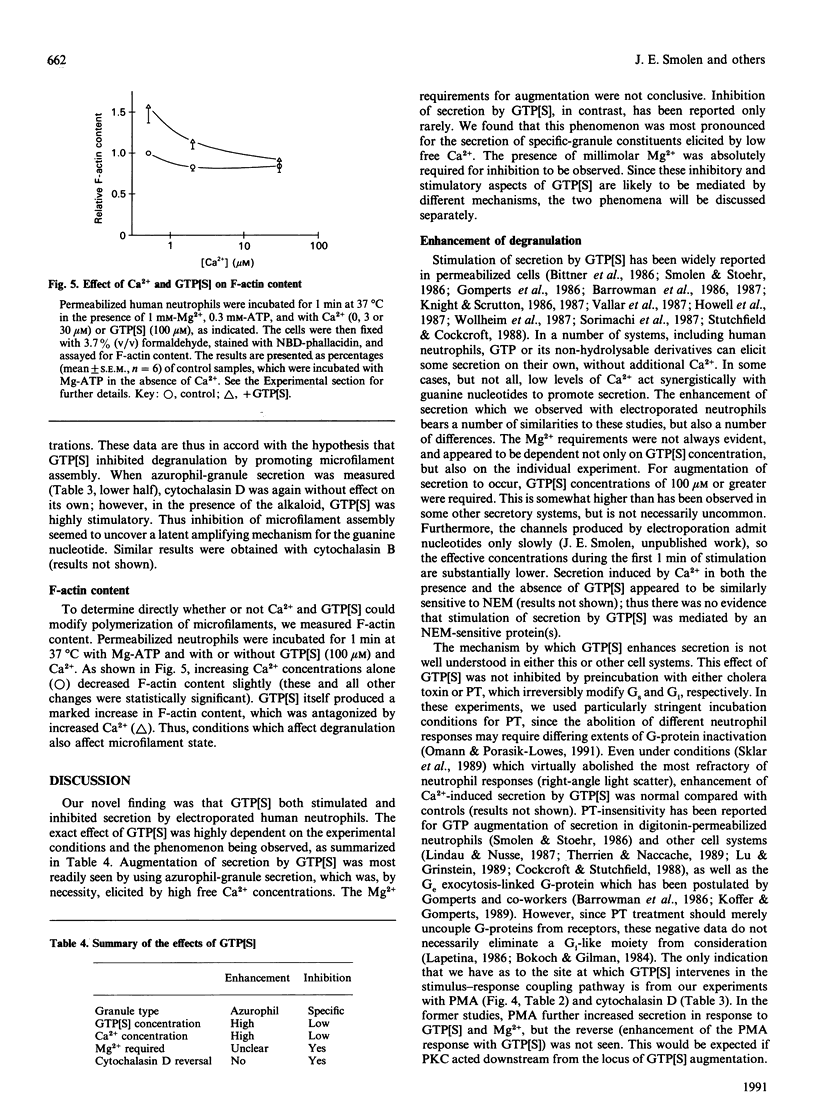
It is generally believed that G-proteins play stimulatory roles on cell activation. In contrast, we found that guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) was a potent inhibitor of Ca(2+)-induced secretion from specific granules (as monitored by vitamin B-12-binding protein). GTP[S] inhibition of specific-granule release occurred in the presence or absence of adenine nucleotides, required Mg2+ (1-3 mM), and was half-maximal at 30 microM-GTP[S]. The dual stimulatory and inhibitory effects of GTP[S] could be readily observed and differentiated when degranulation was monitored over a range of Ca2+ concentrations. Inhibition of specific-granule release by GTP[S] was observed at low Ca2+ concentrations and resulted from shifting the Ca2+ dose-response curves to the right. In contrast, GTP[S] promoted azurophil-granule secretion at relatively high concentrations of Ca2+ and appeared to be due to a general enhancement at all Ca2+ concentrations. A series of hydrolysable and non-hydrolysable nucleotides did not mimic GTP[S] or block its action. Inhibition by GTP[S] occurred in cells which were sensitized with a protein kinase C agonist, suggesting that inhibition of secretion took place distal to this enzyme. However, the inhibitory effects of GTP[S] on specific-granule secretion were reversed by cytochalasin D, which prevents new microfilament formation; this compound also enhanced the stimulation of azurophil-granule release by GTP[S]. We also found that GTP[S] greatly increased the F-actin content of permeabilized neutrophils, whereas Ca2+ (to a lesser extent) decreased F-actin. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that at least two G-proteins are involved in regulating secretion: one which has been previously described as stimulating Ca(2+)-induced secretion (particularly from azurophil granules) and a second, possibly involved in promoting microfilament assembly, which inhibits the discharge of specific granules.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Differential control of azurophilic and specific granule exocytosis in Sendai-virus-permeabilized rabbit neutrophils. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:115–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson T., Särndahl E., Stendahl O., Andersson T. Involvement of GTP-binding proteins in actin polymerization in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2921–2925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. A simple method for the accurate determination of free [Ca] in Ca-EGTA solutions. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):C404–C408. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.5.C404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., Holz R. W., Neubig R. R. Guanine nucleotide effects on catecholamine secretion from digitonin-permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10182–10188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachidonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Rubin R. P. Guanine nucleotide regulation of phospholipase C activity in permeabilized rabbit neutrophils. Inhibition by pertussis toxin and sensitization to submicromolar calcium concentrations. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):97–102. doi: 10.1042/bj2390097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittinger G., Hirschhorn R., Douglas S. D., Weissmann G. Studies on lysosomes. XI. Characterization of a hydrolase-rich fraction from human lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):394–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Morgan A., O'Sullivan A. J. The control of cytoskeletal actin and exocytosis in intact and permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells: role of calcium and protein kinase C. Cell Signal. 1989;1(4):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. Effect of pertussis toxin and neomycin on G-protein-regulated polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. A comparison between HL60 membranes and permeabilized HL60 cells. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 1;256(2):343–350. doi: 10.1042/bj2560343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey G. P., Chan C. K., Grinstein S. Actin assembly in electropermeabilized neutrophils: role of G-proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):700–705. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey G. P., Chan C. K., Trudel S., Grinstein S. Actin assembly in electropermeabilized neutrophils: role of intracellular calcium. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1975–1982. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Cerqueira M., Lind S., Kaplan H. B. Evidence that the superoxide-generating system of human leukocytes is associated with the cell surface. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):249–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI108635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S. Dual role for guanine nucleotides in stimulus-secretion coupling. Fed Proc. 1986 Jun;45(7):2156–2161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W. Receptor-mediated activation of electropermeabilized neutrophils. Evidence for a Ca2+- and protein kinase C-independent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1779–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard T. H., Oresajo C. O. The kinetics of chemotactic peptide-induced change in F-actin content, F-actin distribution, and the shape of neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1078–1085. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell T. W., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Essential synergy between Ca2+ and guanine nucleotides in exocytotic secretion from permeabilized rat mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):191–197. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Scrutton M. C. Effects of guanine nucleotides on the properties of 5-hydroxytryptamine secretion from electropermeabilised human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Scrutton M. C. Secretion of 5-hydroxytryptamine from electropermeabilised human platelets. Effects of GTP and cyclic 3',5'-AMP. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80507-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffer A., Gomperts B. D. Soluble proteins as modulators of the exocytotic reaction of permeabilised rat mast cells. J Cell Sci. 1989 Nov;94(Pt 3):585–591. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopmann W. R., Jr, Jackson R. C. Calcium- and guanine-nucleotide-dependent exocytosis in permeabilized rat mast cells. Modulation by protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):365–373. doi: 10.1042/bj2650365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. Effect of pertussis toxin on the phosphodiesteratic cleavage of the polyphosphoinositides by guanosine 5'-O-thiotriphosphate and thrombin in permeabilized human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 19;884(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limor R., Schvartz I., Hazum E., Ayalon D., Naor Z. Effect of guanine nucleotides on phospholipase C activity in permeabilized pituitary cells: possible involvement of an inhibitory GTP-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):209–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindau M., Nüsse O. Pertussis toxin does not affect the time course of exocytosis in mast cells stimulated by intracellular application of GTP-gamma-S. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80393-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D. J., Grinstein S. Concanavalin A stimulation of O2 consumption in electropermeabilized neutrophils via a pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 14;253(1-2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80949-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luini A., De Matteis M. A. Evidence that receptor-linked G protein inhibits exocytosis by a post-second-messenger mechanism in AtT-20 cells. J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):30–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga L. S., Diaz R., Stahl P. D. Regulatory role for GTP-binding proteins in endocytosis. Science. 1989 Jun 23;244(4911):1475–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.2499930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhan V., Holowka D., Baird B. Microfilaments regulate the rate of exocytosis in rat basophilic leukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 31;171(1):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91380-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmith P. E., Mills G. B., Grinstein S. Guanine nucleotides induce tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the respiratory burst in neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):893–897. doi: 10.1042/bj2570893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omann G. M., Porasik-Lowes M. M. Graded G-protein uncoupling by pertussis toxin treatment of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1303–1308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omann G. M., Porasik M. M., Sklar L. A. Oscillating actin polymerization/depolymerization responses in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16355–16358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Wollheim C. B., Lew P. D. Ca2+ homeostasis in permeabilized human neutrophils. Characterization of Ca2+-sequestering pools and the action of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13777–13782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehm A. G., Wu H., Halenda S. P. Guanine nucleotides inhibit agonist-stimulated arachidonic acid release in both intact and saponin-permeabilized human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Orci L. Movement of proteins through the Golgi stack: a molecular dissection of vesicular transport. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1460–1468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Bokoch G. M., Button D., Smolen J. E. Regulation of ligand-receptor dynamics by guanine nucleotides. Real-time analysis of interconverting states for the neutrophil formyl peptide receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):135–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Mueller H., Omann G., Oades Z. Three states for the formyl peptide receptor on intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8483–8486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Omann G. M., Painter R. G. Relationship of actin polymerization and depolymerization to light scattering in human neutrophils: dependence on receptor occupancy and intracellular Ca++. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1161–1166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P., Peters T. J. The release of granule components from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in response to both phagocytic and chemical stimuli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 24;719(2):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Sandborg R. R. Ca2(+)-induced secretion by electropermeabilized human neutrophils. The roles of Ca2+, nucleotides and protein kinase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 9;1052(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90068-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Stoehr S. J., Bartone D. Protein kinase C is not involved in secretion by permeabilized human neutrophils. Cell Signal. 1989;1(5):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Stoehr S. J., Boxer L. A. Human neutrophils permeabilized with digitonin respond with lysosomal enzyme release when exposed to micromolar levels of free calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 8;886(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Stoehr S. J. Guanine nucleotides reduce the free calcium requirement for secretion of granule constituents from permeabilized human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 28;889(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Stoehr S. J. Micromolar concentrations of free calcium provoke secretion of lysozyme from human neutrophils permeabilized with saponin. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1859–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Guanine nucleotides stimulate polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytotic secretion from HL60 cells permeabilized with streptolysin O. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2500375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therrien S., Naccache P. H. Guanine nucleotide-induced polymerization of actin in electropermeabilized human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1125–1132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B. Guanine nucleotides induce Ca2+-independent insulin secretion from permeabilized RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5049–5056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidman P. J., Melançon P., Block M. R., Rothman J. E. Binding of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein to Golgi membranes requires both a soluble protein(s) and an integral membrane receptor. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1589–1596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Ullrich S., Meda P., Vallar L. Regulation of exocytosis in electrically permeabilized insulin-secreting cells. Evidence for Ca2+ dependent and independent secretion. Biosci Rep. 1987 May;7(5):443–454. doi: 10.1007/BF01362507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Cytochalasin B: effect on lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


