Abstract
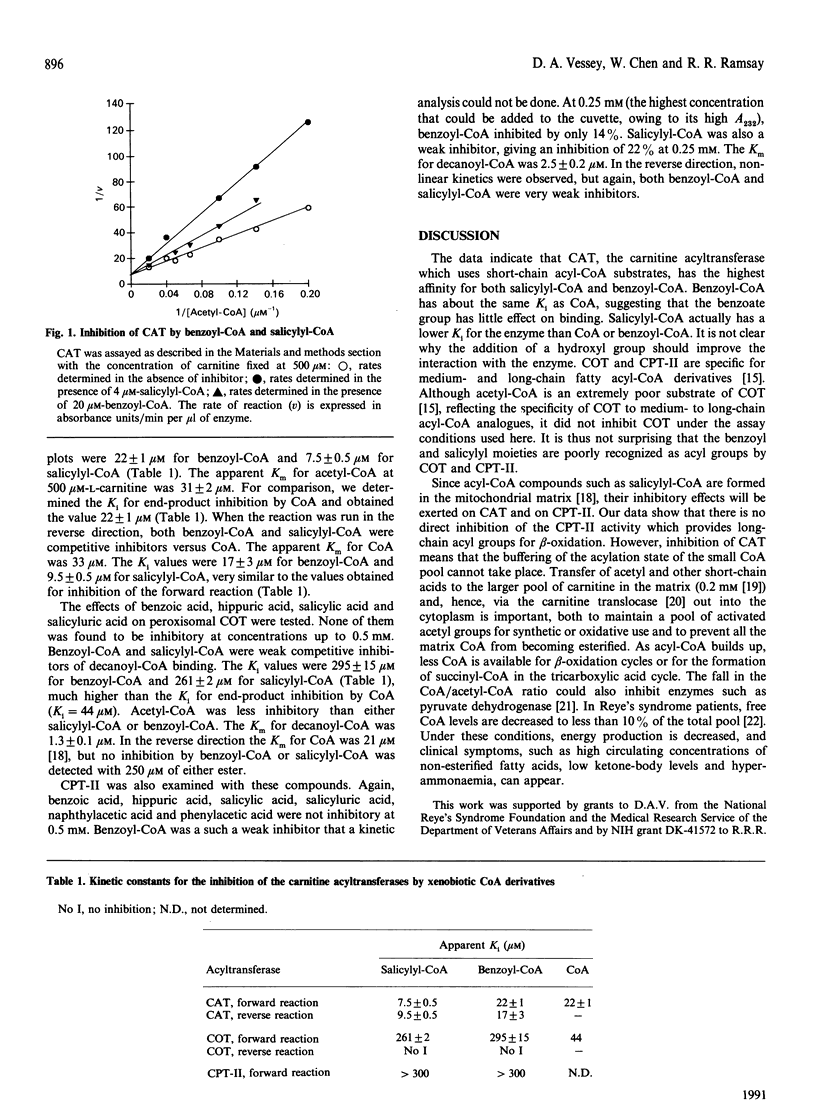
Salicylyl-CoA and benzoyl-CoA were good inhibitors of carnitine acetyltransferase (CAT), competing with acetyl-CoA with Ki values of 7.5 and 22 microM respectively in the forward direction and with CoA in the reverse reaction with similar Ki values. They were also competitive inhibitors of carnitine octanoyltransferase (Ki = 261 and 295 microM respectively), but were only weakly inhibitory to carnitine palmitoyltransferase. Inhibition of energy production by salicylate may result from the inhibition of CAT by salicylyl-CoA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieber L. L. Carnitine. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:261–283. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremer J. Carnitine--metabolism and functions. Physiol Rev. 1983 Oct;63(4):1420–1480. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.4.1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. E., Forman D. T. The biochemistry of Reye's syndrome. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1982;17(3):247–297. doi: 10.3109/10408368209107038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. R., Bieber L. L. Isolation and purification of mitochondrial carnitine octanoyltransferase activities from beef heart. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9861–9868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corkey B. E., Hale D. E., Glennon M. C., Kelley R. I., Coates P. M., Kilpatrick L., Stanley C. A. Relationship between unusual hepatic acyl coenzyme A profiles and the pathogenesis of Reye syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):782–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI113679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatley S. J., Sherratt H. S. The synthesis of hippurate from benzoate and glycine by rat liver mitochondria. Submitochondrial localization and kinetics. Biochem J. 1977 Jul 15;166(1):39–47. doi: 10.1042/bj1660039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. R., McCray P. B., Bale J. F., Jr, Corbett A. J., Flanders D. J. Reye syndrome associated with aspirin therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatrics. 1985 Aug;76(2):202–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heubi J. E., Partin J. C., Partin J. S., Schubert W. K. Reye's syndrome: current concepts. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):155–164. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M., Vessey D. A. The effects of ions on the conjugation of xenobiotics by the aralkyl-CoA and arylacetyl-CoA N-acyltransferases from bovine liver mitochondria. J Biochem Toxicol. 1990 Summer;5(2):125–135. doi: 10.1002/jbt.2570050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killenberg P. G., Davidson E. D., Webster L. T., Jr Evidence for a medium-chain fatty acid: coenzyme A ligase (adenosine monophosphate) that activates salicylate. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 May;7(3):260–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHLER H. R., WAKIL S. J., BOCK R. M. Studies on fatty acid oxidation. I. Enzymatic activation of fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):453–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. R., Derrick J. P., Friend A. S., Tubbs P. K. Purification and properties of the soluble carnitine palmitoyltransferase from bovine liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):271–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2440271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay R. R. The role of carnitine, the carnitine acyltransferases and the carnitine-exchange system [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(1):72–76. doi: 10.1042/bst0060072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starko K. M., Mullick F. G. Hepatic and cerebral pathology findings in children with fatal salicylate intoxication: further evidence for a causal relation between salicylate and Reye's syndrome. Lancet. 1983 Feb 12;1(8320):326–329. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91629-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauner D. A., Nyhan W. L., Sweetman L. Short-chain organic acidemia and Reye's syndrome. Neurology. 1975 Mar;25(3):296–298. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.3.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uziel G., Garavaglia B., Di Donato S. Carnitine stimulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHC) in isolated human skeletal muscle mitochondria. Muscle Nerve. 1988 Jul;11(7):720–724. doi: 10.1002/mus.880110708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. J., Hall W. N., McGee H., Van Amburg G. Aspirin as a risk factor in Reye's syndrome. JAMA. 1982 Jun 11;247(22):3089–3094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Fujii M., Brown F. R., 3rd, Singh I. Effect of salicylic acid on mitochondrial-peroxisomal fatty acid catabolism. Pediatr Res. 1988 Mar;23(3):338–341. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198803000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. S., Torretti D., Williams R. H., Hendriksen D., Woods M. Reye's syndrome associated with long-term aspirin therapy. JAMA. 1984 Feb 10;251(6):754–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


