Abstract
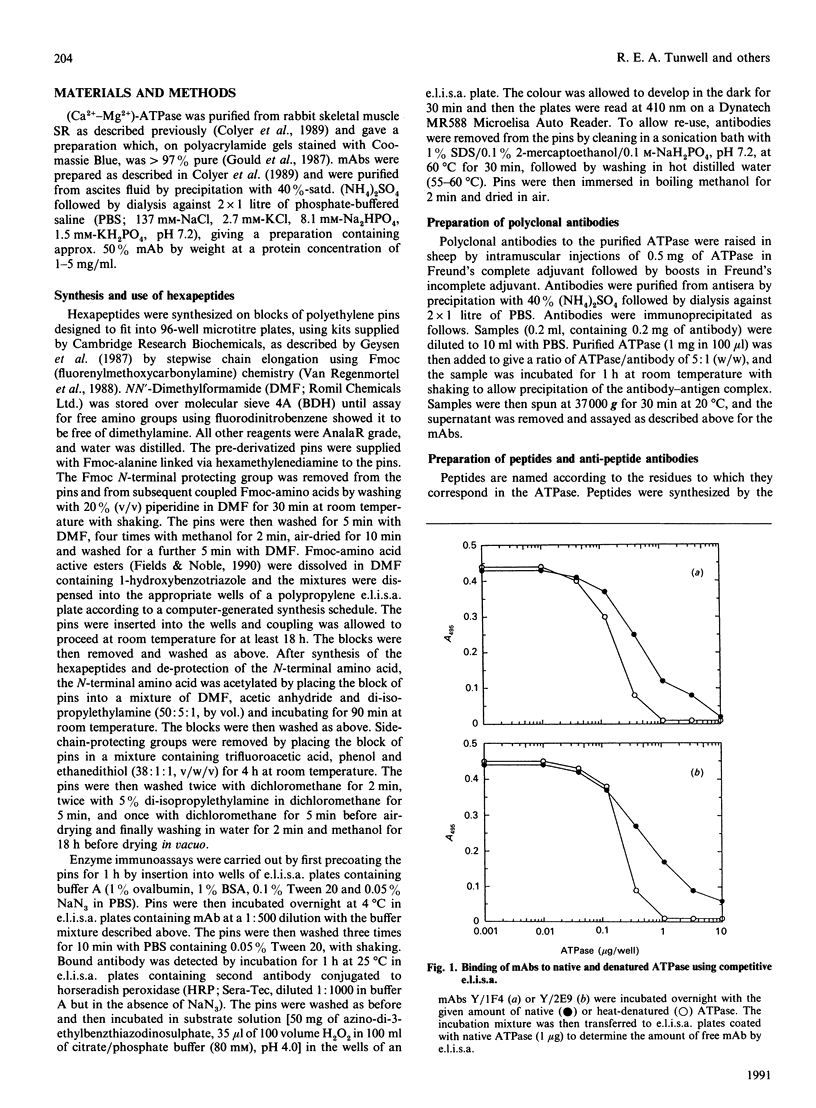
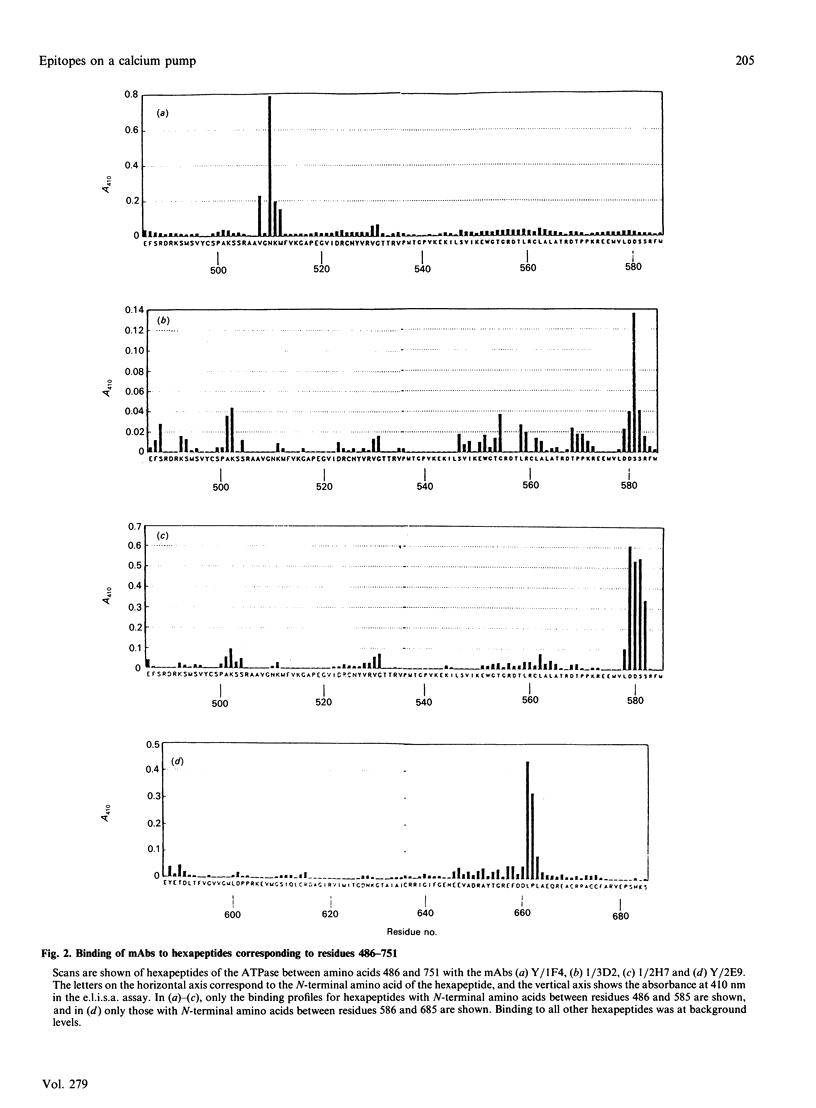
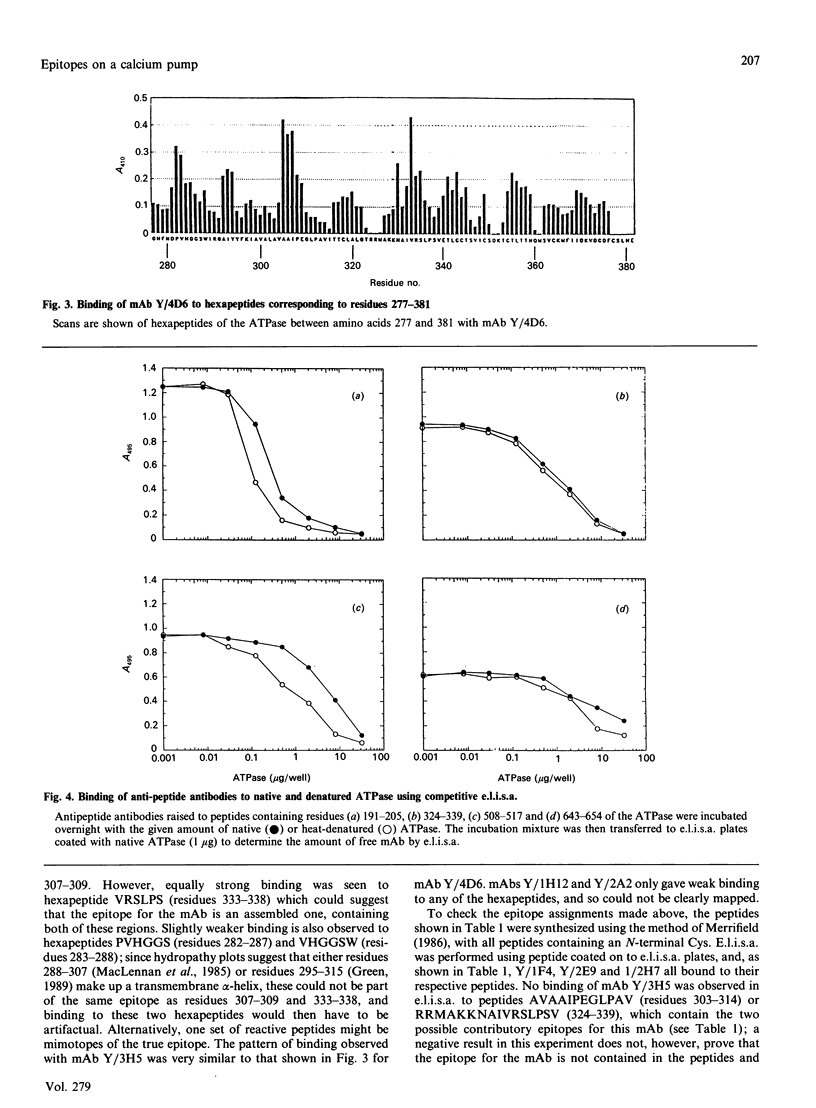
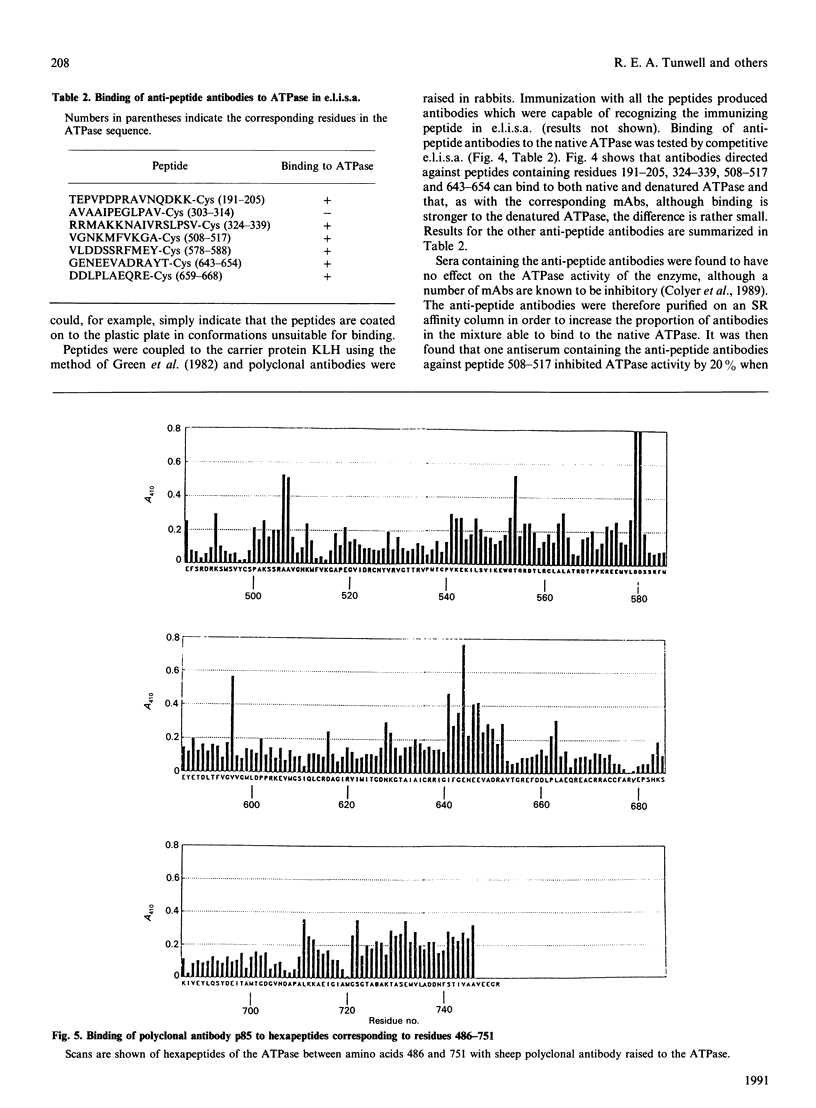
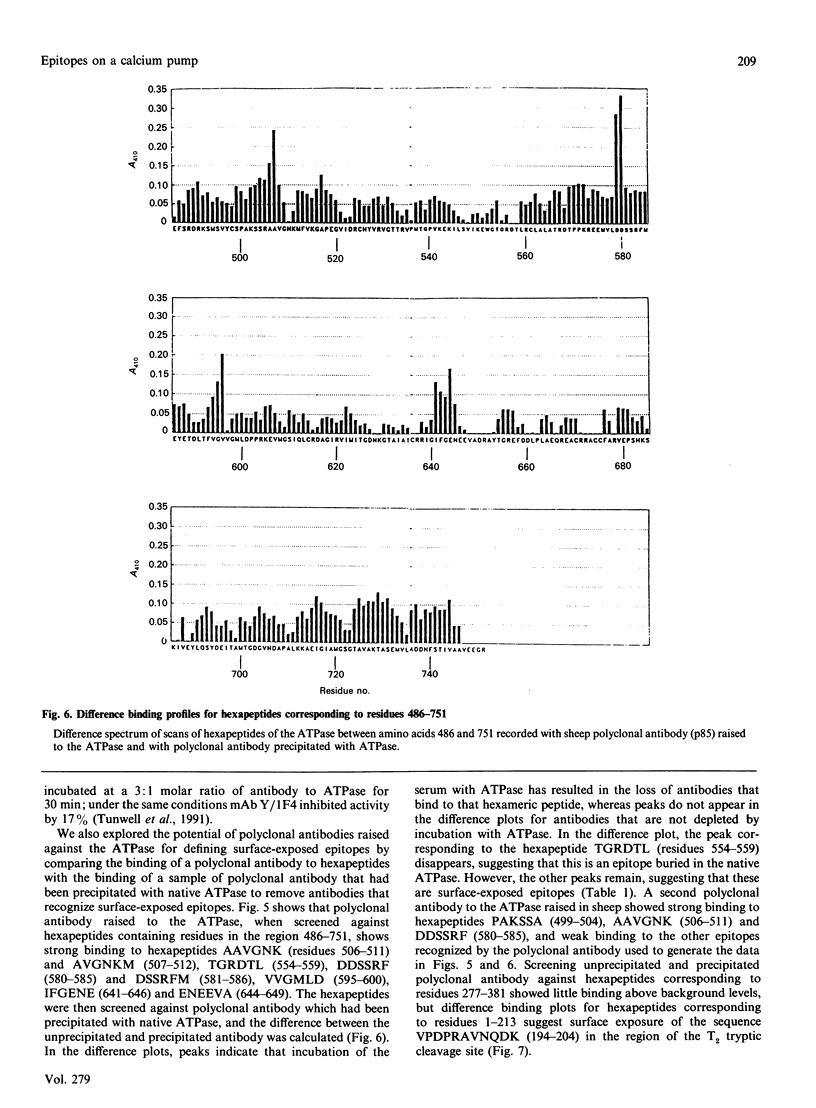
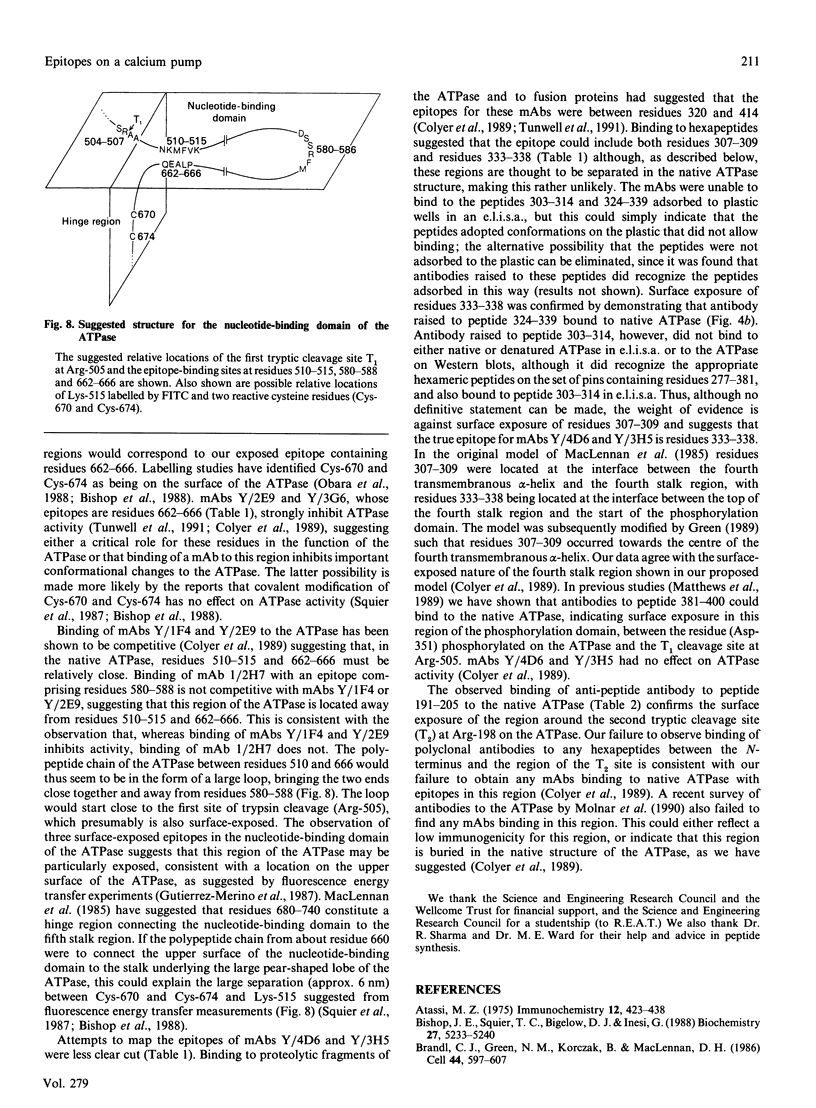
Epitopes for monoclonal antibodies binding to the native (Ca(2+)-Mg2+)-ATPase have been defined by studying binding to sets of hexameric peptides synthesized on plastic pegs. Epitopes have been confirmed by demonstrating the binding of anti-peptide antibodies to the ATPase. A method is presented for definition of surface-exposed epitopes using polyclonal antibodies. Three surface-exposed epitopes have been defined in the nucleotide-binding domain of the ATPase, suggesting considerable surface exposure of this region. Other surface-exposed epitopes have been located in the region of the fourth stalk domain.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atassi M. Z. Antigenic structure of myoglobin: the complete immunochemical anatomy of a protein and conclusions relating to antigenic structures of proteins. Immunochemistry. 1975 May;12(5):423–438. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. E., Squier T. C., Bigelow D. J., Inesi G. (Iodoacetamido)fluorescein labels a pair of proximal cysteines on the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):5233–5240. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Green N. M., Korczak B., MacLennan D. H. Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. M., Loo T. W., Inesi G., MacLennan D. H. Location of high affinity Ca2+-binding sites within the predicted transmembrane domain of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):476–478. doi: 10.1038/339476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colyer J., Mata A. M., Lee A. G., East J. M. Effects on ATPase activity of monoclonal antibodies raised against (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum and their correlation with epitope location. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):439–447. doi: 10.1042/bj2620439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasman G. D., Gilbert W. A. The prediction of transmembrane protein sequences and their conformation: an evaluation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90187-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields G. B., Noble R. L. Solid phase peptide synthesis utilizing 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl amino acids. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Mar;35(3):161–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., East J. M., Rooney E. K., Lee A. G. Binding of long-chain alkyl derivatives to lipid bilayers and to (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7535–7544. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Colyer J., East J. M., Lee A. G. Silver ions trigger Ca2+ release by interaction with the (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase in reconstituted systems. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7676–7679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. ATP-driven cation pumps: alignment of sequences. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Dec;17(6):972–972. doi: 10.1042/bst0170972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Merino C., Munkonge F., Mata A. M., East J. M., Levinson B. L., Napier R. M., Lee A. G. The position of the ATP binding site on the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 26;897(2):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. N., Jamison M. H., MacLennan I. Complications of non-absorbable ligatures in thyroid surgery. Br J Clin Pract. 1985 Aug;39(8):307–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structure predictions of membrane proteins are not that bad. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90188-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Andersen J. P. Structural basis for E1-E2 conformational transitions in Na,K-pump and Ca-pump proteins. J Membr Biol. 1988 Jul;103(2):95–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01870942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakita M., Yamashita T. Reactive sulfhydryl groups of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. III. Identification of cysteine residues whose modification with N-ethylmaleimide leads to loss of the Ca2+-transporting activity. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):103–109. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kison R., Meyer H. E., Schoner W. Characterization of a cysteine-containing peptide after affinity labelling of Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum with the disulfide of 3'(2')-O-biotinyl-thioinosine triphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1989 May 1;181(2):503–511. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Air G. M., Webster R. G., Smith-Gill S. J. Epitopes on protein antigens: misconceptions and realities. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):553–556. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90464-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., MacLennan D. H. Mutation of aspartic acid-351, lysine-352, and lysine-515 alters the Ca2+ transport activity of the Ca2+-ATPase expressed in COS-1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3314–3318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews I., Colyer J., Mata A. M., Green N. M., Sharma R. P., Lee A. G., East J. M. Evidence for the cytoplasmic location of the N- and C-terminal segments of sarcoplasmic reticulum (Ca2+-Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):683–688. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92653-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield B. Solid phase synthesis. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.3961484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchinson C., Wilderspin A. F., Trinnaman B. J., Green N. M. Identification of a labelled peptide after stoicheiometric reaction of fluorescein isothiocyanate with the Ca2+ -dependent adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80710-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar E., Seidler N. W., Jona I., Martonosi A. N. The binding of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to the Ca2(+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum: effects on interactions between ATPase molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 13;1023(2):147–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90410-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munkonge F., East J. M., Lee A. G. Positions of the sites labeled by N-cyclohexyl-N'-(4-dimethylamino-1-naphthyl)carbodiimide on the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 13;979(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny J., Bruccoleri R. E., Saul F. A. On the attribution of binding energy in antigen-antibody complexes McPC 603, D1.3, and HyHEL-5. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4735–4749. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara M., Suzuki H., Kanazawa T. Conformational changes in the vicinity of the N-iodoacetyl-N'-(5-sulfo-1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine attached to the specific thiol of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase throughout the catalytic cycle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3690–3697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Nagano K., Yoshida M. The active site structure of Na+/K+-transporting ATPase: location of the 5'-(p-fluorosulfonyl)benzoyladenosine binding site and soluble peptides released by trypsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Arzamazova N. M., Arystarkhova E. A., Gevondyan N. M., Aldanova N. A., Modyanov N. N. Detailed structural analysis of exposed domains of membrane-bound Na+,K+-ATPase. A model of transmembrane arrangement. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80676-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Luneva N. M., Arystarkhova E. A., Gevondyan N. M., Arzamazova N. M., Kozhich A. T., Nesmeyanov V. A., Modyanov N. N. Topology of Na+,K+-ATPase. Identification of the extra- and intracellular hydrophilic loops of the catalytic subunit by specific antibodies. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):230–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80904-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petithory J. R., Jencks W. P. Phosphorylation of the calcium adenosinetriphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum: rate-limiting conformational change followed by rapid phosphoryl transfer. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4493–4497. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U. Interaction of fluorescein isothiocyanate with nucleotide-binding sites of the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Dec;121(1):187–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reithmeier R. A., MacLennan D. H. The NH2 terminus of the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-adenosine triphosphatase is located on the cytoplasmic surface of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):5957–5960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. L. Distances between the functional sites of the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14421–14423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Portillo F. Catalytic and regulatory sites of yeast plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase studied by directed mutagenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 25;1018(2-3):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Structure and function of proton translocating ATPase in plasma membranes of plants and fungi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 24;947(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull G. E., Schwartz A., Lingrel J. B. Amino-acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of the (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from a complementary DNA. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):691–695. doi: 10.1038/316691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier T. C., Bigelow D. J., Garcia de Ancos J., Inesi G. Localization of site-specific probes on the Ca-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum using fluorescence energy transfer. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4748–4754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes D. L., Green N. M. Structure of CaATPase: electron microscopy of frozen-hydrated crystals at 6 A resolution in projection. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 5;213(3):529–538. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Green N. M. The predicted secondary structures of the nucleotide-binding sites of six cation-transporting ATPases lead to a probable tertiary fold. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano A., Chothia C., Lesk A. M. Structural determinants of the conformations of medium-sized loops in proteins. Proteins. 1989;6(4):382–394. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunwell R. E., O'Connor C. D., Mata A. M., East J. M., Lee A. G. Mapping epitopes on the (Ca(2+)-Mg2+)-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum using fusion proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 9;1073(3):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Regenmortel M. H. The concept and operational definition of protein epitopes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1989 Jun 12;323(1217):451–466. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1989.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu K. Y., Kyte J. Nucleophilic behavior of lysine-501 of the alpha-polypeptide of sodium and potassium ion activated adenosinetriphosphatase consistent with a role in binding adenosine triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):3009–3017. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Tagaya M., Fukui T., Kawakita M. Affinity labeling of the ATP-binding site of Ca2+-transporting ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum by adenosine triphosphopyridoxal: identification of the reactive lysyl residue. J Biochem. 1988 Mar;103(3):452–457. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


