Abstract
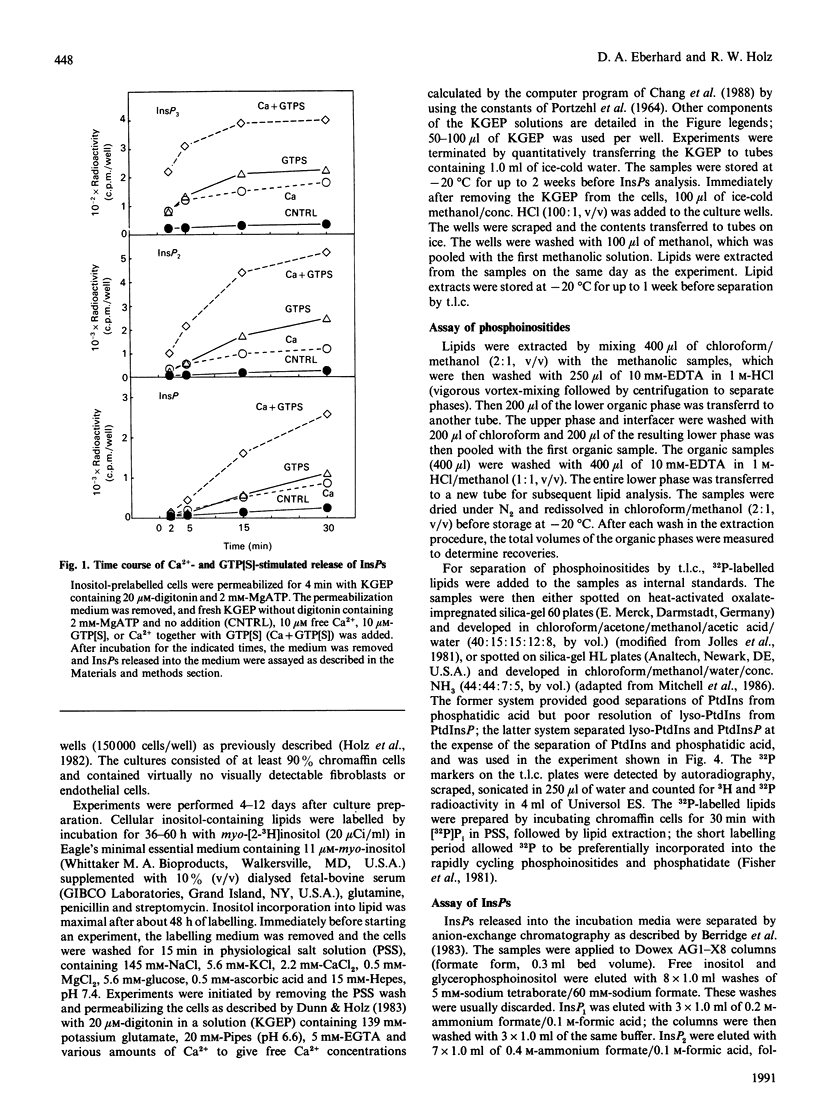
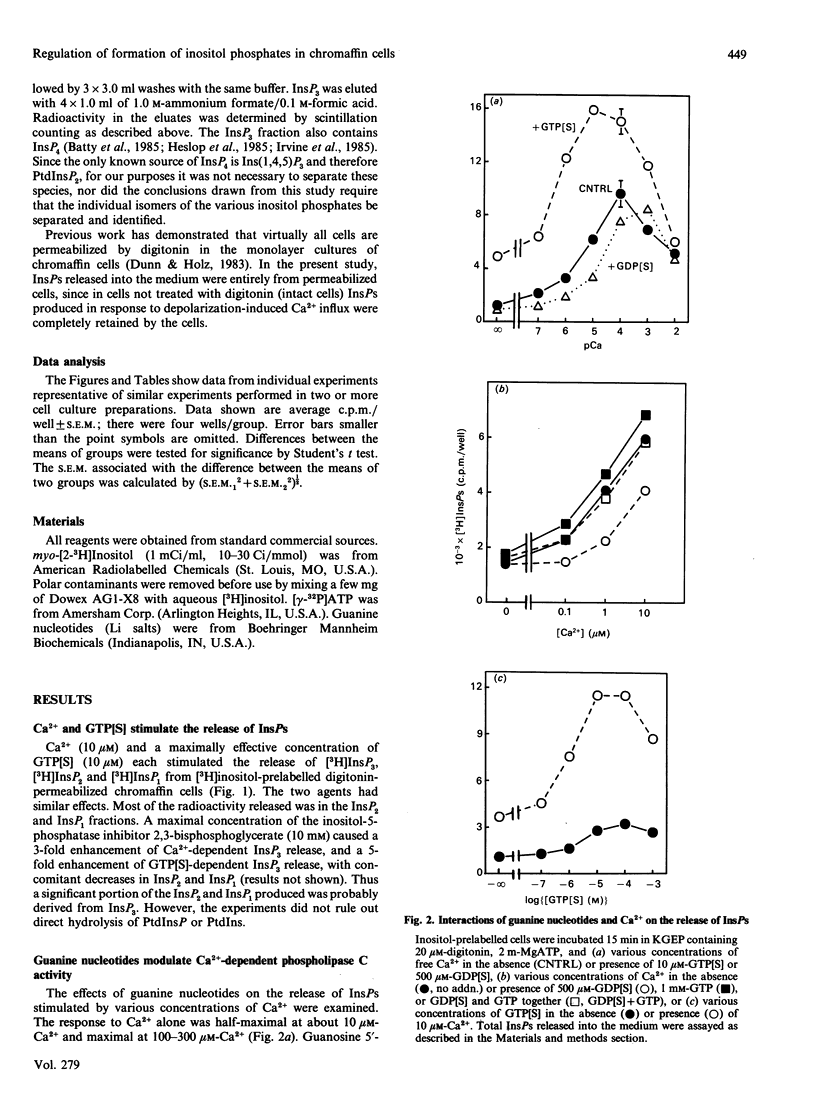
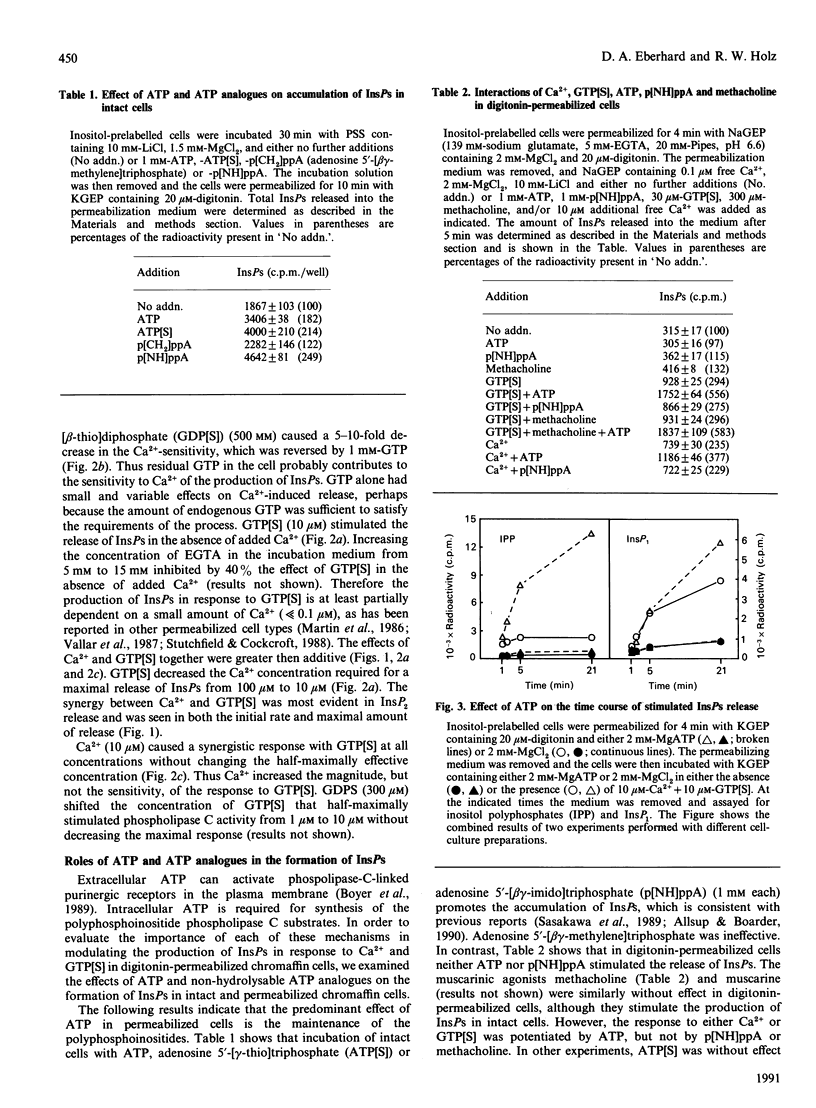
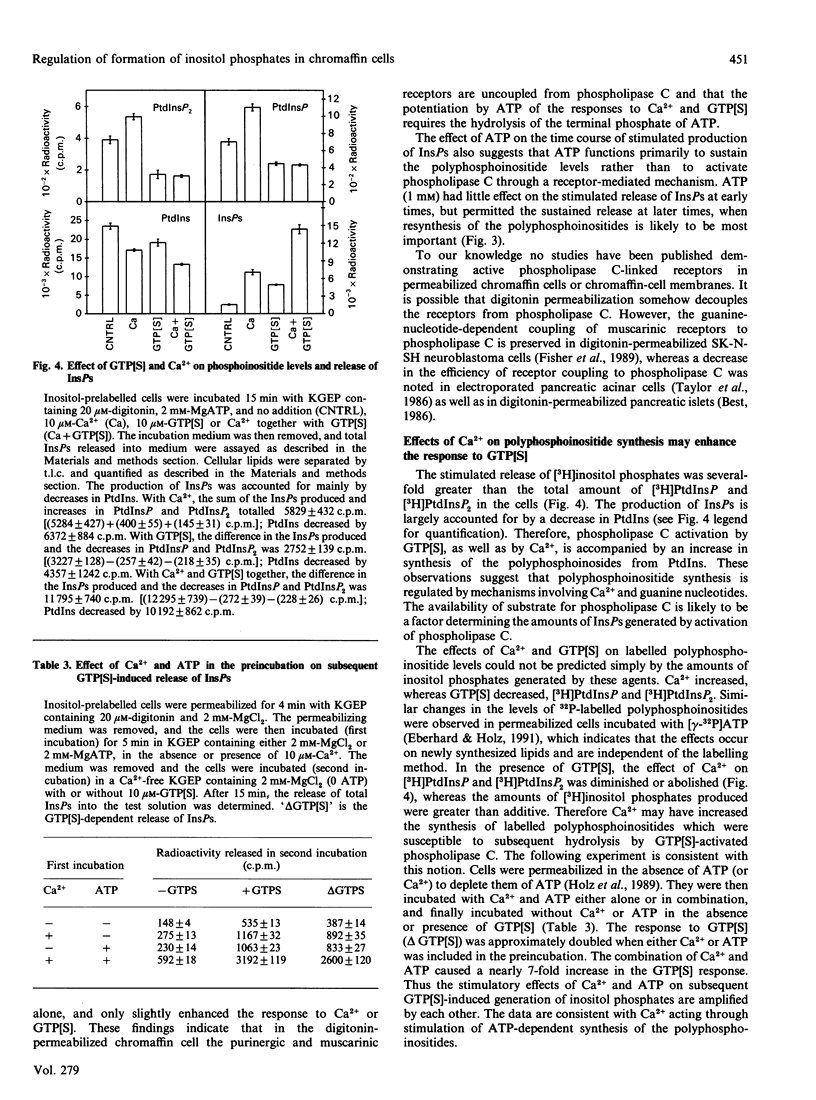
Both micromolar Ca2+ and guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) stimulated the formation of inositol phosphates (InsPs) in digitonin-permeabilized chromaffin cells prelabelled with [3H]inositol. The production of InsPs was potentiated by ATP. Guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate (GDP[S]) caused a GTP-reversible shift to higher concentrations in the Ca(2+)-concentration-response curve for the release of InsPs without changing the maximal response. GTP[S] caused a shift to lower concentrations of Ca2+ and also increased the maximal response. The effects of GTP[S] and Ca2+ were synergistic. Although as much as 80% of the InsPs were derived from phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdInsP) or 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdInsP2), the amount of InsPs produced could be several times the total amount of PtdInsP and PtdInsP2 in the cells and was largely accounted for by a decrease in PtdIns. The levels of labelled PtdInsP and PtdInsP2 increased on stimulation with Ca2+, but decreased on stimulation with GTP[S] or the combination of Ca2+ and GTP[S]. Preincubation with Ca2+ and ATP amplified the subsequent GTP[S]-induced production of InsPs. ATP and its gamma-thio and beta gamma-imido analogues stimulated the formation of InsPs in intact cells. However, only ATP potentiated the responses to Ca2+ and GTP[S] in permeable cells. Our main conclusions are: (1) a GTP-binding protein participates in the Ca(2+)-induced production of InsPs by phospholipase C, and (2) ATP markedly potentiates the stimulated formation of InsPs, an effect with arises from its role in polyphosphoinositide synthesis and does not involve purinergic receptor activation in permeabilized cells. The data also suggest that the different effects of Ca2+ and GTP[S] on polyphosphoinositide synthesis probably contribute to the synergistic action of Ca2+ and GTP[S] on the generation of InsPs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsup D. J., Boarder M. R. Comparison of P2 purinergic receptors of aortic endothelial cells with those of adrenal medulla: evidence for heterogeneity of receptor subtype and of inositol phosphate response. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;38(1):84–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L. A role for calcium in the breakdown of inositol phospholipids in intact and digitonin-permeabilized pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):773–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2380773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. Kinetics of activation of phospholipase C by P2Y purinergic receptor agonists and guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):884–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D., Hsieh P. S., Dawson D. C. Calcium: a program in BASIC for calculating the composition of solutions with specified free concentrations of calcium, magnesium and other divalent cations. Comput Biol Med. 1988;18(5):351–366. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(88)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn L. A., Holz R. W. Catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4989–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Cooper C. L., Low M. G., Holz R. W. Evidence that the inositol phospholipids are necessary for exocytosis. Loss of inositol phospholipids and inhibition of secretion in permeabilized cells caused by a bacterial phospholipase C and removal of ATP. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):15–25. doi: 10.1042/bj2680015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Holz R. W. Calcium promotes the accumulation of polyphosphoinositides in intact and permeabilized bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1991 Jun;11(3):357–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00713279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Holz R. W. Cholinergic stimulation of inositol phosphate formation in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: distinct nicotinic and muscarinic mechanisms. J Neurochem. 1987 Nov;49(5):1634–1643. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb01037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard D. A., Holz R. W. Intracellular Ca2+ activates phospholipase C. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Dec;11(12):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Wallace M. A., Wojcikiewicz R. J. Evidence for involvement of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins in the activation of phospholipases by hormones. FASEB J. 1988 Jul;2(10):2569–2574. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.10.2838362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Domask L. M., Roland R. M. Muscarinic receptor regulation of cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentrations in human SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells: Ca2+ requirements for phospholipase C activation. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;35(2):195–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Holz R. W., Agranoff B. W. Muscarinic receptors in chromaffin cell cultures mediate enhanced phospholipid labeling but not catecholamine secretion. J Neurochem. 1981 Aug;37(2):491–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Berridge M. J. Inositol tetrakis- and pentakisphosphates in GH4 cells. J Exp Biol. 1985 Nov;119:395–401. doi: 10.1242/jeb.119.1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W., Bittner M. A., Peppers S. C., Senter R. A., Eberhard D. A. MgATP-independent and MgATP-dependent exocytosis. Evidence that MgATP primes adrenal chromaffin cells to undergo exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5412–5419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W., Senter R. A., Frye R. A. Relationship between Ca2+ uptake and catecholamine secretion in primary dissociated cultures of adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):635–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husebye E. S., Flatmark T. Phosphatidylinositol kinase of bovine adrenal chromaffin granules. Modulation by hydrophilic and amphiphilic cations. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 1;37(21):4149–4156. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles J., Schrama L. H., Gispen W. H. Calcium-dependent turnover of brain polyphosphoinositides in vitro after prelabelling in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 23;666(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell K. T., Ferrell J. E., Jr, Huestis W. H. Separation of phosphoinositides and other phospholipids by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1986 Nov 1;158(2):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90574-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Sasakawa N., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Functional shift from muscarinic to nicotinic cholinergic receptors involved in inositol trisphosphate and cyclic GMP accumulation during the primary culture of adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):397–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2510397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Boarder M. R. Stimulation of formation of inositol phosphates in primary cultures of bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by angiotensin II, histamine, bradykinin, and carbachol. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):634–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa N., Nakaki T., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Inositol trisphosphate accumulation by high K+ stimulation in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa N., Nakaki T., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Stimulation by ATP of inositol trisphosphate accumulation and calcium mobilization in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):441–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Guanine nucleotides stimulate polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytotic secretion from HL60 cells permeabilized with streptolysin O. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):375–382. doi: 10.1042/bj2500375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Merritt J. E., Putney J. W., Jr, Rubin R. P. Effects of Ca2+ on phosphoinositide breakdown in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):765–772. doi: 10.1042/bj2380765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B. Guanine nucleotides induce Ca2+-independent insulin secretion from permeabilized RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5049–5056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waymire J. C., Bennett W. F., Boehme R., Hankins L., Gilmer-Waymire K., Haycock J. W. Bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: high-yield purification and viability in suspension culture. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 Apr;7(4):329–351. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker M. Polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis is associated with exocytosis in adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80858-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


