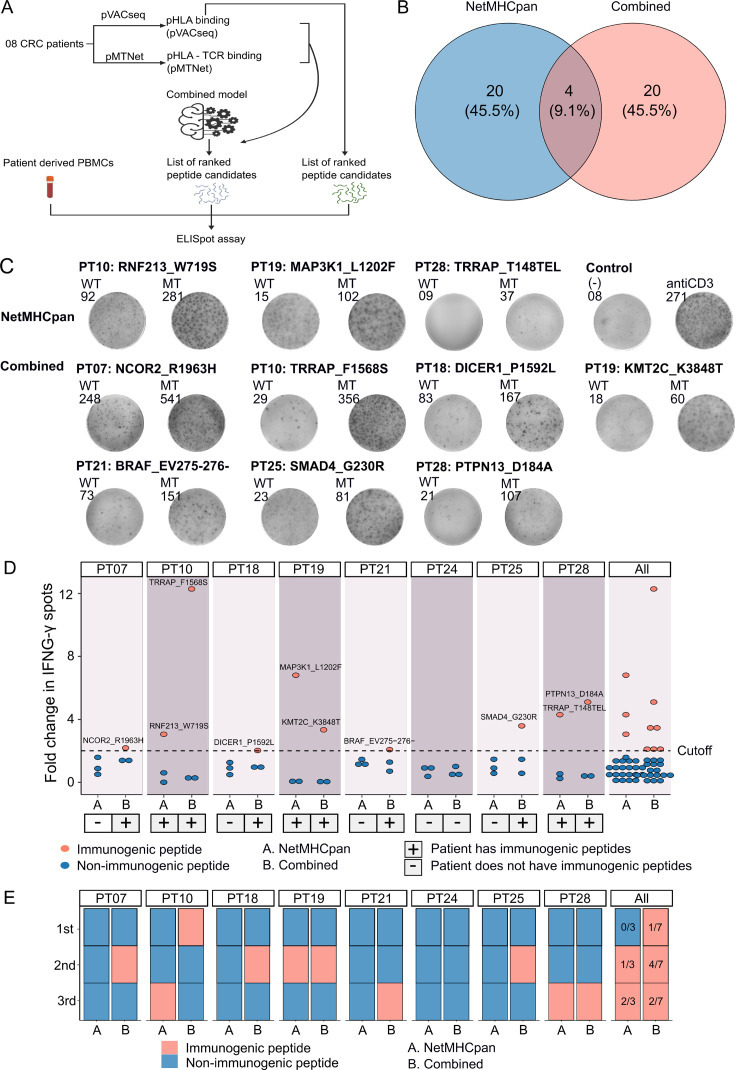
Figure 5. Validation of neoantigens identified in silico from the novel workflow through enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISpot) assays conducted on four colorectal cancer (CRC) patients.
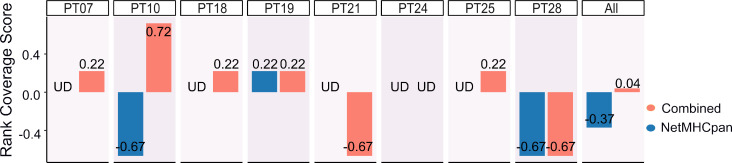
(A) A schematic diagram illustrates the procedural steps of neoantigen prioritization and the ELISpot assay. (B) The count of neoantigens identified from each pipeline. (C) The fold change in IFN-γ spots, relative to the wild-type peptides, is shown for 21 long peptides. Note: Only the mutants that result in a positive value in ELISpot are depicted, along with their corresponding amino acid changes and their associated rankings. (D) ELISpot assays on six long peptides resulting in at least a twofold change in IFN-γ spots. (E) The bar graphs display the ranking of validated long peptides identified from the NetMHCpan tool (blue bar) or the combined method (red bar) for individual patients and all patients.