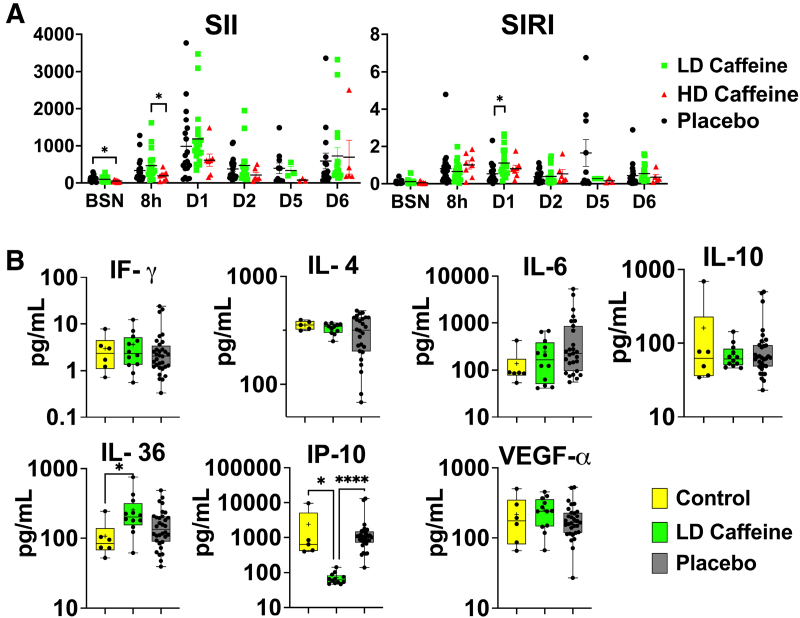
Figure 3.
Peripheral markers of inflammation. A, The peripheral blood cell index systemic immune-inflammation index (SII=ANC×PLT/ALC) was suppressed in high-dose (HD) caffeine at baseline (BSN) compared with placebo, and at 8 hours after umbilical cord occlusion (UCO) compared with low-dose (LD)-caffeine group. Systemic inflammation response index (SIRI=ANC×Mono/ALC) was elevated in the LD-caffeine group compared with the placebo on day 1. The SII and SIRI scores were evaluated by mixed-effect analysis with Tukey correction for multiple comparisons. The summary column graphs are showing means±SEM. HD caffeine: n=3–8; LD caffeine: n=3–19, and placebo: n=10–21. B, At 6 days after the UCO, we measured changes in IP-10 in the LD-caffeine group compared with the placebo, as well as in age-matched control and in IL-36 that was higher in the LD-caffeine group compared with control. No changes were observed in IL (interleukin)-4, IL-6, IF (interferon)-γ, IP (interferon gamma-induced protein 10)-10, or VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor A)-α. We used Mann-Whitney U test. LD caffeine: n=11–12; and placebo: n=26–32. The box graphs show mean by plus sign and median with interquartile range. *P<0.05, ****P<0.0001. LD-caffeine–treated group is presented in green, control is presented in yellow, and placebo is presented in black. ALC indicates absolute lymphocyte count; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; Mono, monocytes; and PLT, platelets.