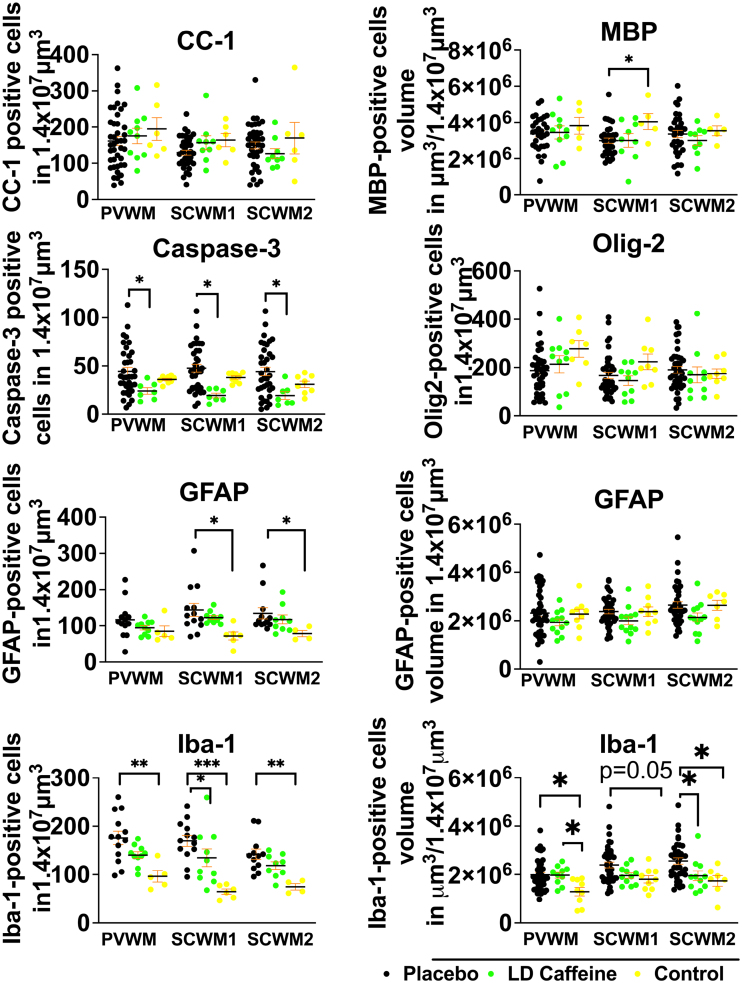
Figure 5.
Quantitative analysis of white matter markers and markers of inflammation: while overall white matter structure was not significantly altered by umbilical cord occlusion (UCO), there is more cell death in the placebo group compared with low-dose (LD) caffeine, reflected by a higher number of cells labeled with cleaved caspase-3. More inflammation was noted in the SCWM2 in the placebo group, reflected by the accumulation of microglia and higher microglial volumes. Placebo lamb histologies (n=31–41) were compared with the LD-caffeine–treated animals (n=7–12) and controls (n=5–9) using ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis test as appropriate. Data are presented as mean±SEM. Brackets show significance as follows: *P<0.05. LD-caffeine–treated group is presented in green, control is presented in yellow, and placebo is presented in black. CC-1 indicates adenomatous polyposis coli protein; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; Iba-1, ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1; MBP, myelin basic protein; PVWM, periventricular white matter; and SCWM, subcortical white matter.