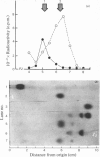
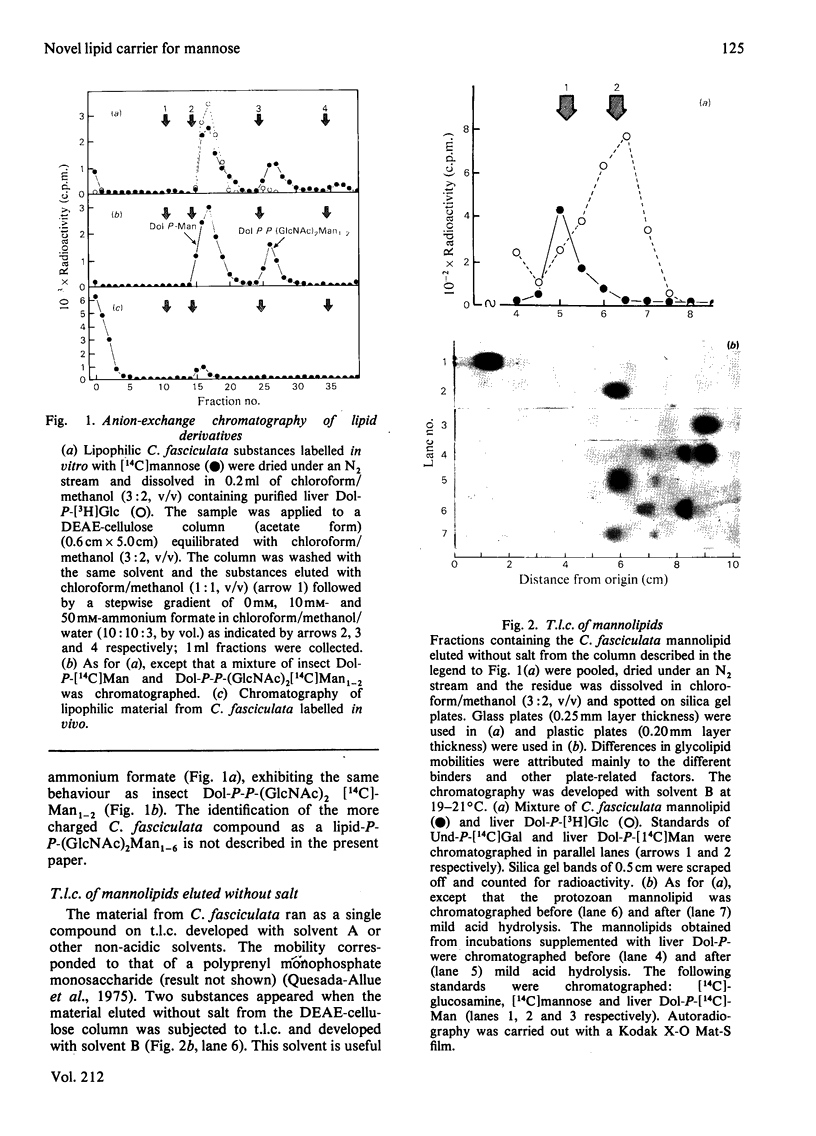
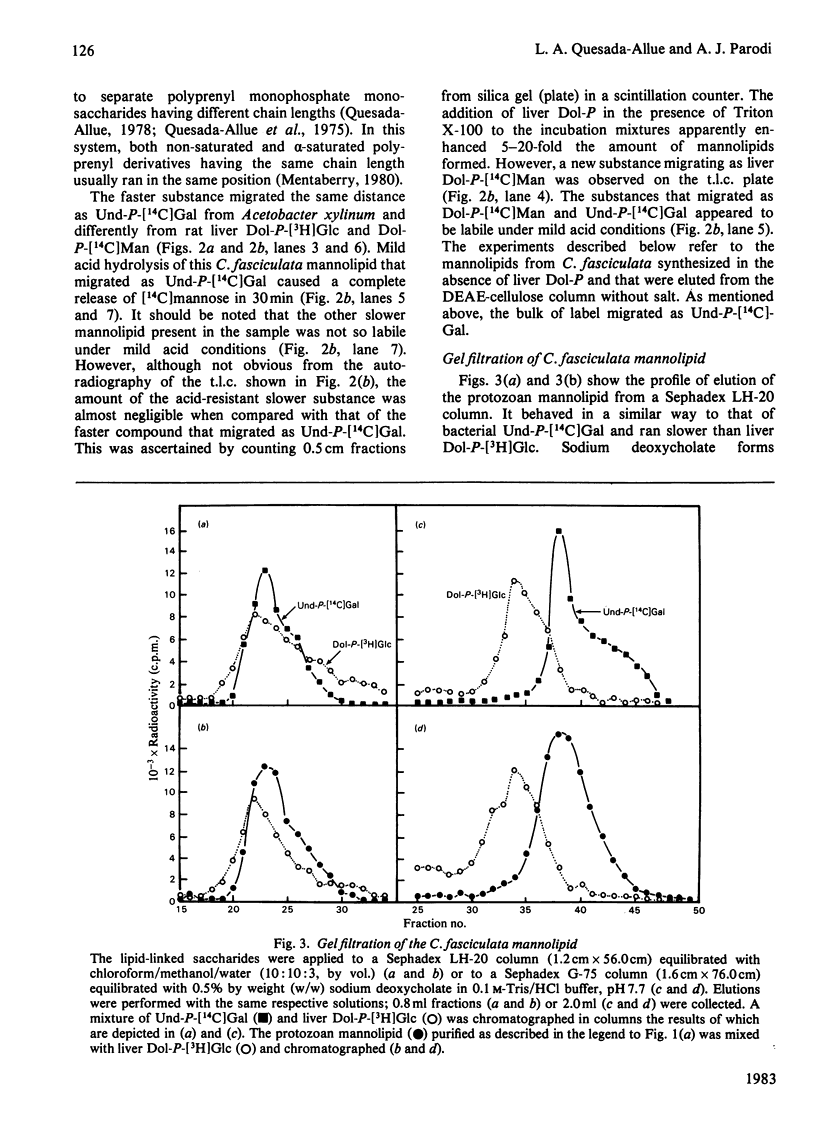
Abstract
Crithidia fasciculata cells incubated with [14C]glucose or membranes derived from the same protozoan incubated with GDP-[14C]mannose were found to synthesize a lipid monophosphate mannose. No glucosylated mild acid-labile compound was formed in vivo or in vitro when UDP-[14C]glucose was used instead of GDP-[14C]mannose. The lipid moiety of the mannosyl derivative formed behaved as a polyprenol having 11 isoprene residues as judged by t.l.c. and be gel filtration in sodium deoxycholate-containing buffers. The mannolipid was not broken on treatment with hot phenol, suggesting the existence of an alpha-saturated isoprene unit. This is the first case reported in which a mannosyl phospholipid involved in sugar transfer in a eukaryotic cell behaves as if it was similar to that of bacterial polyprenols, although having its putative alpha-isoprene unit saturated to the same extent as dolichols from higher organisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair W. L., Jr, Keller R. K. Dolichol metabolism in rat liver. Determination of the subcellular distribution of dolichyl phosphate and its site and rate of de novo biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8990–8996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchi J., Lambros C., Goldberg B., Hutner S. H., de Carvalho G. D. Susceptibility of an insect Leptomonas and Crithidia fasciculata to several established antitrypanosomatid agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):785–790. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens N. H., Parodi A. J., Leloir L. F. Glucose transfer from dolichol monophosphate glucose: the product formed with endogenous microsomal acceptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2857–2860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belocopitow E., Marechal L. R., Quesada Allue L. A. Enzymatic synthesis of polyprenol monophosphate mannose in insects. Mol Cell Biochem. 1977 Jul 5;16(2):127–134. doi: 10.1007/BF01732053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett C. T., Leloir L. F. Dolichyl monophosphate and its sugar derivatives in plants. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 1;161(1):93–101. doi: 10.1042/bj1610093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couso R. O., Ielpi L., García R. C., Dankert M. A. Synthesis of mannosyl cellobiose diphosphate prenol in Acetobacter xylinum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Oct 15;204(2):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmer D. P., Kulow C., Ericson M. C. Glycoprotein Synthesis in Plants: II. Structure of the Mannolipid Intermediate. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jan;61(1):25–29. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy P. J., Kerr J. D., Pennock J. F., Whittle K. J., Feeney J. The plurality of long chain isoprenoid alcohols (polyprenols) from natural sources. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 7;136(1):136–147. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90329-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García R. C., Recondo E., Dankert M. Polysaccharide biosynthesis in Acetobacter xylinum. Enzymatic synthesis of lipid diphosphate and monophospate sugars. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 15;43(1):93–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes G. R., Lucas J. J. A novel N-acetylglucosaminyl polyprene in hen oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7536–7539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung P., Tanner W. Identification of the lipid intermediate in yeast mannan biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas J. J., Waechter C. J. Polyisoprenoid glycolipids involved in glycoprotein biosynthesis. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Apr 28;11(2):67–78. doi: 10.1007/BF01792788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mańkowski T., Jankowski W., Chojnacki T., Franke P. C55-Dolichol: occurrence in pig liver and preparation by hydrogenation of plant undecaprenol. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2125–2130. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi A. J. Biosynthesis of yeast mannoproteins. Synthesis of mannan outer chain and of dolichol derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8343–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi A. J., Leloir L. F. The role of lipid intermediates in the glycosylation of proteins in the eucaryotic cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 23;559(1):1–37. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi A. J., Quesada Allue L. A., Cazzulo J. J. Pathway of protein glycosylation in the trypanosomatid Crithidia fasciculata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6201–6205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi A. J. Synthesis of glycosyl-dolichol derivatives in bakers' yeast and their role in protein glycosylation. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):171–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quesada Allué L. A., Belocopitow E., Maréchal L. R. Glycosyl transfer to an acceptor lipid from insects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1201–1208. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90486-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuvers F., Boer P., Hemming F. W. The presence of dolichol in a lipid diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker's yeast). Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):505–508. doi: 10.1042/bj1690505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma C. B., Babczinski P., Lehle L., Tanner W. The role of dolicholmonophosphate in glycoprotein biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):35–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneloni R. J., Ugalde R. A., Leloir L. F. Addition of glucose to dolichyl diphosphate oligosaccharide and transfer to protein. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):275–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavares I. A., Johnson N. J., Hemming F. W. A sensitive quantitative assay method for dolichols, cholesterol and ubiquinone using high-pressure liquid chromatography [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(6):1771–1773. doi: 10.1042/bst0051771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton M. J., Pennock J. F. Some studies on the biosynthesis of ubiguinone, isoprenoid alcohols, squalene and sterols by marine invertebrates. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(3):471–479. doi: 10.1042/bj1270471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Dankert M., Fennessey P., Robbins P. W. Characterization of a polyisoprenoid compound functional in O-antigen biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1798–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]