Abstract
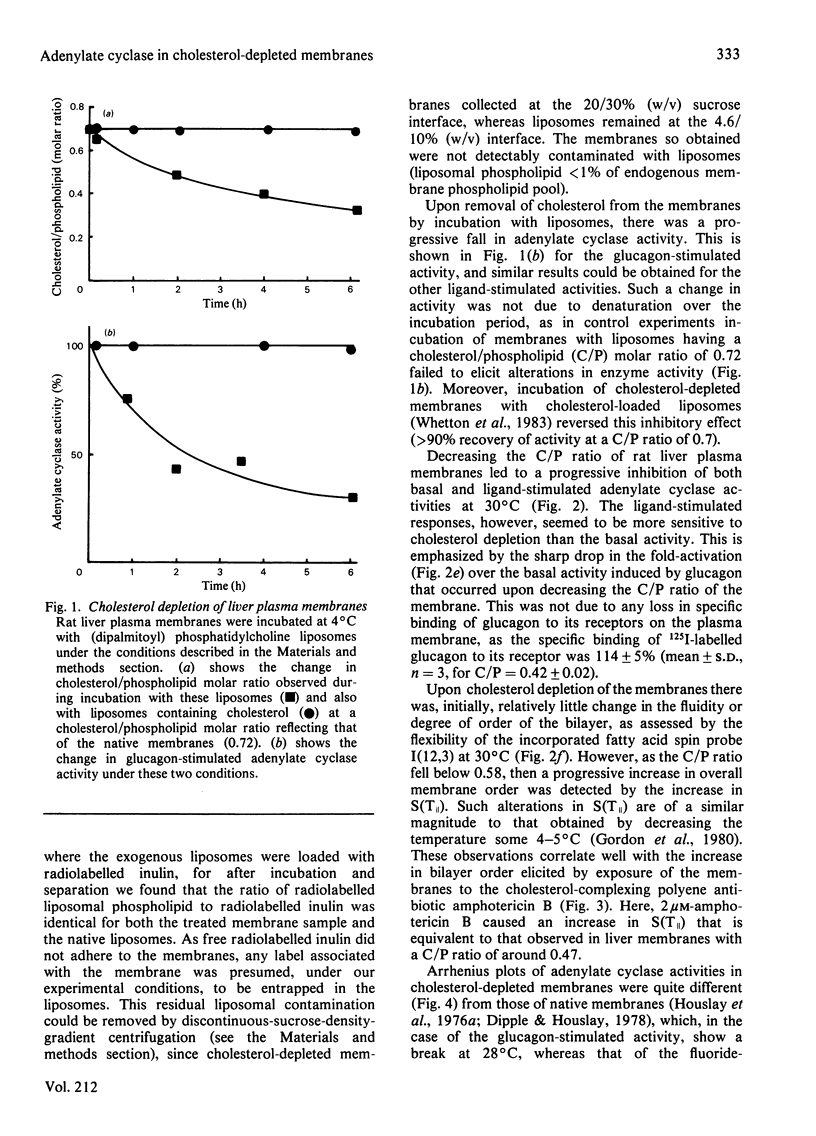
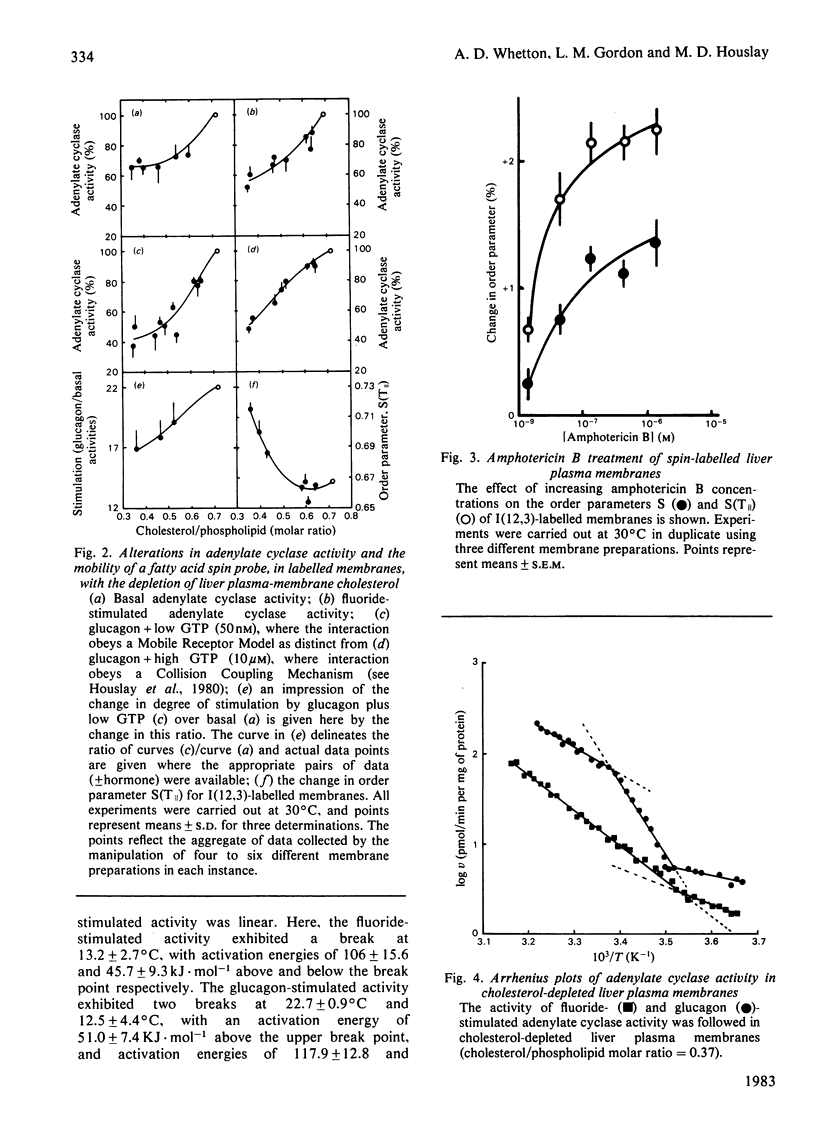
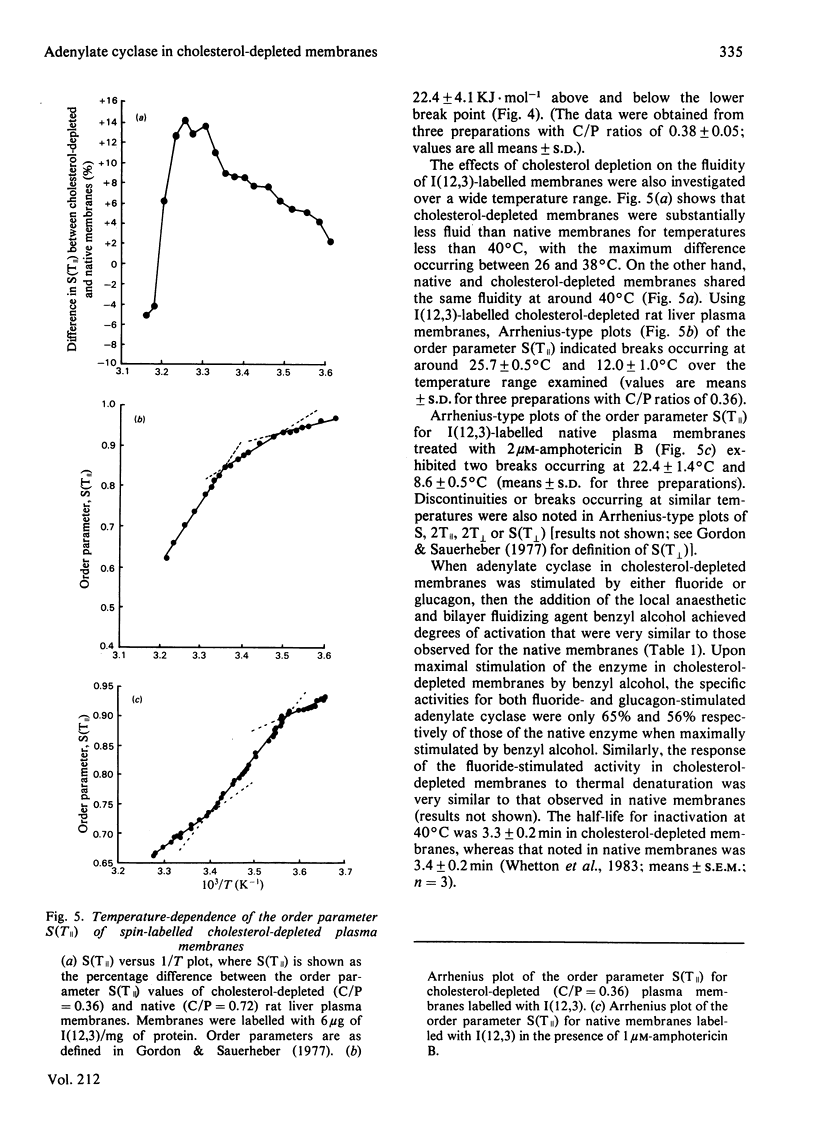
A procedure has been developed that allows for the depletion of rat liver plasma membrane cholesterol by incubation with liposomes at 4 degrees C. Upon cholesterol depletion, adenylate cyclase activity was inhibited and the membranes became more rigid, as determined by the flexibility of an incorporated fatty acid spin probe. Decreasing the cholesterol/phospholipid molar ratio elicited a pronounced drop in the net fold-stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity by glucagon. Two lipid phase separations were detected in cholesterol-depleted membranes at around 25 degrees C and 13 degrees C respectively. Breaks at these temperatures were observed in Arrhenius plots of both the mobility of the spin probe and the glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity for the range 2-40 degrees C, but only the one at the lower temperature for the fluoride-stimulated activity. It is proposed that the lipid phase separation occurring at 25 degrees C is localized in the external half of the bilayer, whereas that at 13 degrees C is due to lipids in the inner half of the bilayer. Similar structural and functional perturbations were manifest if the cholesterol-complexing polyene antibiotic amphotericin B was added to native membranes. The mechanism of adenylate cyclase inhibition achieved by cholesterol depletion and the domain structure of the plasma membrane in relation to cholesterol distribution are discussed. Native cholesterol/phospholipid ratios appear to optimize the functioning of adenylate cyclase in liver plasma membranes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blok M. C., Van Deenen L. L., De Gier J. The effect of cholesterol incorporation on the temperature dependence of water permeation through liposomal membranes prepared from phosphatidylcholines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 4;464(3):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kruyff B., Van Dijck P. W., Demel R. A., Schuijff A., Brants F., Van Deenen L. L. Non-random distribution of cholesterol in phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jul 12;356(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Jansen J. W., van Dijck P. W., van Deenen L. L. The preferential interaction of cholesterol with different classes of phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 14;465(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipple I., Houslay M. D. Amphoptericin B has very different effects on the glucagon and fluoride-stimulated adenylate cyclase activities of rat liver plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 1;106(1):21–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dipple I., Houslay M. D. The activity of glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase from rat liver plasma membranes is modulated by the fluidity of its lipid environment. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):179–190. doi: 10.1042/bj1740179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. M., Sauerheber R. D., Esgate J. A., Dipple I., Marchmont R. J., Houslay M. D. The increase in bilayer fluidity of rat liver plasma membranes achieved by the local anesthetic benzyl alcohol affects the activity of intrinsic membrane enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4519–4527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. M., Sauerheber R. D., Esgate J. A. Spin label studies on rat liver and heart plasma membranes: effects of temperature, calcium, and lanthanum on membrane fluidity. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(3):299–326. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon L. M., Sauerheber R. D. Studies on spin-labelled egg lecithin dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 1;466(1):34–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Dipple I., Elliott K. R. Guanosine 5'-triphosphate and guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate effect a collision coupling mechanism between the glucagon receptor and catalytic unit of adenylate cyclase. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):649–658. doi: 10.1042/bj1860649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Dipple I., Rawal S., Sauerheber R. D., Esgate J. A., Gordon L. M. Glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase detects a selective perturbation of the inner half of the liver plasma-membrane bilayer achieved by the local anaesthetic prilocaine. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):131–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1900131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Warren G. B., Metcalfe J. C. The lipid environment of the glucagon receptor regulates adenylate cyclase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 17;436(2):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Metcalfe J. C., Warren G. B., Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A. The glucagon receptor of rat liver plasma membrane can couple to adenylate cyclase without activating it. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 17;436(2):489–494. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D. Mobile receptor and collision coupling mechanisms for the activation of adenylate cyclase by glucagon. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:111–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Palmer R. W. Changes in the form of Arrhenius plots of the activity of glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase and other hamster liver plasma-membrane enzymes occurring on hibernation. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):909–919. doi: 10.1042/bj1740909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E. Activation and attenuation of adenylate cyclase. The role of GTP-binding proteins as macromolecular messengers in receptor--cyclase coupling. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj1950001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham L., Whetton A. D., Houslay M. D. The local anaesthetic and bilayer fluidising agent, benzyl alcohol decreases the thermostability of the integral membrane protein adenylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 5;140(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80526-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Montesano R., Meda P., Malaisse-Lagae F., Brown D., Perrelet A., Vassalli P. Heterogeneous distribution of filipin--cholesterol complexes across the cisternae of the Golgi apparatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):293–297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel R. J., Honeyman T. W., McMahon K. K., Serio R., Clark R. B. Inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation in hamster adipocytes with phosphatidic acid: differences and similarities with alpha adrenergic effects. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(6):437–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoeven R. P., Emmelot P., Krol J. H., Oomen-Meulemans E. P. Studies on plasma membranes. XXII. Fatty acid profiles of lipid classes in plasma membranes of rat and mouse livers and hepatomas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 24;380(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Gordon L. M., Houslay M. D. Elevated membrane cholesterol concentrations inhibit glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):437–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2100437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Johannsson A., Wilson S. R., Wallace A. V., Houslay M. D. The thermodependence of the activity of integral enzymes in liver plasma membranes: evidence consistent with a functionally asymmetric lipid bilayer. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijck P. W. Negatively charged phospholipids and their position in the cholesterol affinity sequence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 19;555(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoeven R. P., Emmelot P. Studies on plasma membranes. 18. Lipid class composition of plasma membranes isolated from rat and mouse liver and hepatomas. J Membr Biol. 1972;9(2):105–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


