Abstract
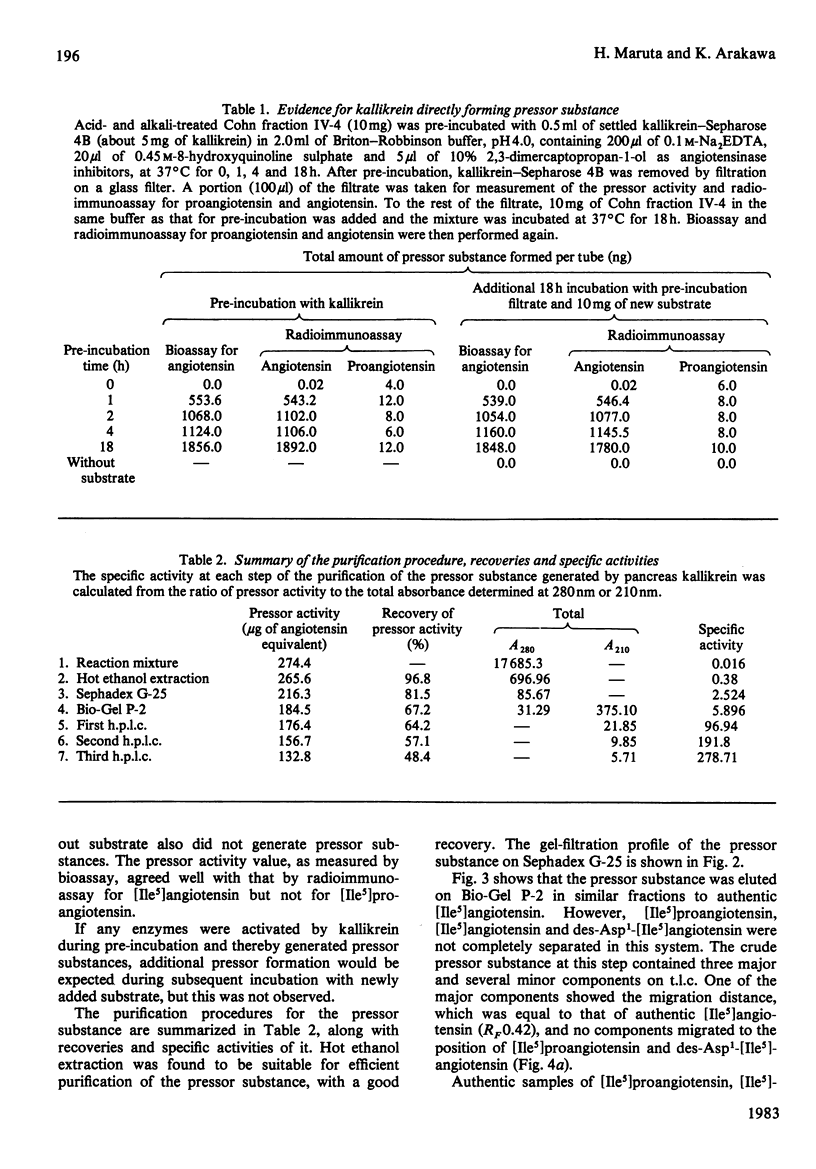
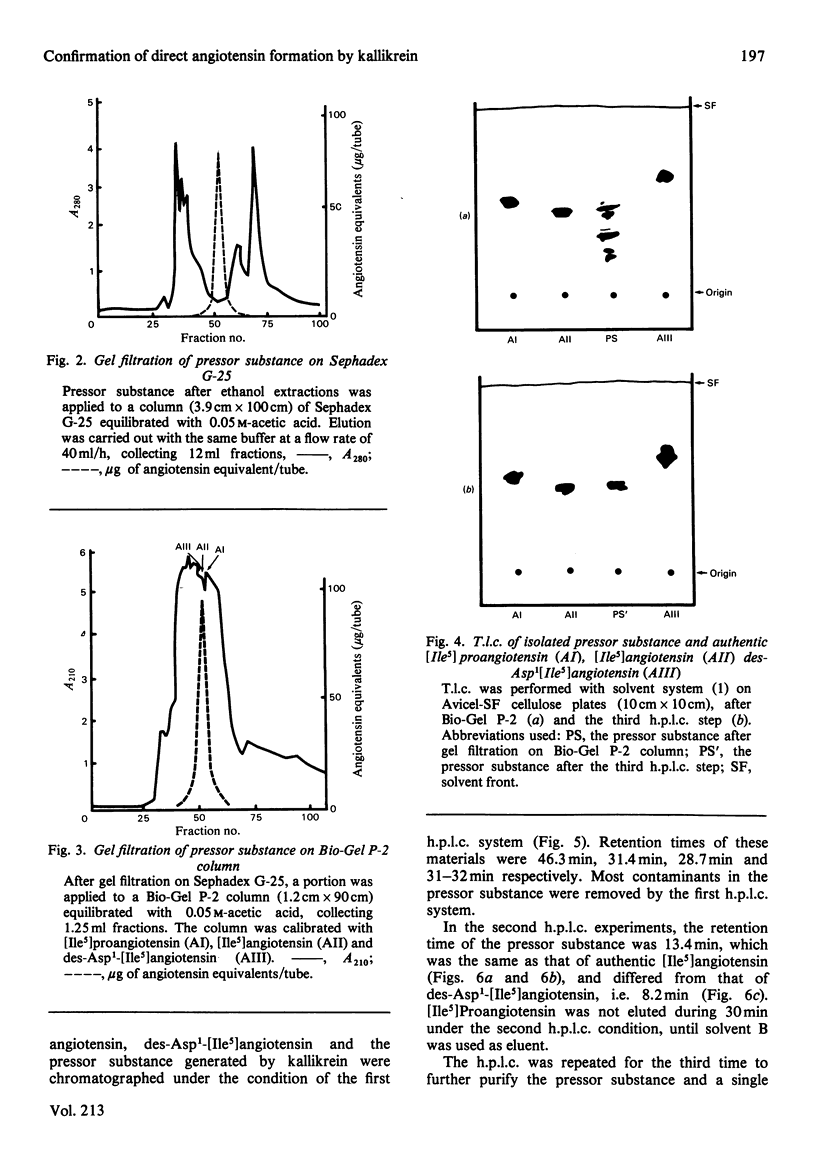
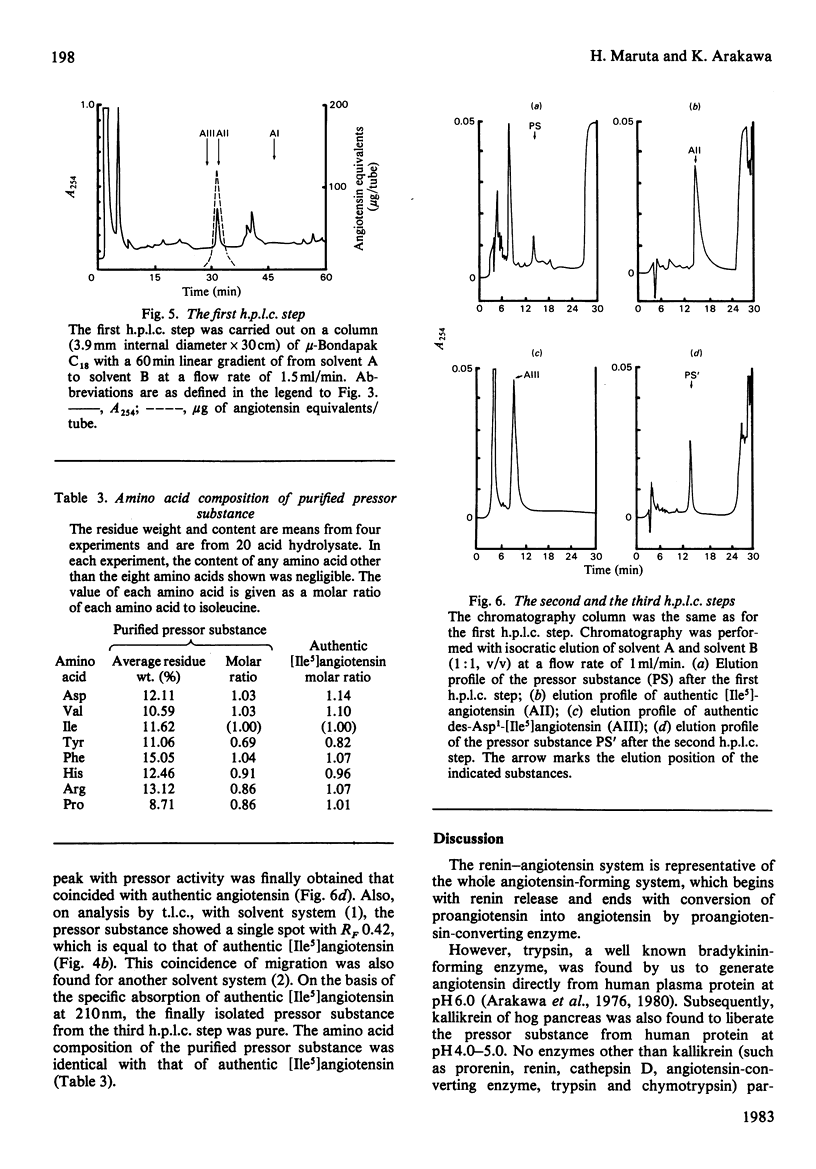
This study was undertaken to confirm our previous preliminary observation that hog pancreas kallikrein (EC 3.4.21.35) directly liberated an angiotensin-like substance from human plasma protein Cohn fraction IV-4 at an acidic pH of 4.0-5.0. First, the possibility of proangiotensin or des-Asp1-angiotensin being the pressor substance was ruled out by t.l.c. Secondly, the pressor substance was purified by Sephadex G-25 and Bio-Gel P-2 gel filtration, and finally by high-performance liquid chromatography. The amino acid composition of the isolated pressor substance (residues/mol) was: Asp, 1.03; Val, 1.03; Ile, 1.00; Tyr, 0.69; Phe, 1.04; His, 0.91; Arg, 0.86; Pro, 0.86. This composition was identical with that of angiotensin. Since the reaction mixture was not contaminated with common proteolytic enzymes, such as trypsin, chymotrypsin, renin, cathepsin D and proangiotensin-converting enzyme, and other enzymes activated by kallikrein, it is clear that hog kallikrein directly produces angiotensin in vitro.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa K., Ikeda M., Fukuyama J., Sakai T. A pressor formation by trypsin from renin-denatured human plasma protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Mar;42(3):599–602. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-3-599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa K., Maruta H. Ability of kallikrein to generate angiotensin II-like pressor substance and a proposed 'kinin-tensin enzyme system'. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):705–706. doi: 10.1038/288705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa K., Minohara A., Uemura N., Sakai T., Ikeda M. Characterization of renin-like activity in human plasma protein IV-4 fraction. Endocrinol Jpn. 1975 Oct;22(5):427–432. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.22.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa K., Yuki M., Ikeda M. Chemical identity of tryptensin with angiotensin. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):647–653. doi: 10.1042/bj1870647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Lysosomal acid proteinase of rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):601–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1040601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain M. D., Catt K. J., Coghlan J. P. Effect of circulating fragments of angiotensin II on radioimmunoassay in arterial and venous blood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Dec;29(12):1639–1643. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-12-1639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. B., Pettinger W. A. Organ specificity of angiotensin II and Des-aspartyl angiotensin II in the conscious rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Aug;198(2):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. B., Schmitz J. M. (7-Ile) angiotensin III: a relatively selective antagonist of angiotensin steroidogenesis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 1;54(3):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coblyn J. S., Austen K. F., Wintroub B. U. Purification and characterization of a human neutrophil neutral protease. The neutral peptide-generating protease. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):998–1005. doi: 10.1172/JCI109400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Cheung H. S. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jul;20(7):1637–1648. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT D. F., HORTON E. W., LEWIS G. P. The isolation of bradykinin, a plasma kinin from ox blood. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:60–65. doi: 10.1042/bj0780060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel R. L., Cain J. P., Williams G. H. Double antibody radioimmunoassay of renin activity and angiotensin II in human peripheral plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Apr;81(4):632–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisé C., Boucher R., Thibault G., Genest J. Formation of angiotensin II by tonin from partially purified human angiotensinogen. Can J Biochem. 1981 Apr;59(4):250–255. doi: 10.1139/o81-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABERMANN E., BLENNEMANN G. UBER SUBSTRATE UND REAKTIONSPRODUKTE DER KININBILDENDEN ENZYME TRYPSIN, SERUM- UND PANKREASKALLIKREIN SOWIE VON CROTALUSGIFT. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1964 Nov 6;249:357–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL B. C. A modified spectrophotometric determination of chymotrypsin, trypsin, and thrombin. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Dec;37:1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitomi Y., Niinobe M., Fujii S. A sensitive colorimetric assay for human urinary kallikrein. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Jan 31;100(3):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen P. J., Amery A. K., Fagard R. H., Katz F. H. Radioimmunoassay of angiotensin II in unextracted plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Sep 1;88(2):403–412. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90447-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Geller R. G., Alexander R. W., Gill J. R., Jr, Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in normal man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):812–819. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Routhier R., Caron M., Chrétien M., Demassieux S., Boucher R., Genest J. N-Terminal amino acid sequence of rat tonin: homology with serine proteases. Can J Biochem. 1978 Sep;56(9):920–925. doi: 10.1139/o78-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sexton J. M., Britton S. L., Beierwaltes W. H., Fiksen-Olsen M. J., Romero J. C. Formation of angiotensin III from [des-Asp1]angiotensin I in the mesentric vasculature. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):H218–H223. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.237.2.H218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibault G., Genest J. Tonin, an esteroprotease from rat submaxillary glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;660(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnaer J. A., Verhoef J., Wiegant V. M., de Jong W. Separation and quantification of angiotensins and some related peptides by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1980 Sep 12;183(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81710-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. A neutrophil-dependent pathway for the generation of a neutral peptide mediator: partial characterization of components and control by alpha-1-antitrypsin. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):812–824. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Klickstein L. B., Kaempfer C. E., Austen K. F. A human neutrophil-dependent pathway for generation of angiotensin II: purification and physicochemical characterization of the plasma protein substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa N., Takahashi N., Inagami T., Page D. L. Isolation of completely inactive plasma prorenin and its activation by kallikreins. A possible new link between renin and kallikrein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 15;569(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]