Abstract
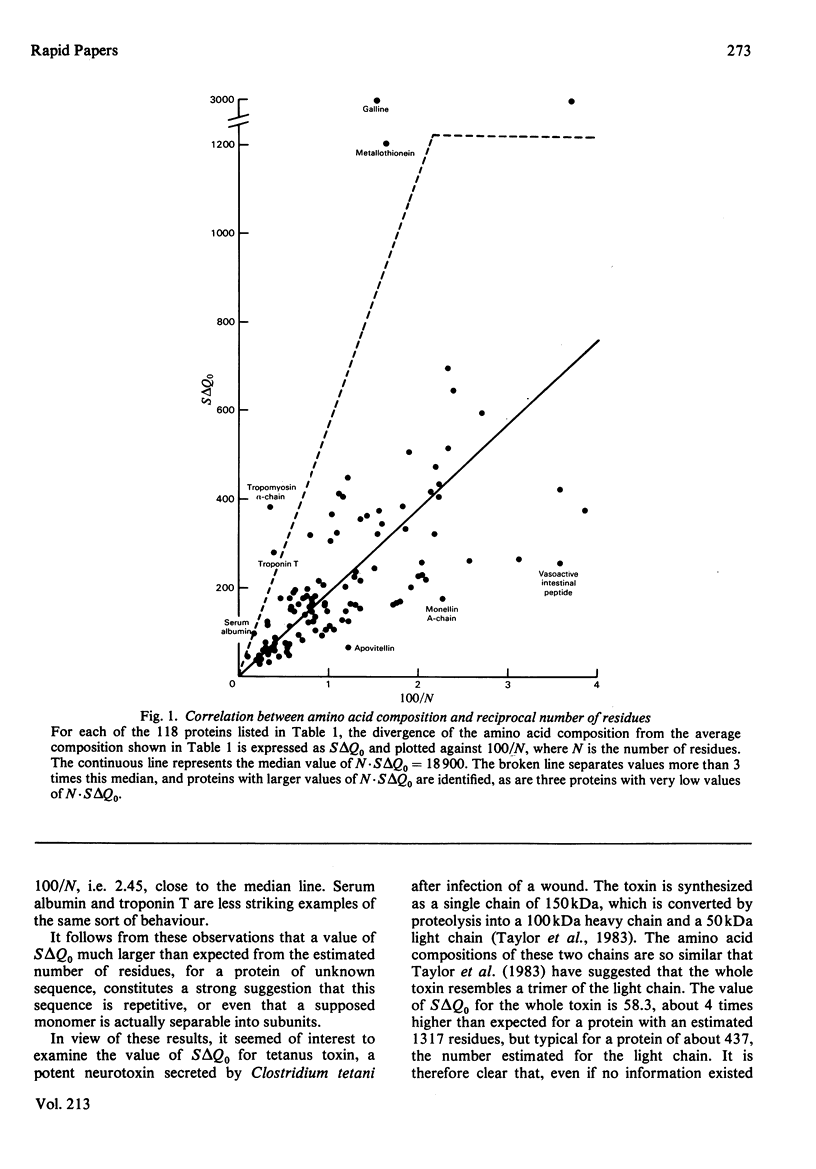
Natural peptides and small proteins in general have amino acid compositions that diverge much more from the average composition of all proteins than do those of proteins. The effect is large and consistent enough to provide a rough check on the measured molecular mass of a protein and to indicate whether it is likely to have a significantly repetitive structure. For example, the alpha-chain of tropomyosin, a highly repetitive protein, has no amino acid composition that would be characteristic of a much smaller protein. The observation provides support for the suggestion [Taylor, Britton & van Heyningen (1983) Biochem. J. 209, 897-899] that tetanus toxin resembles a trimer of the light chain produced by proteolysis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cornish-Bowden A. Assessment of protein sequence identity from amino acid composition data. J Theor Biol. 1977 Apr 21;65(4):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(77)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. Critical values for testing the significance of amino acid composition indexes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90450-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. How reliably do amino acid composition comparisons predict sequence similarities between proteins? J Theor Biol. 1979 Feb 21;76(4):369–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A., Marson A. Evaluation of the non-randomness of protein compositions. J Mol Evol. 1977 Dec 29;10(3):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF01764598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halmquist R., Moise H. Compositional nonrandomness: a quantitatively conserved evolutionary invariant. J Mol Evol. 1975 Oct 3;6(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01732670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longley W. Regular repeats in the sequence of tropomyosin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977 Jan;9(1):49–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1977.tb01835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. F., Britton P., van Heyningen S. Similarities in the heavy and light chains of tetanus toxin suggested by their amino acid compositions. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):897–899. doi: 10.1042/bj2090897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


