Abstract
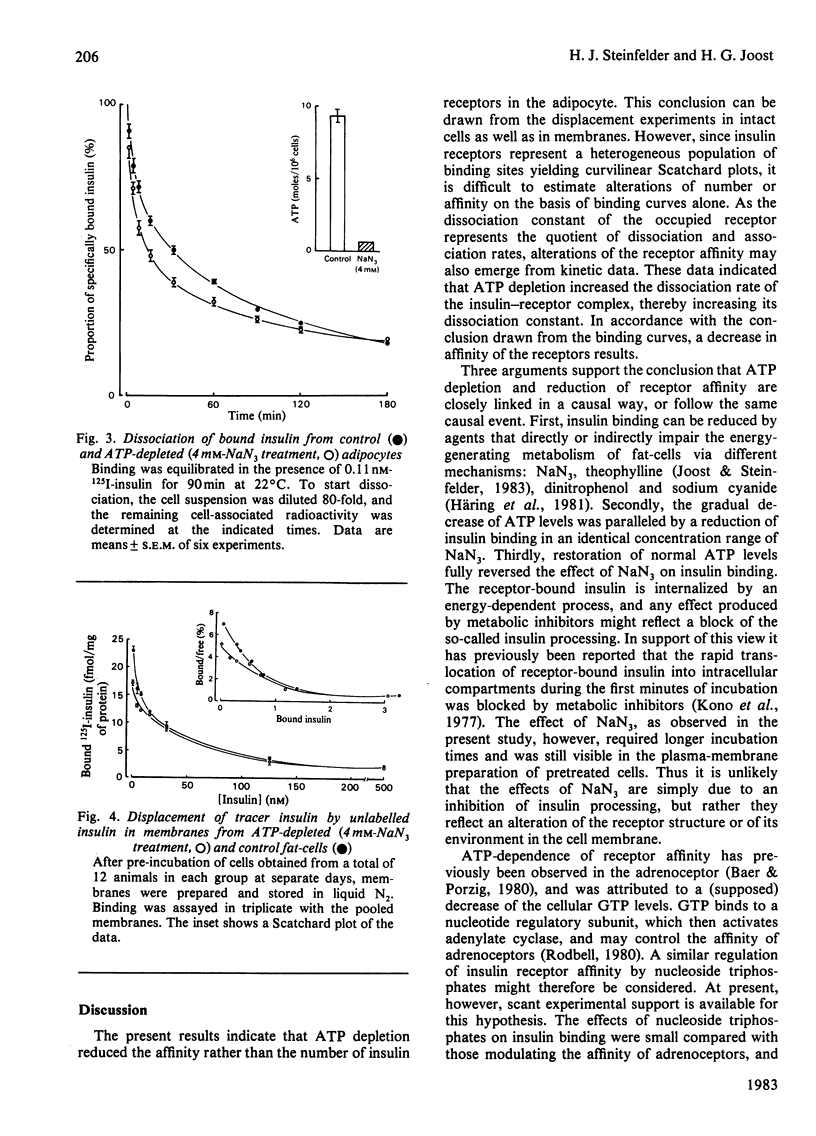
The effects of the metabolic inhibitor NaN3 on insulin receptors in isolated rat fat-cells were investigated. The agent reduced insulin binding in parallel to a decrease of the ATP content of cells. Both effects were observed in the same concentration range of NaN3, and were fully reversible. According to the binding curves the affinity rather than the number of receptors was reduced. Kinetic experiments revealed an increased dissociation rate of the insulin-receptor complex. The effects outlasted cell disruption, since the receptor affinity was still lowered in plasma membranes obtained from NaN3-treated cells. Thus an inhibition of insulin internalization could not account for the observed effects. It is suggested that the observed ATP-dependence of insulin receptor affinity reflects a reversible structural alteration of the receptor, or of some closely related membrane protein.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann E., Allmann D. W., Green D. E. The membrane systems of the mitochondrion. I. The S fraction of the outer membrane of beef heart mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jul;115(1):153–164. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(66)81051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer M., Porzig H. Cell metabolism affects the density of beta-adrenergic receptors in intact rat reticulocytes. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80794-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro J. F., Amatruda J. M. Insulin receptors in hepatocytes: postreceptor events mediate down regulation. Science. 1980 Nov 28;210(4473):1029–1031. doi: 10.1126/science.7001632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corin R. E., Donner D. B. Insulin receptors convert to a higher affinity state subsequent to hormone binding. A two-state model for the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin B., Solomons C. C., Emler C. A., Schalch D. S., Sussman K. E. Decreased insulin binding and degradation associated with depressed intracellular ATP content. Diabetes. 1980 Mar;29(3):221–226. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N. Inhibition of adenosine cyclic 3', 5'-monophosphate accumulation in fat cells by adenosine, N6-(phenylisopropyl) adenosine, and related compounds. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;9(5):595–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehlmann M., Carpentier J. L., Le Cam A., Thamm P., Saunders D., Brandenburg D., Orci L., Freychet P. Biochemical and morphological evidence that the insulin receptor is internalized with insulin in hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):82–87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filetti S., Takai N. A., Rapoport B. Insulin receptor down-regulation, prevention at a post-receptor site. Endocrinology. 1981 Jun;108(6):2409–2411. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-6-2409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Osterlind K., Vinten J., Gammeltoft S. A procedure for measurement of distribution spaces in isolated fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 24;286(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Freychet P., LeCam A., Orci L. Intracellular translocation of iodine-125-labeled insulin: direct demonstration in isolated hepatocytes. Science. 1978 May 19;200(4343):782–785. doi: 10.1126/science.644321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Arend W., Holze S. A. Effects of tolbutamide on insulin binding to isolated fat cells of the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 1;31(7):1227–1231. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Steinfelder H. J. Modulation of insulin sensitivity by adenosine. Effects on glucose transport, lipid synthesis, and insulin receptors of the adipocyte. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;22(3):614–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Sarver J. A., Vega F. V., Pointer R. H. Actions of insulin in fat cells. Effects of low temperature, uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation, and respiratory inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2226–2233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newby A. C., Luzio J. P., Hales C. N. The properties and extracellular location of 5'-nucleotidase of the rat fat-cell plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;146(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj1460625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinfelder H. J., Joost H. G. In vitro effects of theophylline on insulin receptors in adipocytes: correlation with the lipolytic action of the agent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91938-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Gould M. K. Insulin-stimulated sugar transport and 125I-insulin binding by rat soleus muscle: permissive effect of ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



