Abstract
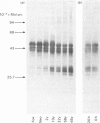
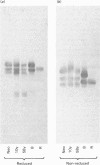
Link proteins were identified immunologically in human articular-cartilage protein preparations from various individuals. Irrespective of age, all cartilages contained three link proteins of mol.wts. 48000, 44000 and 41000. However, with increasing age, multiple additional components of mol.wts. 26000-30000 were commonly observed under conditions where disulphide bonds were reduced.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J., Caterson B. The purification and cyanogen bromide cleavage of the 'link proteins' from cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet F., Périn J. P., Jollès P. Isolation and chemical characterization of two distinct "link proteins" from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 15;532(2):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90578-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion B. R., Poole A. R. Immunity to homologous cartilage proteoglycans in rabbits with chronic inflammatory arthritis. Coll Relat Res. 1981 Sep;1(5):453–473. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(81)80029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén A., Björnsson S., Heinegård D. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregate formation. Role of link protein. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1970669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory J. D. Multiple aggregation factors in cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):383–386. doi: 10.1042/bj1330383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C. Interaction of cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronic acid. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(1):101–120. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H., Shulman H. J., Sandson J. I. Immunochemistry of cartilage proteoglycan. Immunodiffusion and gel-electrophoretic studies. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(1):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj1260163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson G. E., Muir H., Swanson S. A., Freeman M. A. Correlations between stiffness and the chemical constituents of cartilage on the human femoral head. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 21;215(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Pidoux I., Reiner A., Rosenberg L. An immunoelectron microscope study of the organization of proteoglycan monomer, link protein, and collagen in the matrix of articular cartilage. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):921–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Reiner A., Tang L. H., Rosenberg L. Proteoglycans from bovine nasal cartilage. Immunochemical studies of link protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9295–9305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Jollès P. Comparative studies on human and bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan complex components. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Nov 1;21(2):71–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00240278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Poole A. R., Mort J. S. The heterogeneity of link proteins isolated from human articular cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11908–11914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J. Age-related changes in the structure of the proteoglycan subunits from human articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang L. H., Rosenberg L., Reiner A., Poole A. R. Proteoglycans from bovine nasal cartilage. Properties of a soluble form of link protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10523–10531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasan N. S., Lash J. W. Heterogeneity of proteoglycans in developing chick limb cartilage. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):179–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1640179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]