Abstract
The increases in the amount of active, non-phosphorylated, pyruvate dehydrogenase caused by positive inotropic agents (from a control value of about 10%, to 40% of total enzyme) in the perfused rat heart could be completely blocked by prior perfusion with 2.5 micrograms of Ruthenium Red/ml. A similar increase caused by 5 mM-pyruvate was not blocked. This concentration of Ruthenium Red caused a 25% decrease in contractile force of hearts perfused in the absence of positive inotropic agents; however, in their presence the contractile force reached the same value in the absence or presence of Ruthenium Red. Neither control nor stimulated phosphorylase a content was affected by Ruthenium Red. Verapamil (0.1 microM) also decreased control contraction (by 40%), but did not block the activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase caused by a rise in extracellular [Ca2+]. The results support the hypothesis that positive inotropic agents activate pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat heart by increasing intramitochondrial [Ca2+].
Full text
PDF
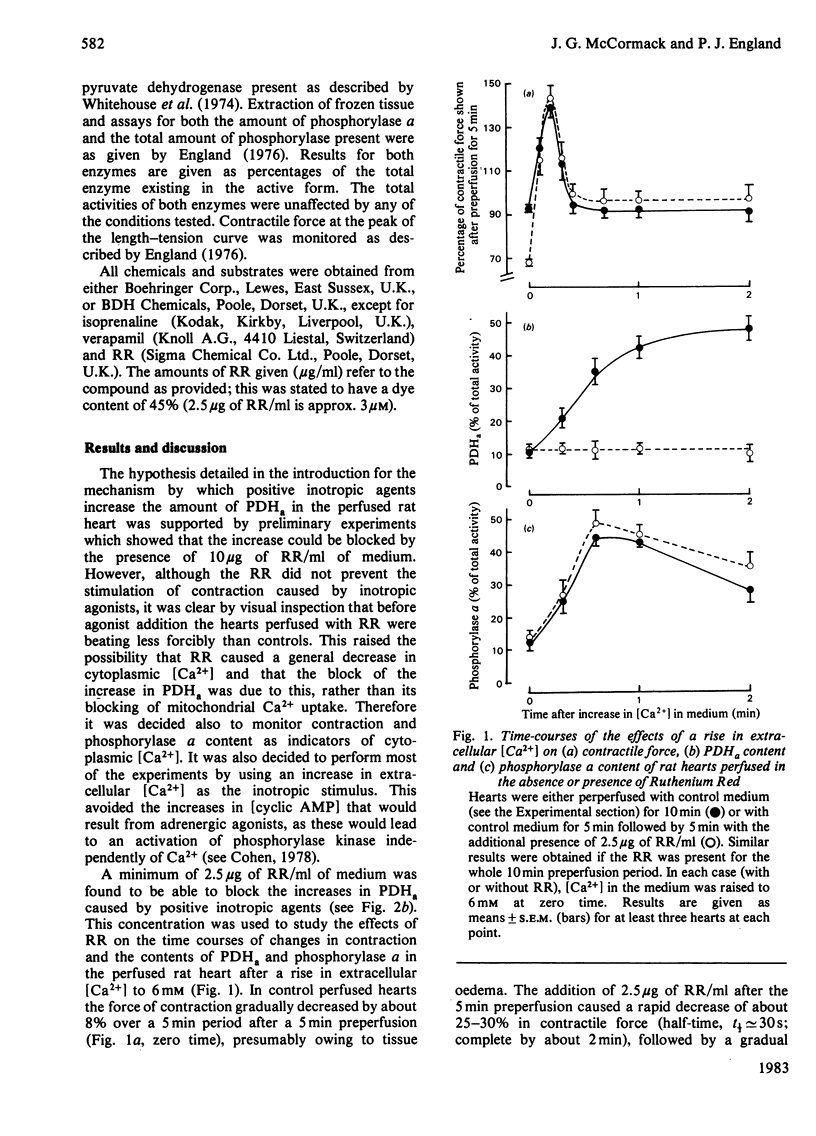

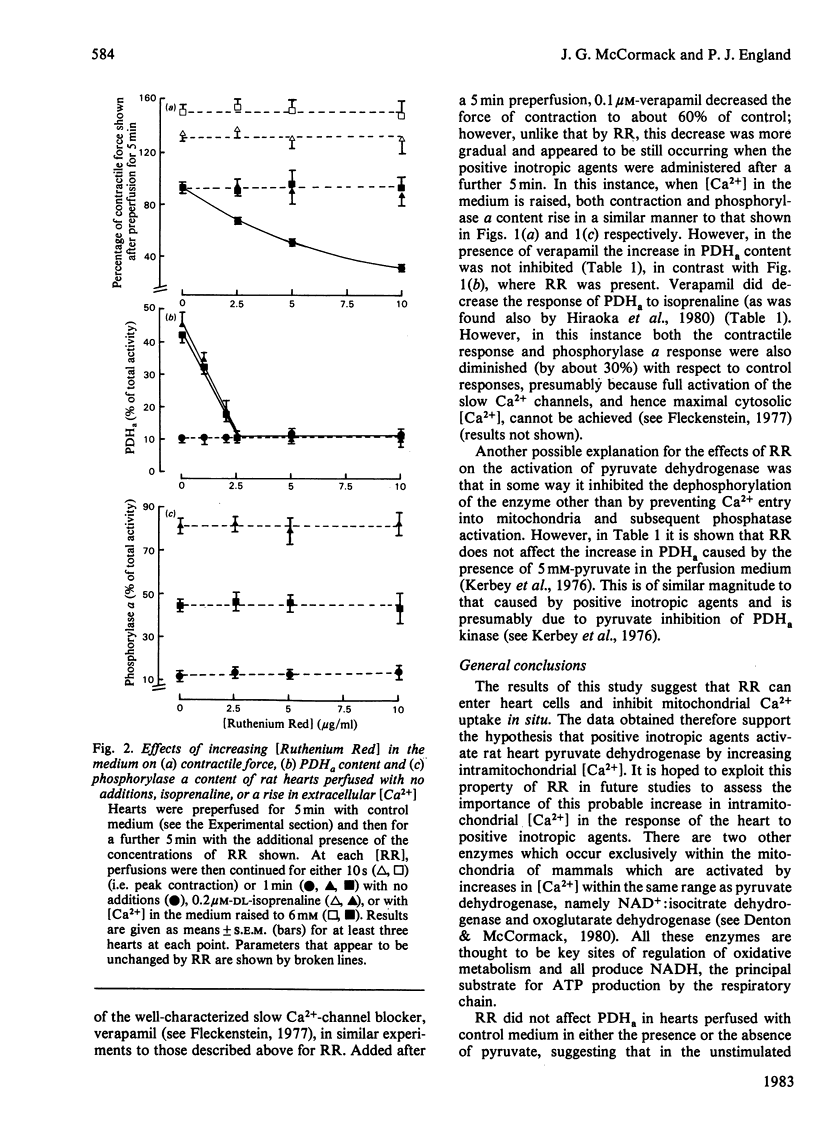

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen P. The role of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;14:117–196. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152814-0.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G., Edgell N. J. Role of calcium ions in the regulation of intramitochondrial metabolism. Effects of Na+, Mg2+ and ruthenium red on the Ca2+-stimulated oxidation of oxoglutarate and on pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in intact rat heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):107–117. doi: 10.1042/bj1900107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G. On the role of the calcium transport cycle in heart and other mammalian mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 22;119(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., Randle P. J., Martin B. R. Stimulation by calcium ions of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate phosphatase. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(1):161–163. doi: 10.1042/bj1280161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J. Studies on the phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin during modification of contraction in perfused rat heart. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):295–304. doi: 10.1042/bj1600295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleckenstein A. Specific pharmacology of calcium in myocardium, cardiac pacemakers, and vascular smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1977;17:149–166. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka T., DeBuysere M., Olson M. S. Studies of the effects of beta-adrenergic agonists on the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in the perfused rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7604–7609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardami E., Gratzer W. B. Interaction of cardiac myosin and its light chains with calcium ions and regulation of binding by phosphorylation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1982 Feb;14(2):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(82)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbey A. L., Randle P. J., Cooper R. H., Whitehouse S., Pask H. T., Denton R. M. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat heart. Mechanism of regulation of proportions of dephosphorylated and phosphorylated enzyme by oxidation of fatty acids and ketone bodies and of effects of diabetes: role of coenzyme A, acetyl-coenzyme A and reduced and oxidized nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):327–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1540327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marban E., Rink T. J., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Free calcium in heart muscle at rest and during contraction measured with Ca2+ -sensitive microelectrodes. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):845–850. doi: 10.1038/286845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. The activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase in the perfused rat heart by adrenaline and other inotropic agents. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):639–643. doi: 10.1042/bj1940639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Edgell N. J., Denton R. M. Studies on the interactions of Ca2+ and pyruvate in the regulation of rat heart pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. Effects of starvation and diabetes. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 15;202(2):419–427. doi: 10.1042/bj2020419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L. Specific inhibition of mitochondrial Ca++ transport by ruthenium red. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 22;42(2):298–305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng C. F., Kane J. J., Straub K. D., Murphy M. L. Improvement of mitochondrial energy production in ischemic myocardium by in vivo infusion of ruthenium red. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1980 Jan-Feb;2(1):45–54. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198001000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasington F. D., Gazzotti P., Tiozzo R., Carafoli E. The effect of ruthenium red on Ca 2+ transport and respiration in rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 21;256(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Cooper R. H., Randle P. J. Mechanism of activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by dichloroacetate and other halogenated carboxylic acids. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):761–774. doi: 10.1042/bj1410761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



