Abstract
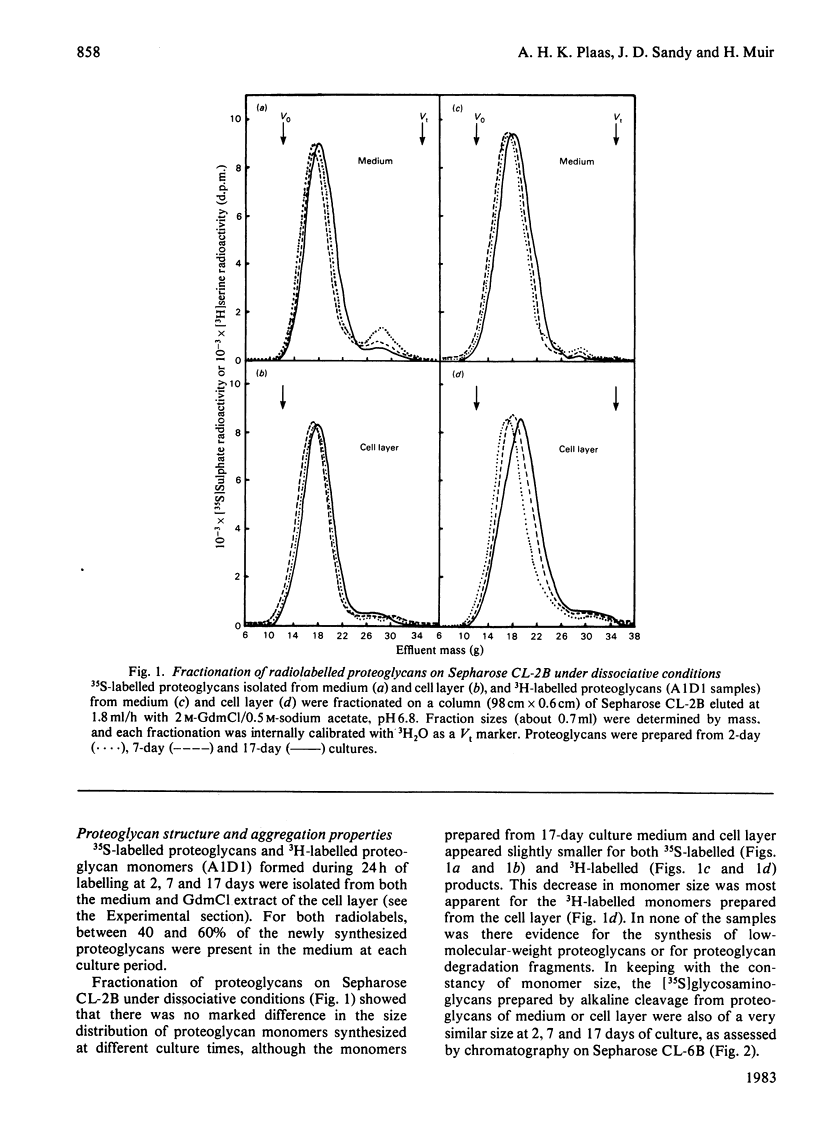
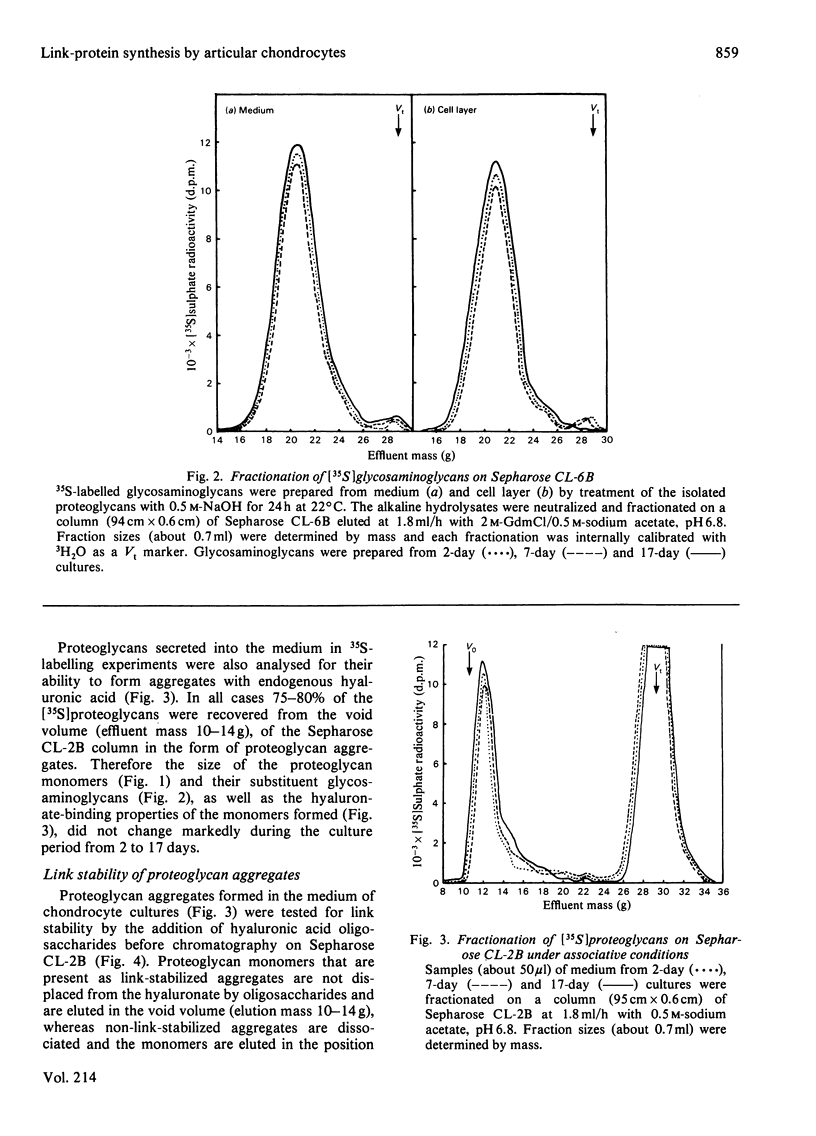
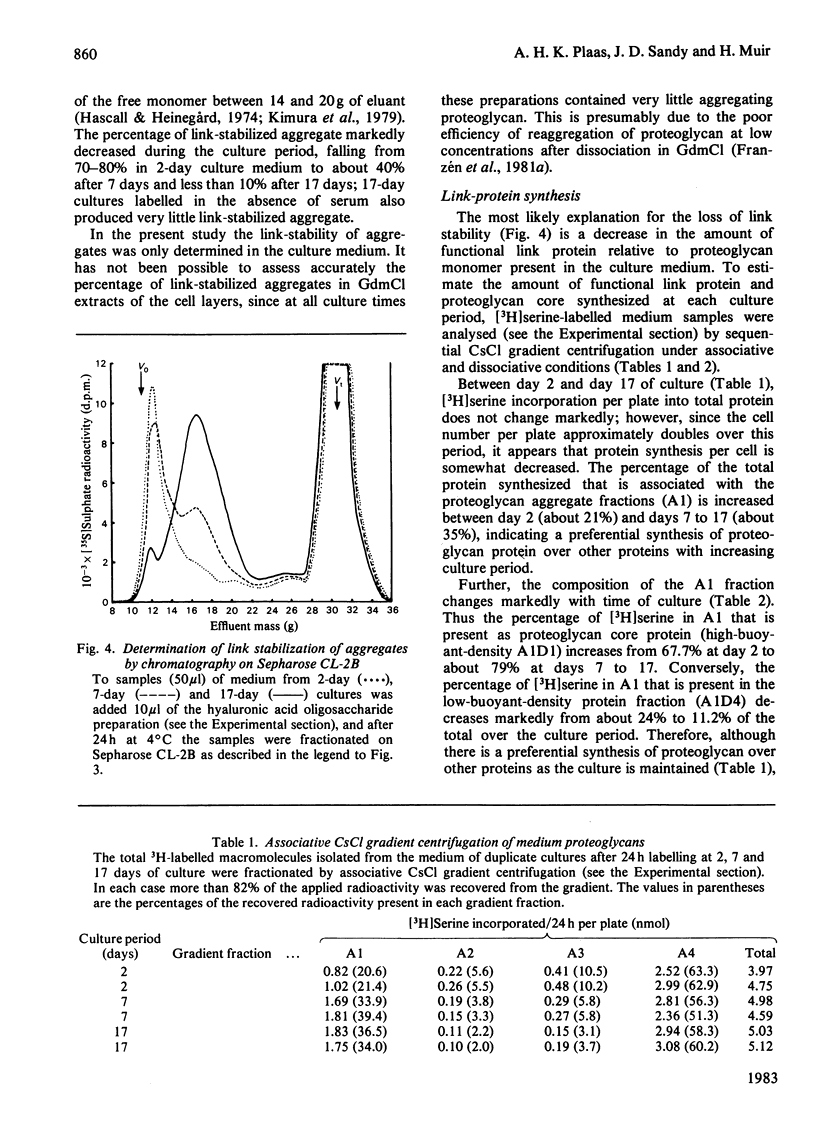
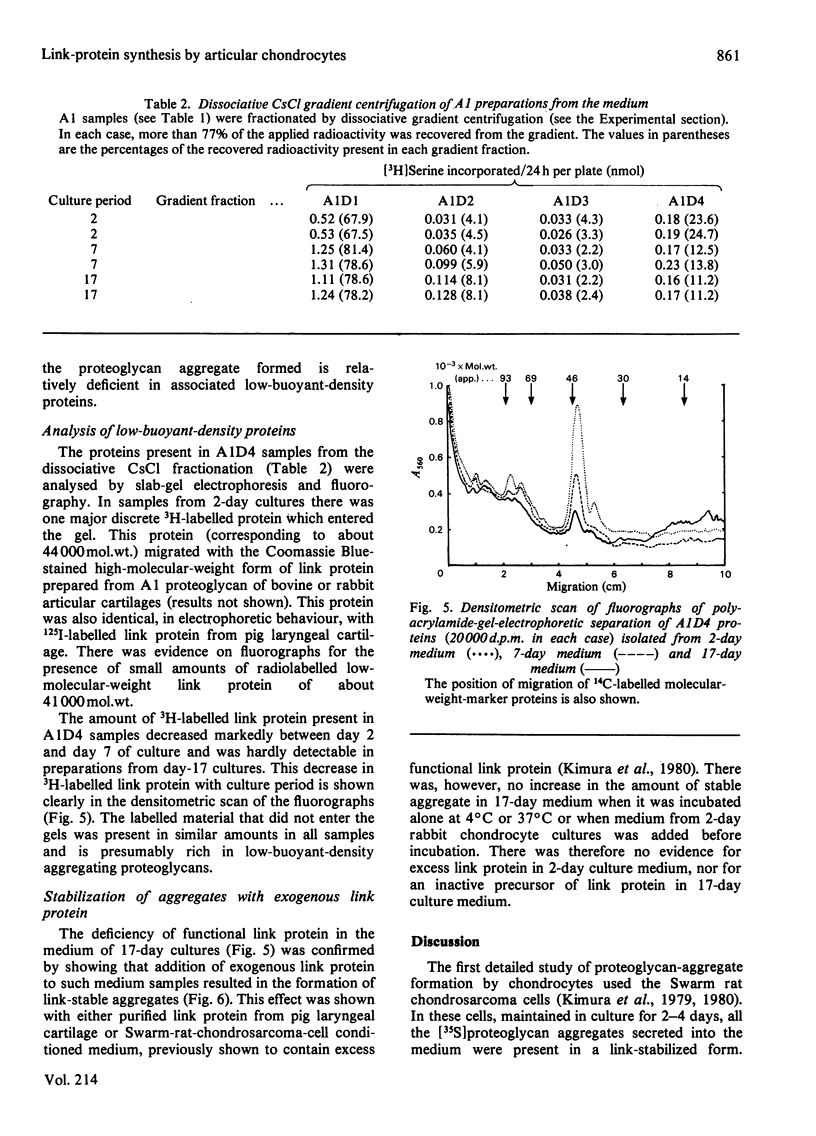
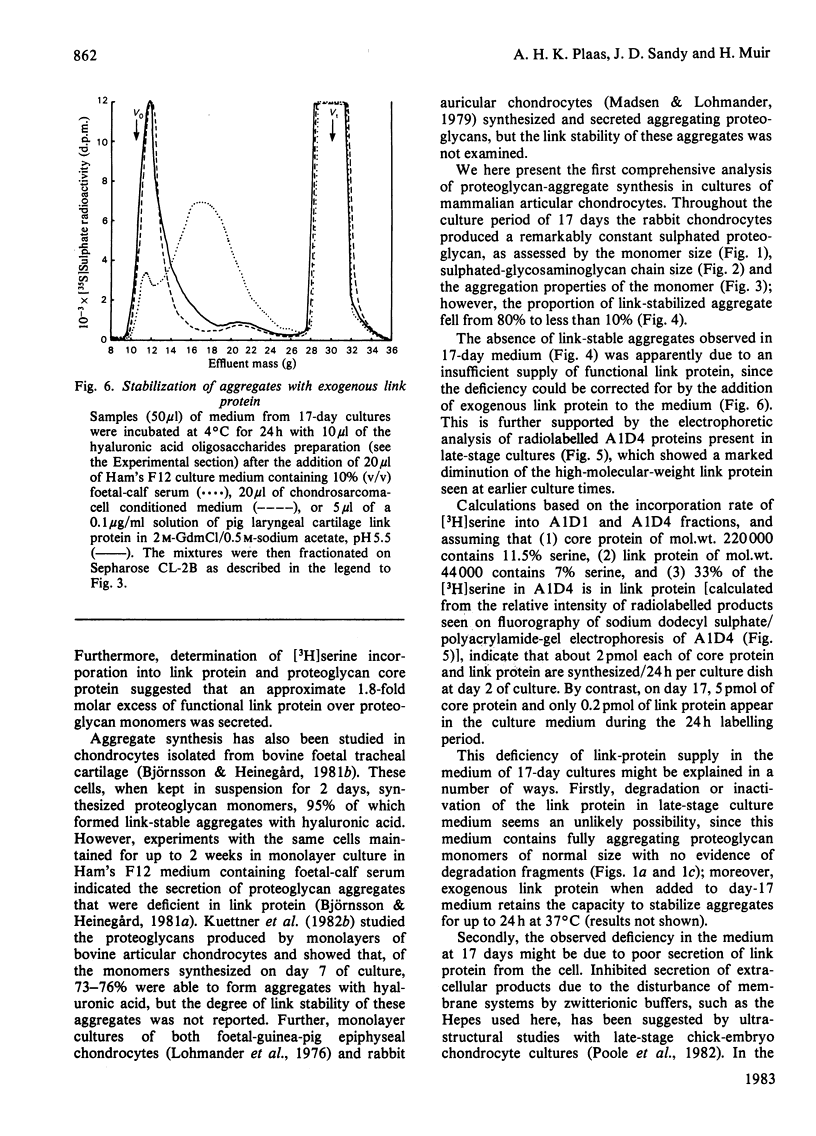
The synthesis of link-stabilized proteoglycan aggregates by rabbit articular chondrocytes was investigated by [35S]sulphate labelling of primary monolayer cultures maintained for up to 21 days. (1) At all culture times the cells secreted a high-molecular-weight cartilage-type proteoglycan monomer of which 75%-80% formed aggregates with hyaluronic acid. (2) At 2 days of culture all of the aggregates were in link-stabilized form, but by 21 days only 5% were link-stabilized, as shown by displacement of monomers from the aggregate by hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides. (3) The addition of purified link protein to 21-day culture medium increased the proportion of link-stable aggregate from 5% to 70%. (4) Analysis of [3H]serine-labelled proteoglycan aggregates in the medium showed a marked decrease with culture time in the ratio of 3H-labelled link protein to 3H-labelled core protein present. The results suggest that the secretion of proteoglycan monomers and link protein by articular chondrocytes changes independently during prolonged monolayer culture.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayliss M. T., Ali S. Y. Isolation of proteoglycans from human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):123–132. doi: 10.1042/bj1690123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D., Padilla S. R., Nimni M. E. The progeny of rabbit articular chondrocytes synthesize collagen types I and III and type I trimer, but not type II. Verifications by cyanogen bromide peptide analysis. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):865–872. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D., Shaffer J. D. Dedifferentiated chondrocytes reexpress the differentiated collagen phenotype when cultured in agarose gels. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björnsson S., Heinegård D. Assembly of proteoglycan aggregates in cultures of chondrocytes from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):17–29. doi: 10.1042/bj1990017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björnsson S., Heinegård D. Fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans isolated from chondrocyte cell cultures. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):249–258. doi: 10.1042/bj1970249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakesley R. W., Boezi J. A. A new staining technique for proteins in polyacrylamide gels using coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):580–582. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter J. A. Proteoglycan structure in calcifying cartilage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983 Jan-Feb;(172):207–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. R. The link proteins as specific components of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates in vivo. Associative extraction of proteoglycan aggregate from swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2394–2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. The interaction of link proteins with proteoglycan monomers in the absence of hyaluronic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. S., Harvey W., Benya P. D., Nimni M. E. New collagen markers of 'derepression' synthesized by rabbit articular chondrocytes in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway W. A., Murphy G., Sandy J. D., Gavrilovic J., Cawston T. E., Reynolds J. J. Purification and characterization of a rabbit bone metalloproteinase that degrades proteoglycan and other connective-tissue components. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):741–752. doi: 10.1042/bj2090741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser J. H., Conrad H. E. Formation of matrix vesicles by cultured chick embryo chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12607–12611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E. The role of link-protein in the structure of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1770237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. I. The role of hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4232–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Hardingham T. E., Hascall V. C. Assembly of newly synthesized proteoglycan and link protein into aggregates in cultures of chondrosarcoma chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7134–7143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J. H., Hardingham T. E., Hascall V. C., Solursh M. Biosynthesis of proteoglycans and their assembly into aggregates in cultures of chondrocytes from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2600–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettner K. E., Pauli B. U., Gall G., Memoli V. A., Schenk R. K. Synthesis of cartilage matrix by mammalian chondrocytes in vitro. I. Isolation, culture characteristics, and morphology. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):743–750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., De Luca S., Nilsson B., Hascall V. C., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Heinegard D. Oligosaccharides on proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6084–6091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander S., Moskalewski S., Madsen K., Thyberg J., Friberg U. Influence of colchicine on the synthesis and secretion of proteoglycans and collagen by fetal guinea pig chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen K., Lohmander S. Production of cartilage-typic proteoglycans in cultures of chondrocytes from elastic cartilage. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Aug;196(1):192–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90566-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D., Hardingham T. Monensin inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan, but not of hyaluronate, in chondrocytes. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 15;202(1):249–254. doi: 10.1042/bj2020249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D., Hardingham T. The effects of cycloheximide on the biosynthesis and secretion of proteoglycans by chondrocytes in culture. Biochem J. 1981 May 15;196(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1960521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norby D. P., Malemud C. J., Sokoloff L. Differences in the collagen types synthesized by lapine articular chondrocytes in spinner and monolayer culture. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Mar;20(2):709–716. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes B. W., Handley C. J., Lisner F., Lowther D. A. An ultrastructural and biochemical study of high density primary cultures of embryonic chick chondrocytes. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1977 Apr;38:239–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Thompson R. C., Jr Characterization of a hyaluronic acid-dermatan sulfate proteoglycan complex from dedifferentiated human chondrocyte cultures. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1015–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole C. A., Reilly H. C., Flint M. H. The adverse effects of HEPES, TES, and BES zwitterion buffers on the ultrastructure of cultured chick embryo epiphyseal chondrocytes. In Vitro. 1982 Sep;18(9):755–765. doi: 10.1007/BF02796499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Poole A. R., Mort J. S. The heterogeneity of link proteins isolated from human articular cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11908–11914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. K., Griswold M. D. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with 2,5-diphenyloxazole in acetic acid and its comparison with existing procedures. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj2090281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L., Malemud C. J., Green W. T., Jr Sulfate incorporation by articular chondrocytes in monolayer culture. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Mar-Apr;13(2):118–124. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava V. M., MaleMud C. J., Sokoloff L. Chondroid expression by lapine articular chondrocytes in spinner culture following monolayer growth. Connect Tissue Res. 1974;2(2):127–136. doi: 10.3109/03008207409152098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treadwell B. V., Shader L., Towle C. A., Mankin D. P., Mankin H. J. Purification of the 'link proteins' from bovine articular cartilage and comparison with 'link proteins' from nasal septum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


