Abstract
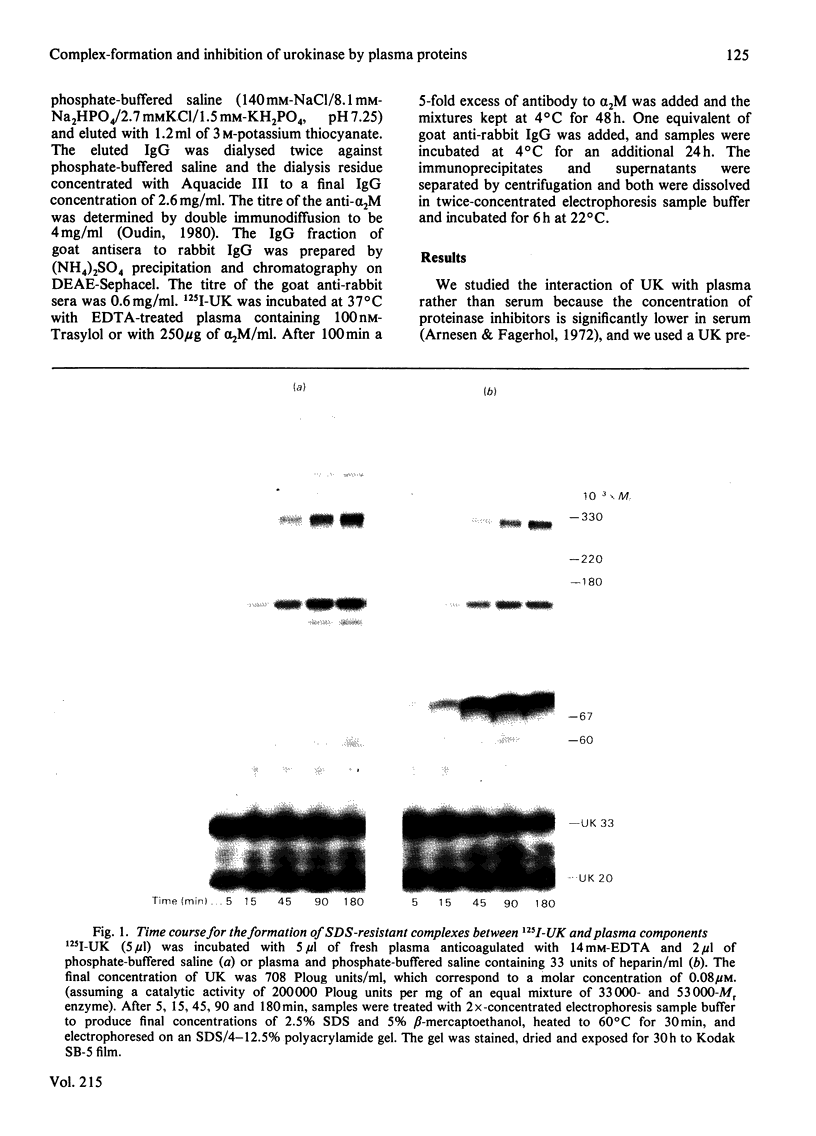
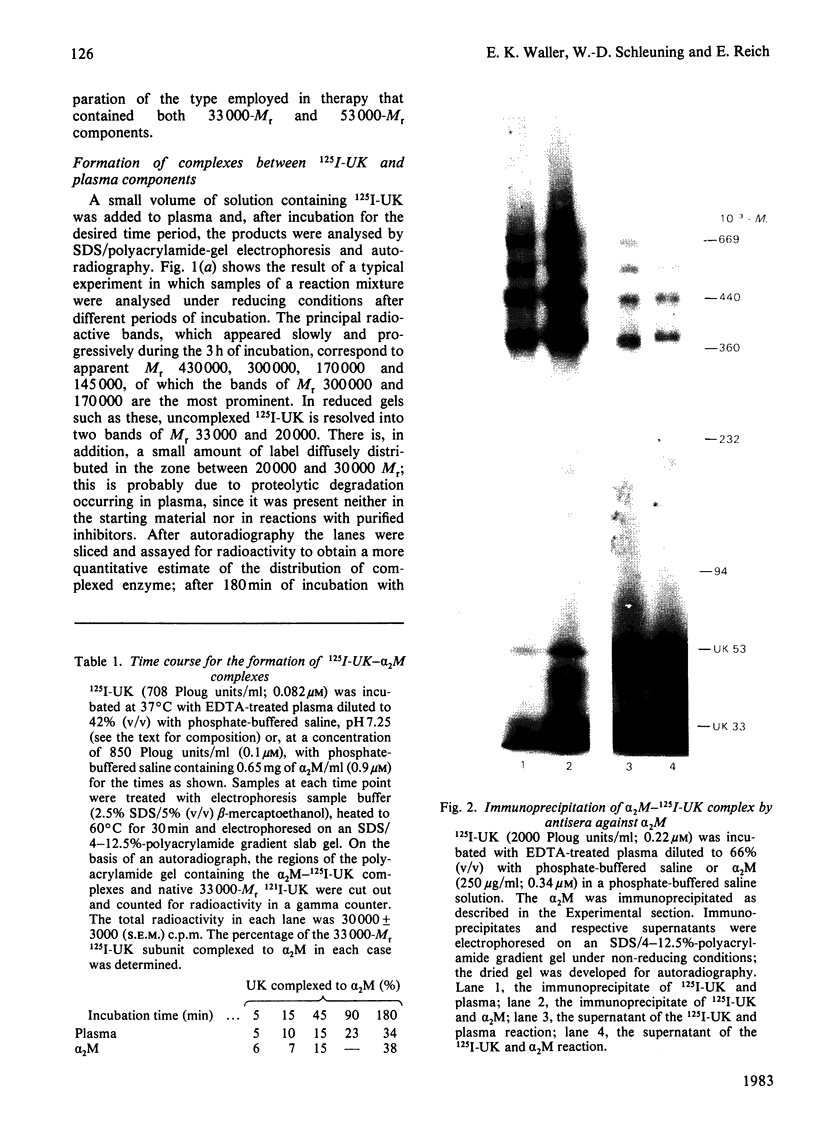
We have studied the formation of covalent complexes between 125I-urokinase (125I-UK) and proteins in human plasma. Although 125I-UK reacts with many proteinase inhibitors in purified systems, the predominant complexes formed in plasma are with antithrombin III (ATIII) and alpha 2-macroglobulin (alpha 2M). 125I-UK interacts with purified alpha 2M or alpha 2M in plasma to form a characteristic pattern of multiple complexes whose Mr values by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis are in the range of 380 000-720 000, under non-reducing conditions, and 180 000-430 000 after reduction. We also examined the inhibition of UK amidolytic activity by plasma and by purified ATIII. In the presence of saturating concentrations of ATIII and heparin, an apparent first-order rate constant of 6.8 X 10(-1) s-1 was calculated for the inhibition of urokinase. In contrast, the rate constant for the formation of covalent ATIII-UK complexes was lower, suggesting the inhibition of UK proceeds first via the formation of transient non-covalent intermediates that are then transformed more slowly into covalent end products. The observed rate constants for enzyme inhibition or complex-formation with plasma or purified inhibitors are insufficient to account for the reported clearance rate of injected UK in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnesen H., Fagerhol M. K. 2 -Macroglobulin, 1 -antitrypsin, and antithrombin III in plasma and serum during fibrinolytic therapy with urokinase. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 May;29(3):259–263. doi: 10.3109/00365517209080240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck M., Blombäck B., Olsson P., Svendsen L. The assay of antithrombin using a synthetic chromogenic substrate for thrombin. Thromb Res. 1974 Nov;5(5):621–632. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmensen I., Christensen F. Inhibition of urokinase by complex formation with human alpha1-antitrypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 8;429(2):591–599. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
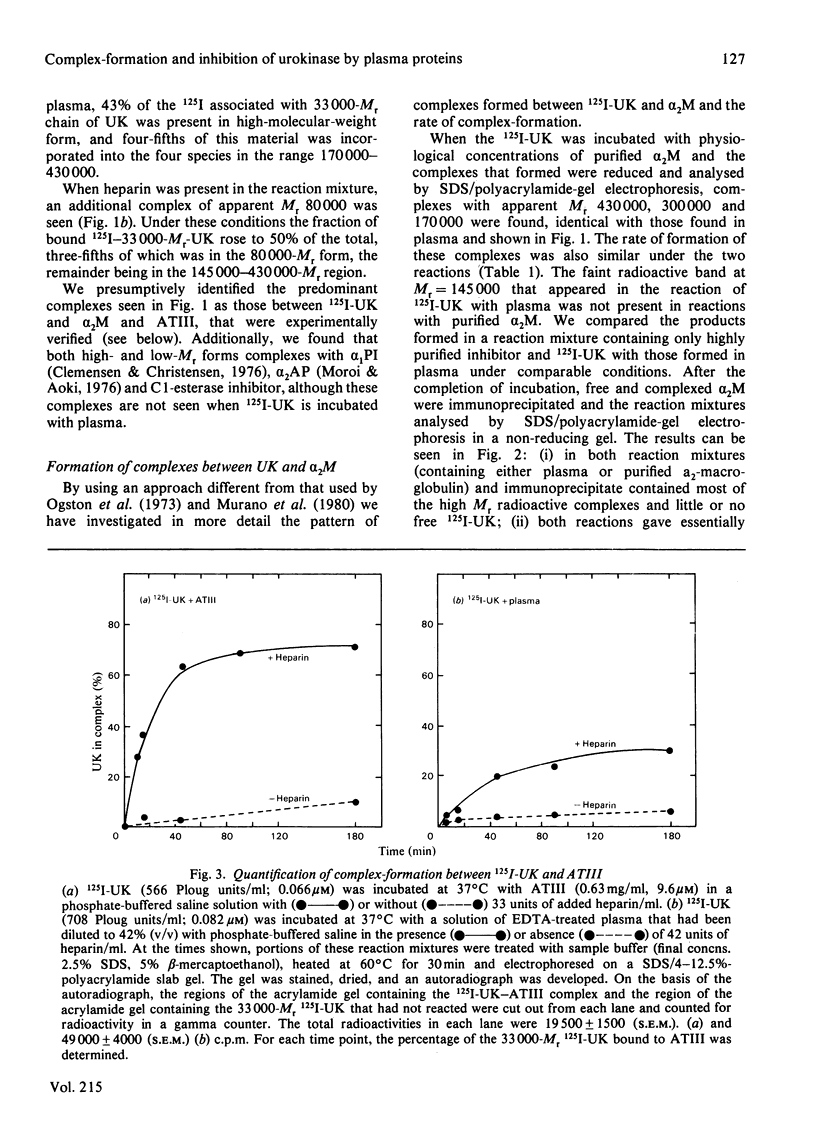
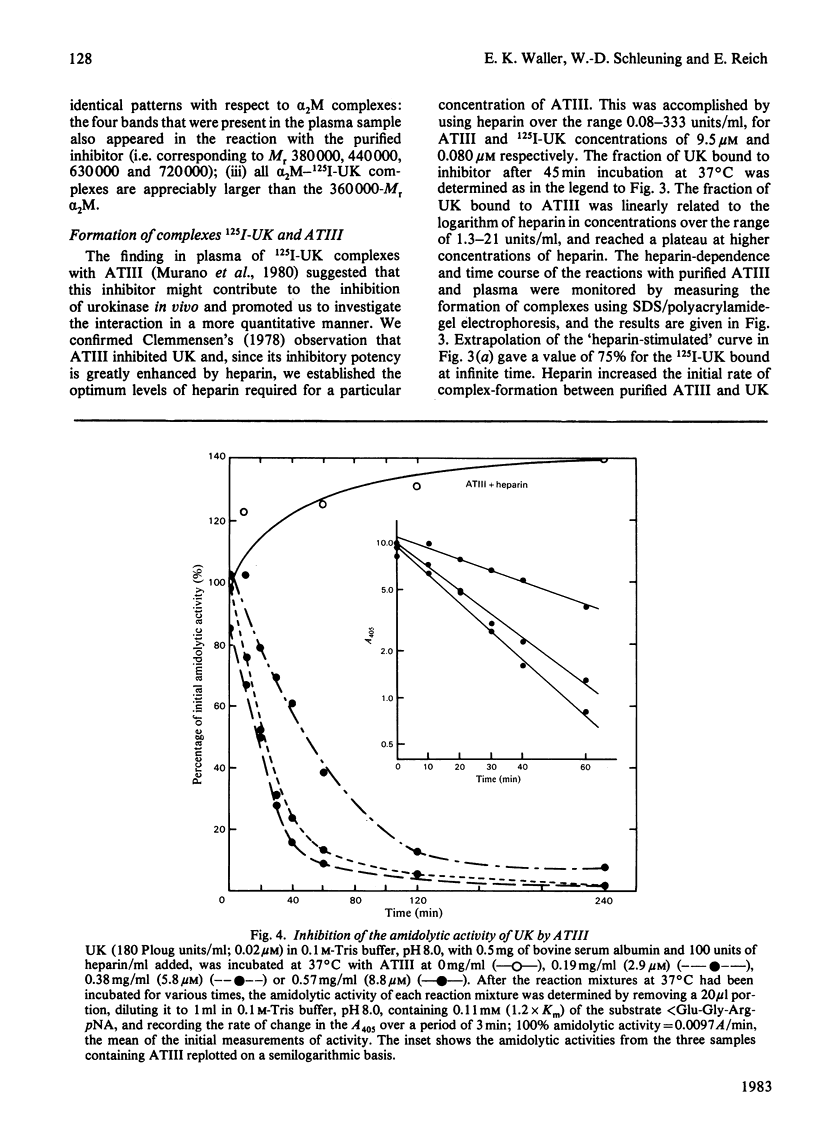
- Clemmensen I. Inhibition of urokinase by complex formation with human antithrombin III in absence and presence of heparin. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Jun 30;39(3):616–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S., GENTON E., HIRSH J., BACHMANN F. THE DEVELOPMENT OF UROKINASE AS A THROMBOLYTIC AGENT. MAINTENANCE OF A SUSTAINED THROMBOLYTIC STATE IN MAN BY ITS INTRAVENOUS INFUSION. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 May;65:713–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore M. J. Inhibition of the amidolytic activity of urokinase by human plasma. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):289–291. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Studies on human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin-enzyme interactions. Evidence for proteolytic modification of the subunit chain structure. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):508–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Bladh B., Astedt B. Purification of urokinase by affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 12;445(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Creeth J. M., Kekwick R. A. Thio reduction of human 2 -macroglobulin. The subunit structure. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):187–197. doi: 10.1042/bj1270187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
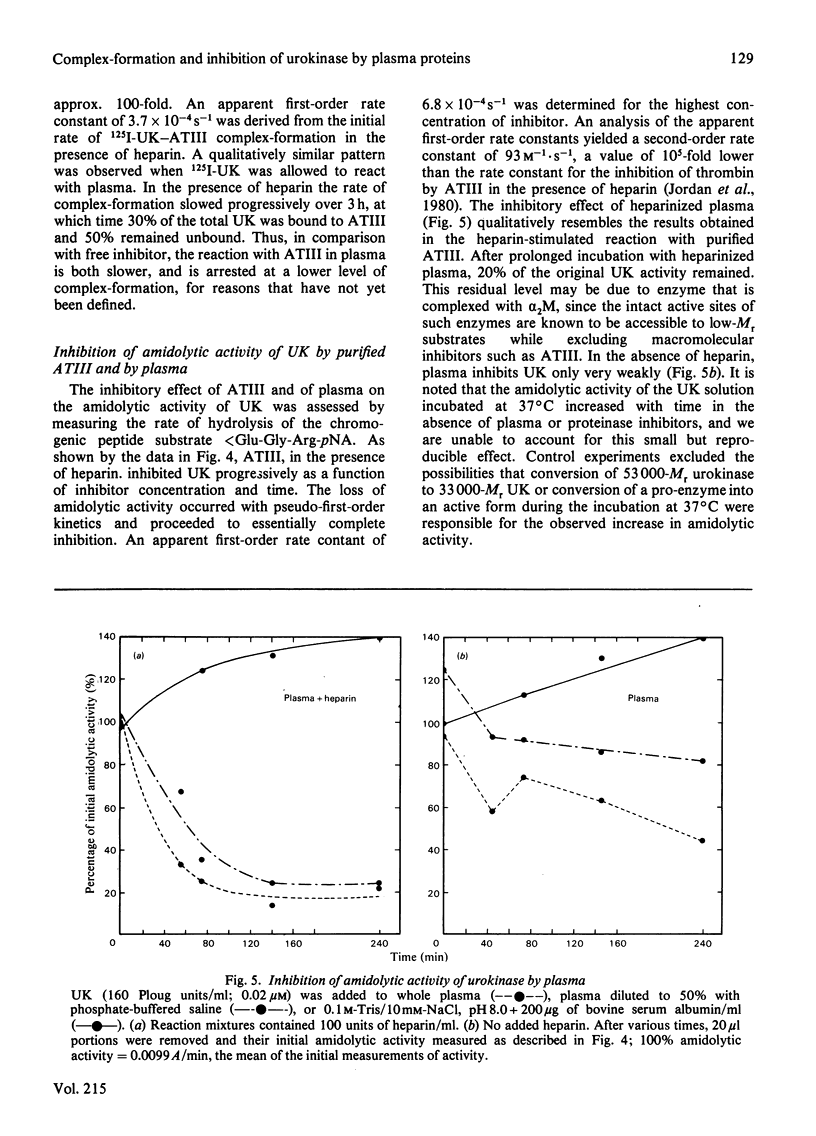
- Jordan R. E., Oosta G. M., Gardner W. T., Rosenberg R. D. The kinetics of hemostatic enzyme-antithrombin interactions in the presence of low molecular weight heparin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10081–10090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5956–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murano G., Aronson D., Williams L., Brown L. The inhibition of high and low molecular weight urokinase in plasma. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):430–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogston D., Bennett B., Herbert R. J., Douglas A. S. The inhibition of urokinase by alpha 2 -macroglobulin. Clin Sci. 1973 Jan;44(1):73–79. doi: 10.1042/cs0440073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudin J. Immunochemical analysis by antigen-antibody precipitation in gels. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):166–198. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Travis J., Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Purification of human alpha-2-macroglobulin by chromatography on Cibacron Blue Sepharose. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):274–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90750-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Ogston D. The inhibition of tissue activator and urokinase by human plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Jun 28;47(3):265–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]