Abstract
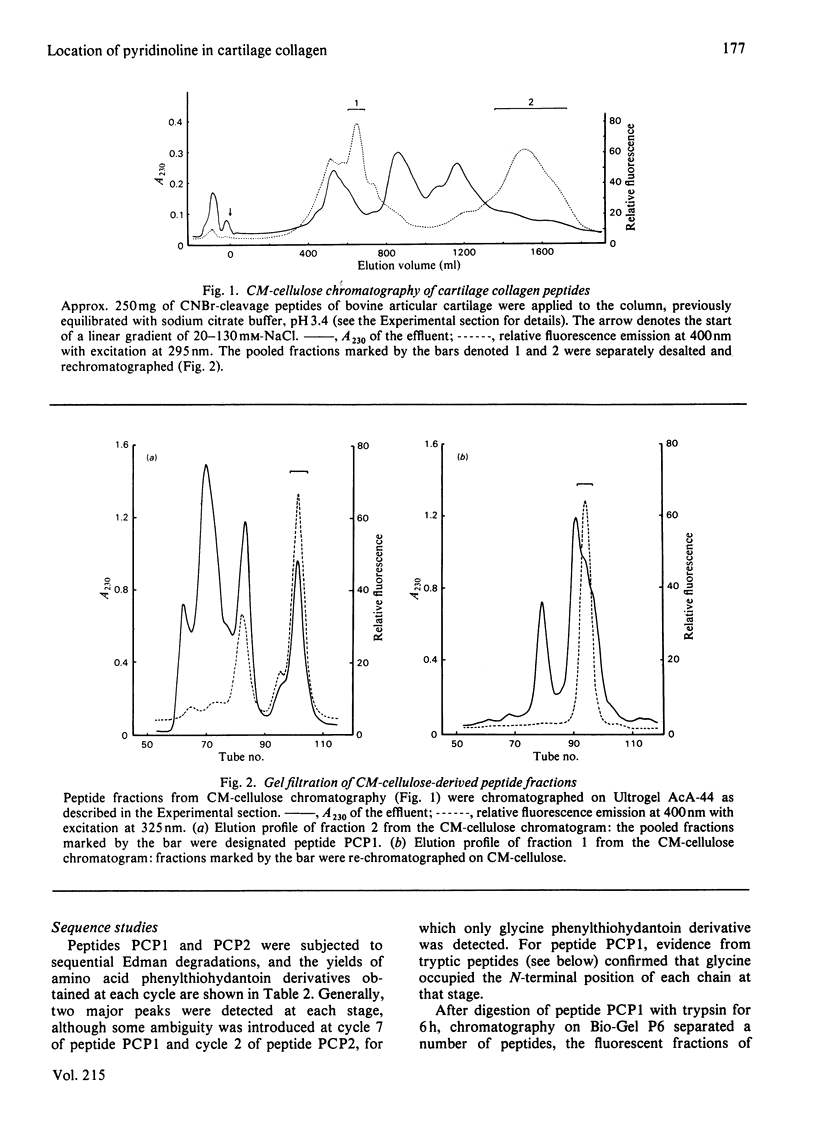
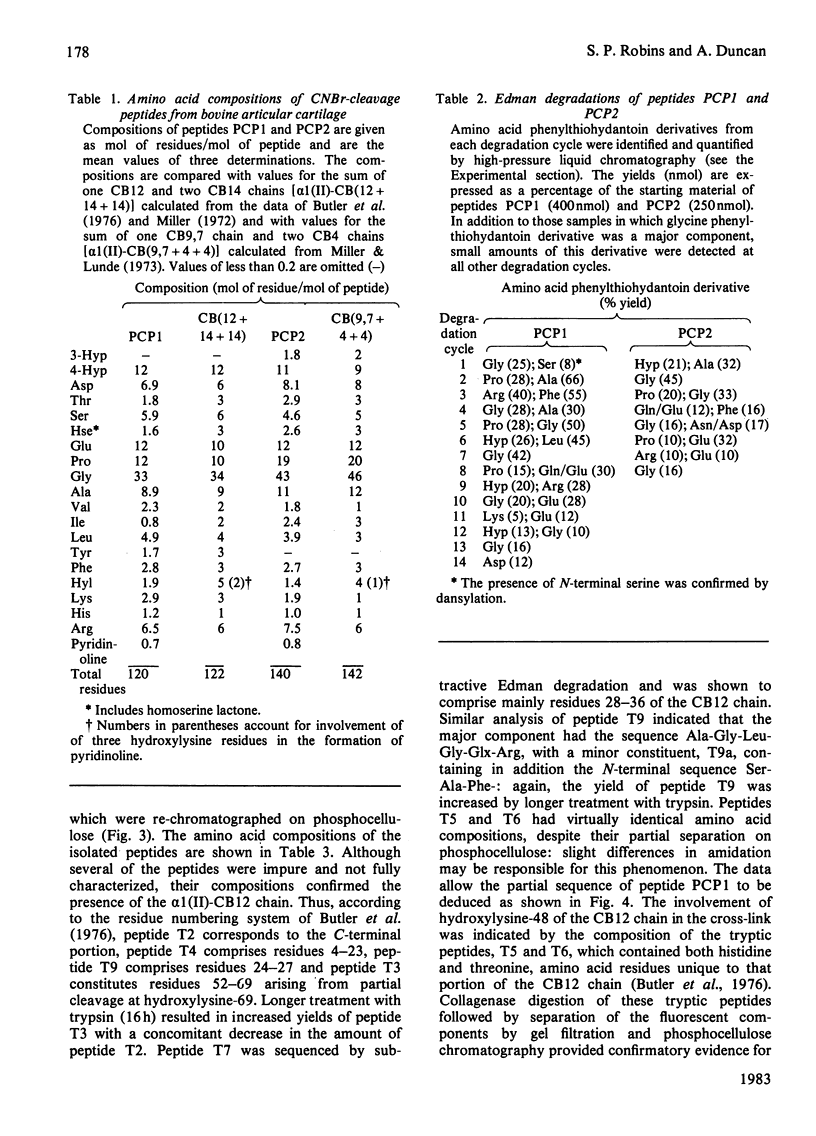
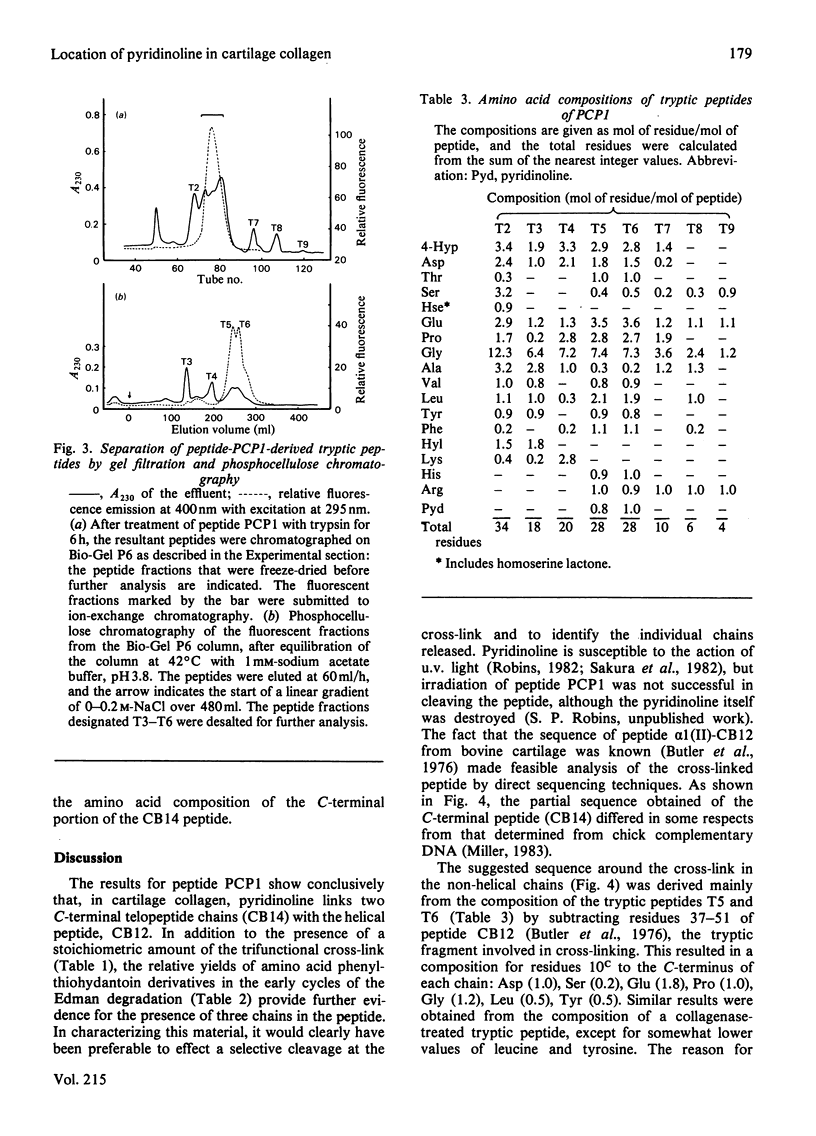
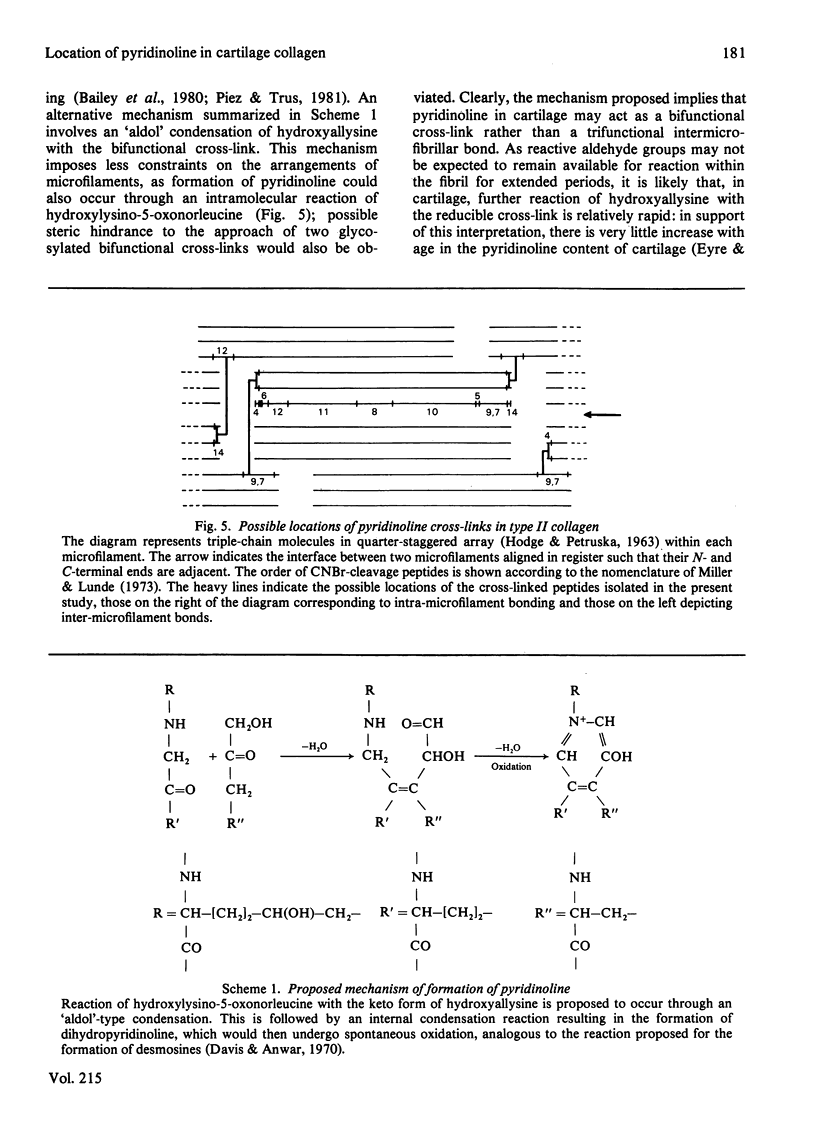
The location of pyridinoline in 18-month-old bovine articular cartilage was investigated by fractionation of CNBr-derived peptides by ion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration. Two peptides, PCP1 and PCP2, were isolated and were shown to contain stoichiometric amounts of pyridinoline. From its amino acid composition and sequence studies, peptide PCP1 was shown to comprise two C-terminal non-helical chains (CB14) linked through pyridinoline to the alpha 1(II)-CB12 portion of the helix. The CB14 chains appeared to be labile at their C-terminal ends, resulting in lower-than-expected amounts of homoserine, and only the N-terminal portion of the peptide was sequenced. Similar studies of peptide PCP2 showed that it contained two N-terminal non-helical chains (CB4) linked to the alpha 1(II)-CB9,7 portion of the helix. The isolated peptides therefore confirmed the function of pyridinoline in stabilizing the 4D stagger of adjacent molecules. The possibility that the cross-link could act both as an intra- and an inter-microfibrillar cross-link was considered. A mechanism of formation of pyridinoline was postulated that, together with other evidence, appears to support the view that, in cartilage, pyridinoline acts primarily as an intramicrofibrillar cross-link and does not contribute to increased stability during maturation through lateral aggregation and bonding of filaments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayad S., Abedin M. Z., Grundy S. M., Weiss J. B. Isolation and characterisation of an unusual collagen from hyaline cartilage and intervertebral disc. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Light N. D., Atkins E. D. Chemical cross-linking restrictions on models for the molecular organization of the collagen fibre. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):408–410. doi: 10.1038/288408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balian G., Click E. M., Bornstein P. Structure of rat skin collagen 1-CB8. Amino acid sequence of the hydroxylamine-produced fragment HA1. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4470–4478. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgeson R. E., Hollister D. W. Collagen heterogeneity in human cartilage: identification of several new collagen chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):1124–1131. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T., Finch J. E., Jr, Miller E. J. The covalent structure of cartilage collagen. Evidence for sequence heterogeneity of bovine alpha1(II) chains. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):639–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T., Miller E. J., Finch J. E., Jr The covalent structure of cartilage collagen. Amino acid sequence of the NH2-terminal helical portion of the alpha 1 (II) chain. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):3000–3006. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. R., Anwar R. A. On the mechanism of formation of desmosine and isodesmosine cross-links of elastin. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Jun 17;92(12):3778–3782. doi: 10.1021/ja00715a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R. Collagen: molecular diversity in the body's protein scaffold. Science. 1980 Mar 21;207(4437):1315–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.7355290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Oguchi H. The hydroxypyridinium crosslinks of skeletal collagens: their measurement, properties and a proposed pathway of formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90347-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D. Evidence for natural existence of pyridinoline crosslink in collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):948–953. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D., Moriguchi T., Ishida T., Hayashi H. The structure of pyridinoline, a collagen crosslink. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 14;84(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto D., Moriguchi T. Pyridinoline, a non-reducible crosslink of collagen. Quantitative determination, distribution, and isolation of a crosslinked peptide. J Biochem. 1978 Mar;83(3):863–867. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel W., Glanville R. W. Covalent crosslinking between molecules of type I and type III collagen. The involvement of the N-terminal, nonhelical regions of the alpha 1 (I) and alpha 1 (III) chains in the formation of intermolecular crosslinks. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(1):205–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D., Bailey A. J. Polymeric C-terminal cross-linked material from type-I collagen. A modified method for purification, anomalous behaviour on gel filtration, molecular weight estimation, carbohydrate content and lipid content. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):111–124. doi: 10.1042/bj1890111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light N. D., Bailey A. J. The chemistry of the collagen cross-links. Purification and characterization of cross-linked polymeric peptide material from mature collagen containing unknown amino acids. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 1;185(2):373–381. doi: 10.1042/bj1850373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J., Lunde L. G. Isolation and characterization of the cyanogen bromide peptides from the alpha 1(II) chain of bovine and human cartilage collagen. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3153–3159. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Structural studies on cartilage collagen employing limited cleavage and solubilization with pepsin. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4903–4909. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piez K. A., Trus B. L. A new model for packing of type-I collagen molecules in the native fibril. Biosci Rep. 1981 Oct;1(10):801–810. doi: 10.1007/BF01114803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P. Analysis of the crosslinking components in collagen and elastin. Methods Biochem Anal. 1982;28:329–379. doi: 10.1002/9780470110485.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P. Cross-linking of collagen. Isolation, structural characterization and glycosylation of pyridinoline. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 1;215(1):167–173. doi: 10.1042/bj2150167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakura S., Fujimoto D., Sakamoto K., Mizuno A., Motegi K. Photolysis of pyridinoline, a cross-linking amino acid of collagen, by ultraviolet light. Can J Biochem. 1982 May;60(5):525–529. doi: 10.1139/o82-064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokomaki M., Duance V. C., Bailey A. J. Identification of a new disulphide bonded collagen from cartilage. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 17;121(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


