Abstract
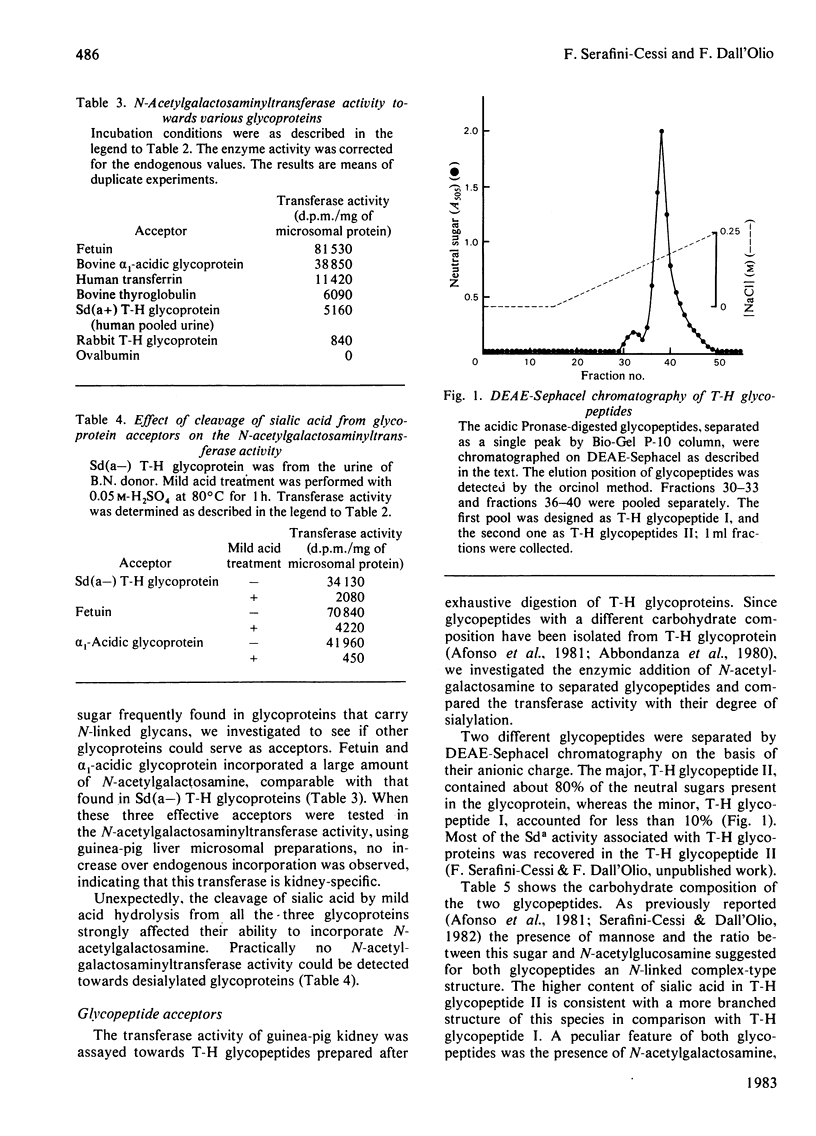
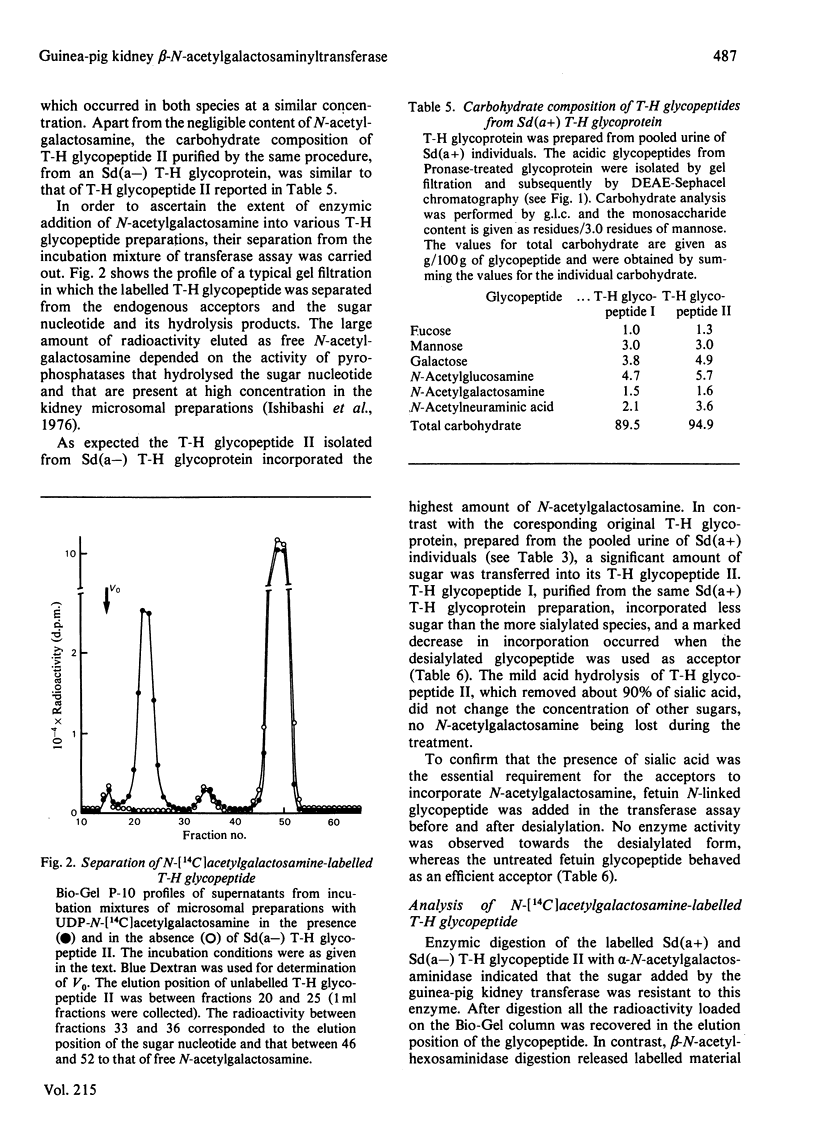
A beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase that preferentially transferred N-acetylgalactosamine to Sd(a-) Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein was found in guinea-pig kidney microsomal preparations. This enzyme was kidney-specific and was able to transfer the sugar to other glycoproteins, such as fetuin and alpha 1-acidic glycoprotein. The presence of sialic acid in the acceptors was essential for the transferase activity when either glycoproteins or their Pronase glycopeptides were used as acceptors. Two glycopeptides (Tamm-Horsfall glycopeptides I and II) with a different carbohydrate composition were separated by DEAE-Sephacel chromatography from Pronase-digested Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. The amount of N-acetylgalactosamine transferred to glycopeptides by the enzyme correlated with their degree of sialylation. Enzymic digestion of N-[14C]acetylgalactosamine-labelled Tamm-Horsfall glycopeptide II showed that the transferred sugar was susceptible to beta-N-hexosaminidase. The amount of sugar cleaved by beta-hexosaminidase was strongly increased when the labelled Tamm-Horsfall glycopeptide II was pretreated with mild acid hydrolysis, a procedure that removed the sialic acid residues. Alkaline borohydride treatment of the labelled Tamm-Horsfall glycopeptide II did not release radioactivity, thus indicating that enzymic glycosylation took place at the N-asparagine-linked oligosaccharide units of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbondanza A., Franceschi C., Licastro F., Serafini-Cessi F. Properties of a glycopeptide isolated from human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. Interaction with leucoagglutinin and anti-(human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein) antibodies. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):525–528. doi: 10.1042/bj1870525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer T. A., Rearick J. I., Paulson J. C., Prieels J. P., Sadler J. E., Hill R. L. Biosynthesis of mammalian glycoproteins. Glycosylation pathways in the synthesis of the nonreducing terminal sequences. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12531–12534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer T. A., Sadler J. E., Rearick J. I., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Glycosyltransferases and their use in assessing oligosaccharide structure and structure-function relationships. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1981;52:23–175. doi: 10.1002/9780470122976.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartron J. P., Blanchard D. Association of human erythrocyte membrane glycoproteins with blood-group Cad specificity. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):497–504. doi: 10.1042/bj2070497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald A. S., Soh C. P., Watkins W. M., Morgan W. T. N-Acetyl-D-galactosaminyl-beta-(1 goes to 4)-d-galactose: a terminal non-reducing structure in human blood group Sda-active Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):58–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91940-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCOIS C., MARSHALL R. D., NEUBERGER A. Carbohydrates in protein. 4. The determination of mannose in hen's-egg albumin by radioisotope dilution. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:335–341. doi: 10.1042/bj0830335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher A. P., Neuberger A., Ratcliffe W. A. Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein. The chemical composition. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):417–424. doi: 10.1042/bj1200417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi T., Atsuta T., Makita A. Effects of uridine nucleotides and nucleotide pyrophosphatase on glycolipid alpha and beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activities in guinea pig microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi T., Kijimoto S., Makita A. Biosynthesis of globoside and Forssman hapten from trihexosylceramide and properties of beta-N-acetyl-galactosaminyltransferase of guinea pig kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jan 23;337(1):92–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLER E. B., ZAMECNIK P. C. The effect of guanosine diphosphate and triphosphate on the incorporation of labeled amino acids into proteins. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jul;221(1):45–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius T., Finne J., Rauvala H. The poly(glycosyl) chains of glycoproteins. Characterisation of a novel type of glycoprotein saccharides from human erythrocyte membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T., Li S. C. Biosynthesis and catabolism of glycosphingolipids. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1982;40:235–288. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., Elson L. A. A colorimetric method for the determination of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylchrondrosamine. Biochem J. 1934;28(3):988–995. doi: 10.1042/bj0280988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. A., Pickles M. M., Terry A. M. The Sda blood group antigen in tissues and body fluids. Vox Sang. 1970 Nov-Dec;19(5):472–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1970.tb01779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Conte R. Precipitin reaction between Sda-active human Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein and anti-Sda-serum. Vox Sang. 1982 Mar;42(3):141–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1982.tb01084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F. Sialyltransferase activity in regenerating rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):381–386. doi: 10.1042/bj1660381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soh C. P., Morgan W. T., Watkins W. M., Donald A. S. The relationship between the N-acetylgalactosamine content and the blood group Sda activity of Tamm and Horsfall urinary glycoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1132–1139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90607-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., HORSFALL F. L., Jr A mucoprotein derived from human urine which reacts with influenza, mumps, and Newcastle disease viruses. J Exp Med. 1952 Jan;95(1):71–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins W. M. Genetics and biochemistry of some human blood groups. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 Jun 5;202(1146):31–53. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


