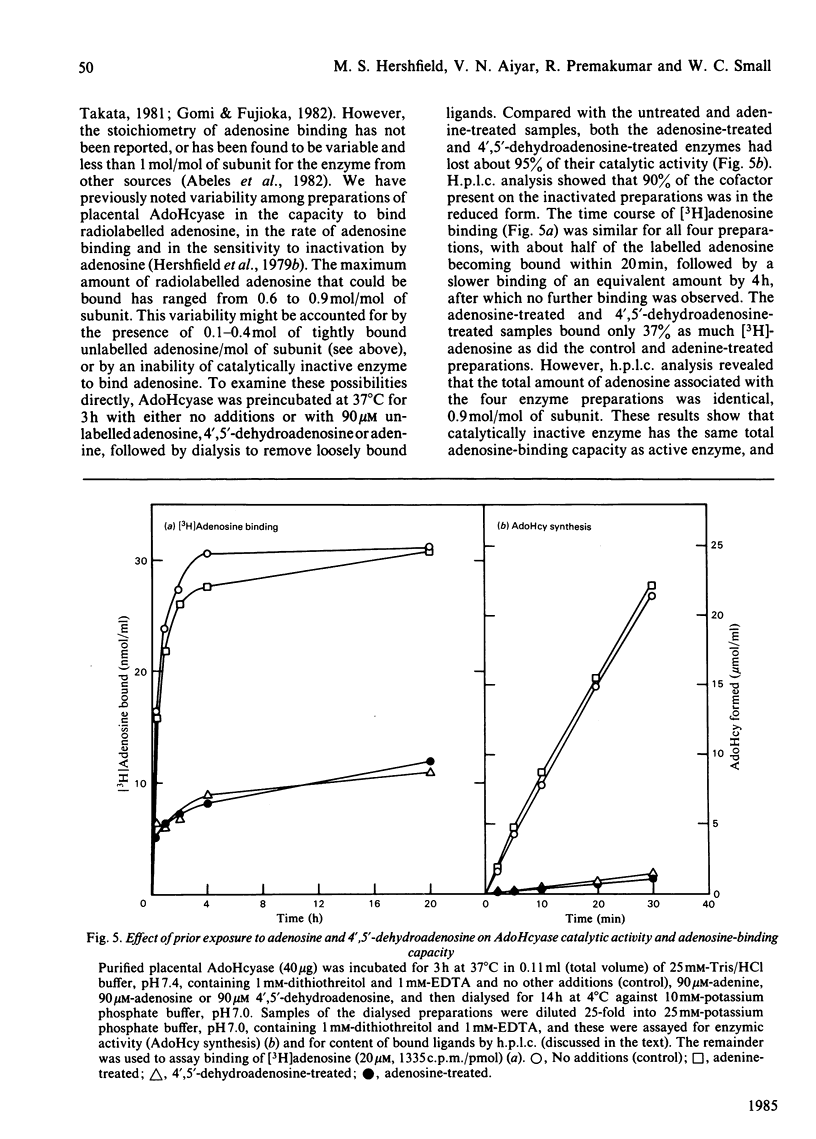
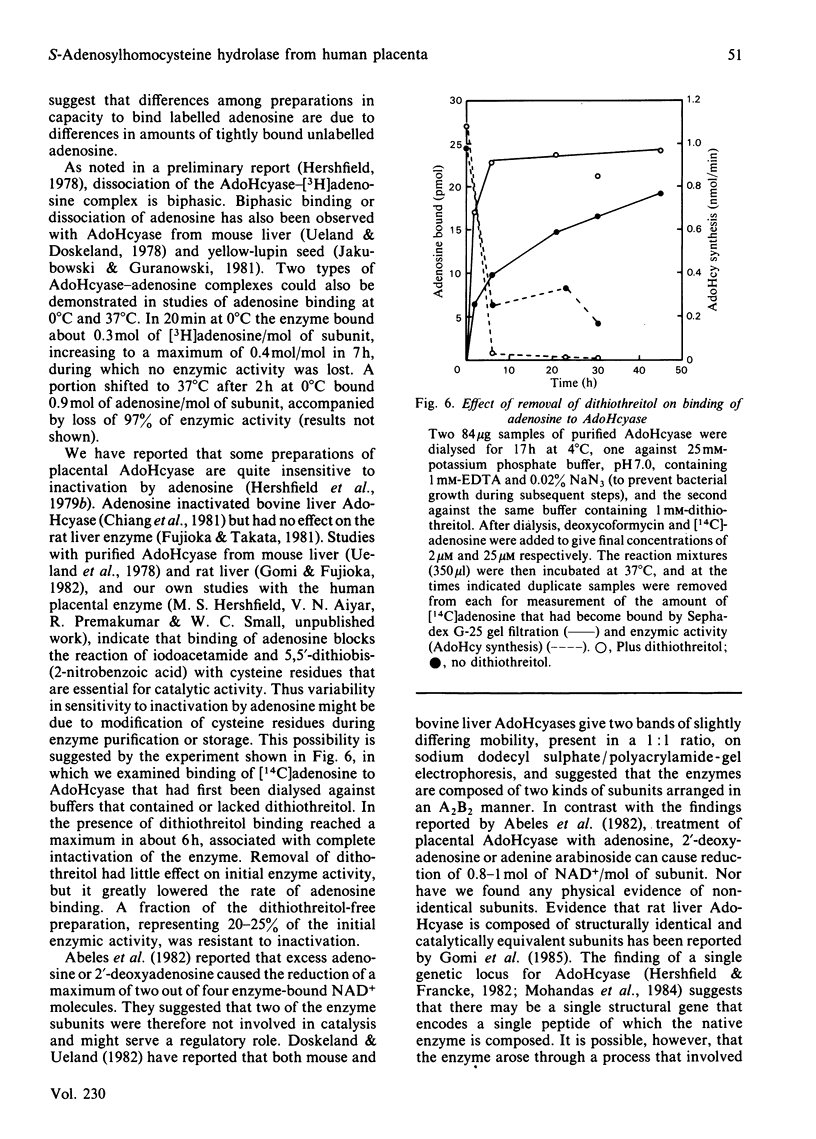
Abstract
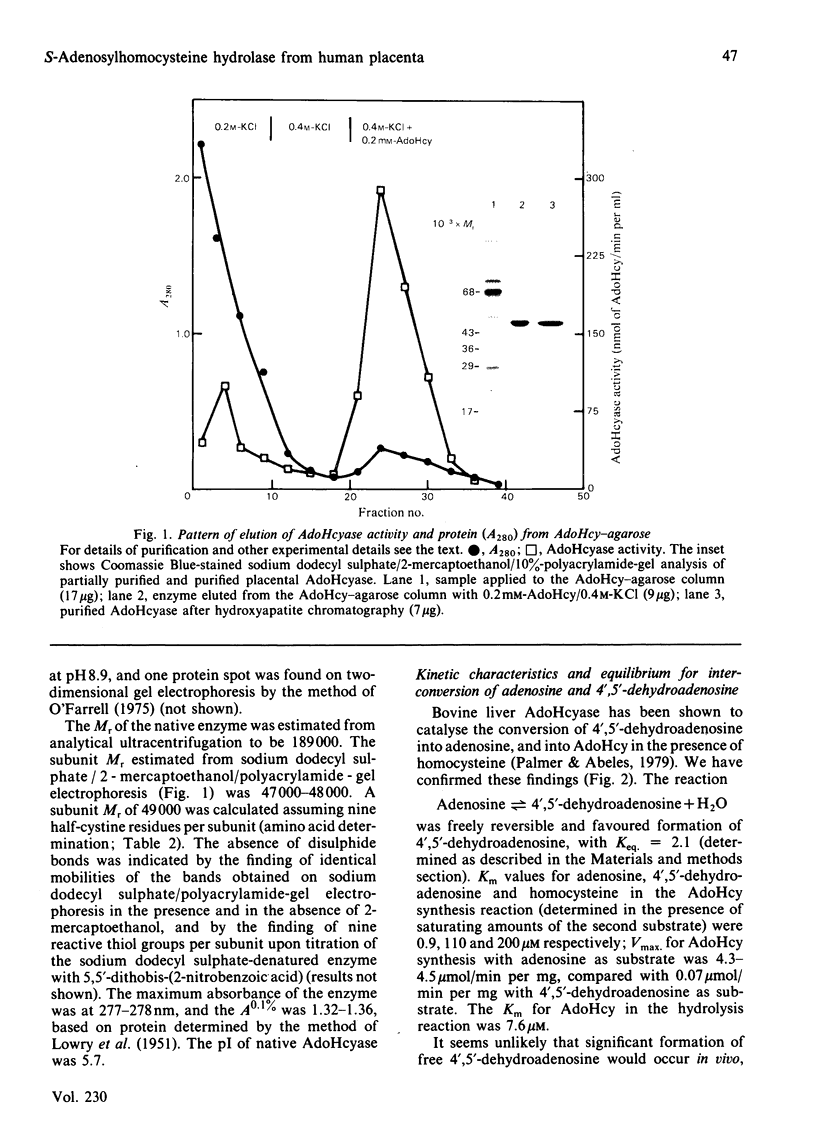
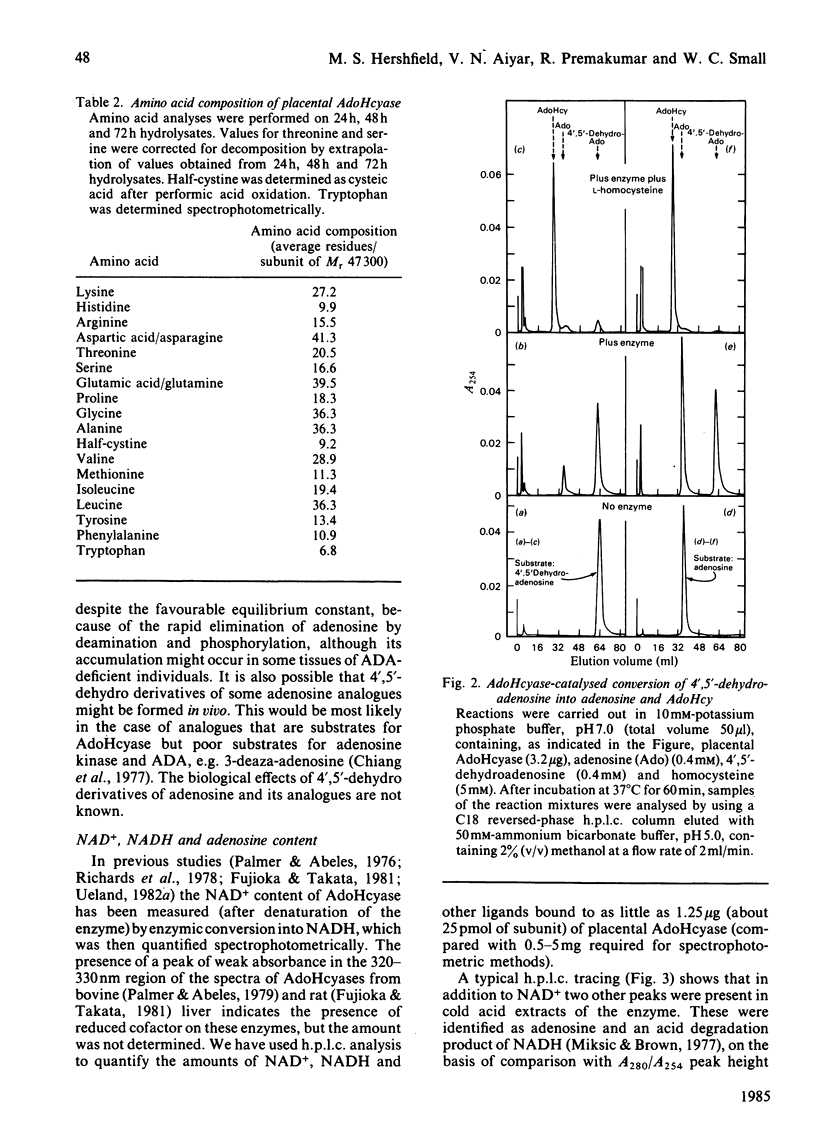
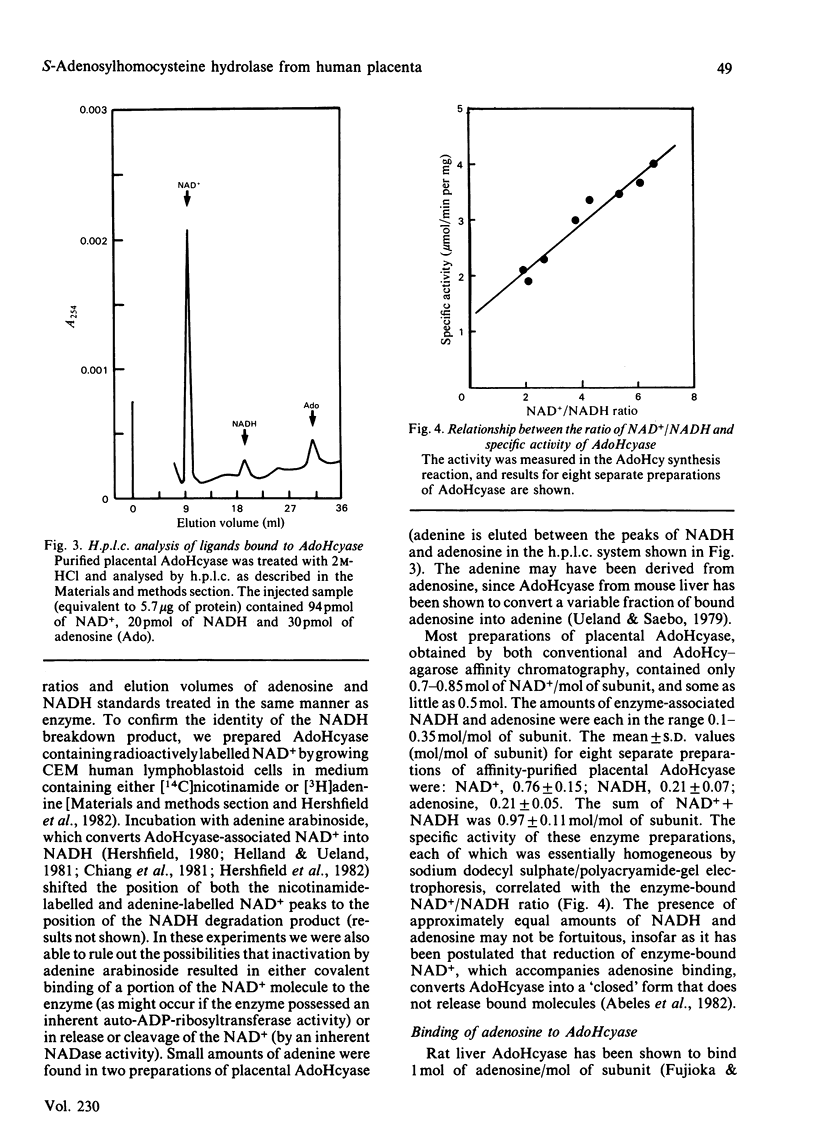
S-Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (EC 3.3.1.1) was purified to homogeneity from human placenta by using S-adenosylhomocysteine-agarose affinity chromatography. The enzyme is a tetramer with a native Mr of 189 000 and subunit Mr of 47 000-48 000; there were nine cysteine residues per subunit and no disulphide bonds. The pI was 5.7. H.p.l.c. analysis revealed that the enzyme contained four molecules of tightly bound cofactor (NAD) per tetramer, of which 10-50% was in the reduced form. The enzyme had four binding sites per tetramer for adenosine, of which 10-35% were found to be occupied. Two types of adenosine-binding sites could be distinguished on the basis of differences in rates of dissociation of the enzyme-adenosine complex, and by examining binding of adenosine at 0 degree C and 37 degrees C. The enzyme catalysed the interconversion of adenosine and 4',5'-dehydroadenosine; the equilibrium constant for this reaction was 2.1 and favoured 4',5'-dehydroadenosine formation. Variability in the specific activity of preparations of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase was related to the NAD+/NADH ratio of the preparation. The capacity to bind radioactively labelled adenosine depended on the adenosine content of the purified enzyme. The rate of adenosine binding and the sensitivity of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase to inactivation by adenosine were both diminished in the absence of dithiothreitol.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles R. H., Fish S., Lapinskas B. S-Adenosylhomocysteinase: mechanism of inactivation by 2'-deoxyadenosine and interaction with other nucleosides. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5557–5562. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briske-Anderson M., Duerre J. A. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase from rat liver. Can J Biochem. 1982 Feb;60(2):118–123. doi: 10.1139/o82-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabannes B., Cronenberger L., Pachéco H. Purification de la S-adénosyl-L-homocystéine hydrolase du foie de rat par chromatographie d'affinité. Experientia. 1979 Aug 15;35(8):1014–1016. doi: 10.1007/BF01949913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang P. K., Guranowski A., Segall J. E. Irreversible inhibition of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by nucleoside analogs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Mar;207(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang P. K., Richards H. H., Cantoni G. L. S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase: analogues of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine as potential inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;13(5):939–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LA HABA G., CANTONI G. L. The enzymatic synthesis of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine from adenosine and homocysteine. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):603–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Døskeland S. O., Ueland P. M. Comparison of some physicochemical and kinetic properties of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase from bovine liver, bovine adrenal cortex and mouse liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 9;708(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka M., Takata Y. S-Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase from rat liver. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1631–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi T., Fujioka M. Inactivation of rat liver S-adenosylhomocysteinase by iodoacetamide. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):4171–4176. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi T., Ishiguro Y., Fujioka M. S-Adenosylhomocysteinase from rat liver. Evidence for structurally identical and catalytically equivalent subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2789–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helland S., Ueland P. M. The relation between the functions of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine as inactivator and substrate of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Sep;218(3):758–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S. Apparent suicide inactivation of human lymphoblast S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by 2'-deoxyadenosine and adenine arabinoside. A basis for direct toxic effects of analogs of adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):22–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Francke U. The human genes for S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and adenosine deaminase are syntenic on chromosome 20. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):739–742. doi: 10.1126/science.7079734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Kredich N. M., Koller C. A., Mitchell B. S., Kurtzberg J., Kinney T. R., Falletta J. M. S-adenosylhomocysteine catabolism and basis for acquired resistance during treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with 2'-deoxycoformycin alone and in combination with 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3451–3458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Kredich N. M., Ownby D. R., Ownby H., Buckley R. In vivo inactivation of erythrocyte S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by 2'-deoxyadenosine in adenosine deaminase-deficient patients. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):807–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI109367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Kredich N. M. Resistance of an adenosine kinase-deficient human lymphoblastoid cell line to effects of deoxyadenosine on growth, S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase inactivation, and dATP accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4292–4296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Krodich N. M. S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase is an adenosine-binding protein: a target for adenosine toxicity. Science. 1978 Nov 17;202(4369):757–760. doi: 10.1126/science.715439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Kurtzberg J., Harden E., Moore J. O., Whang-Peng J., Haynes B. F. Conversion of a stem cell leukemia from a T-lymphoid to a myeloid phenotype induced by the adenosine deaminase inhibitor 2'-deoxycoformycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski H., Guranowski A. S-Adenosylhomocysteinase from yellow lupin seeds: stoichiometry and reactions of the enzyme-adenosine complex. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6877–6881. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajander E. O., Raina A. M. Affinity-chromatographic purification of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase. Some properties of the enzyme from rat liver. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):503–512. doi: 10.1042/bj1930503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Nochumson S., Chin W., Paik W. K. A rapid method for the purification of S-adenosylmethionine: protein-carboxyl O-methyltransferase by affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M., Hershfield M. S. S-adenosylhomocysteine toxicity in normal and adenosine kinase-deficient lymphoblasts of human origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2450–2454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kredich N. M., Martin D. V., Jr Role of S-adenosylhomocysteine in adenosinemediated toxicity in cultured mouse T lymphoma cells. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):931–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksic J. R., Brown P. R. Complementary use of the reversed-phase and anion-exchange modes of high-pressure liquid chromatography for studies of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Chromatogr. 1977 Nov 11;142:641–649. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)92074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Suh E. J., Hershfield M. S. Regional localization of the human genes for S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (cen----q131) and adenosine deaminase (q131----qter) on chromosome 20. Hum Genet. 1984;66(4):292–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00287630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. L., Abeles R. H. Mechanism for enzymatic thioether formation. Mechanism of action of S-adenosylhomocysteinase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5817–5819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. L., Abeles R. H. The mechanism of action of S-adenosylhomocysteinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1217–1226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip T., Lenoir G., Rolland M. O., Philip I., Hamet M., Lauras B., Fraisse J. Regional assignment of the ADA locus on 20q13.2 leads to qter by gene dosage studies. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(2-3):187–189. doi: 10.1159/000131481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards H. H., Chiang P. K., Cantoni G. L. Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Crystallization of the purified enzyme and its properties. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4476–4480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader W. P., Stacy A. R., Pollara B. Purification of human erythrocyte adenosine deaminase by affinity column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4026–4032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischfield J. A., Creagan R. P., Nichols E. A., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of a gene for adenosine deaminase to human chromosome 20. Hum Hered. 1974;24(1):1–11. doi: 10.1159/000152631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland M., Saebø J. Cyclic AMP-adenosine binding protein/S-adenosylhomocysteinase from mouse liver. A fraction of adenosine bound is converted to adenine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 18;585(4):512–526. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Døskeland S. O. An adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-adenosine binding protein from mouse liver. A study on its interaction with adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1667–1676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Helland S. Binding of adenosine to intracellular S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):747–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M. Pharmacological and biochemical aspects of S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Pharmacol Rev. 1982 Sep;34(3):223–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M. S-Adenosylhomocysteinase from mouse liver. Inactivation of the enzyme in the presence of metabolites. Int J Biochem. 1982;14(3):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(82)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueland P. M., Skotland T., Døskeland S. O., Flatmark T. An adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-adenosine binding protein from mouse liver: some physicochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 28;533(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90547-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]